- Wavefunctions
- Equations Wave–particle duality and time evolution Non-relativistic time-independent Schrödinger equation Non-relativistic time-dependent Schrödinger equation Photoemission Quantum uncertainty Angular momentum The Hydrogen atom
- See also
- Footnotes
- Sources
- Further reading
This article summarizes equations in the theory of quantum mechanics.
Wavefunctions
A fundamental physical constant occurring in quantum mechanics is the Planck constant, h. A common abbreviation is {{nowrap|ħ {{=}} h/2π}}, also known as the reduced Planck constant or Dirac constant.
| Wavefunction | ψ, Ψ | To solve from the Schrödinger equation | varies with situation and number of particles | |
| Wavefunction probability density | ρ | 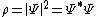 | m−3 | [L]−3 |
| Wavefunction probability current | j | Non-relativistic, no external field:  star * is complex conjugate | m−2 s−1 | [T]−1 [L]−2 |
The general form of wavefunction for a system of particles, each with position ri and z-component of spin sz i. Sums are over the discrete variable sz, integrals over continuous positions r.
For clarity and brevity, the coordinates are collected into tuples, the indices label the particles (which cannot be done physically, but is mathematically necessary). Following are general mathematical results, used in calculations.
| Property or effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Wavefunction for N particles in 3d |
| In function notation: in bra–ket notation:  for non-interacting particles:  |
| Position-momentum Fourier transform (1 particle in 3d) |
|  |
| General probability distribution |
|  |
| General normalization condition |  | |
Equations
Wave–particle duality and time evolution
| Property or effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Planck–Einstein equation and de Broglie wavelength relations |
|  |
| Schrödinger equation |
| General time-dependent case: Time-independent case:  |
| Heisenberg equation |
|  |
| Time evolution in Heisenberg picture (Ehrenfest theorem) |
of a particle. |  For momentum and position;  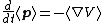 |
Non-relativistic time-independent Schrödinger equation
Summarized below are the various forms the Hamiltonian takes, with the corresponding Schrödinger equations and forms of wavefunction solutions. Notice in the case of one spatial dimension, for one particle, the partial derivative reduces to an ordinary derivative.
| One particle | N particles | |
| One dimension |  |  where the position of particle n is xn. |
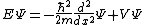 |  | |
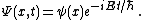 There is a further restriction — the solution must not grow at infinity, so that it has either a finite L2-norm (if it is a bound state) or a slowly diverging norm (if it is part of a continuum):[1] 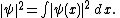 |  for non-interacting particles  | |
| Three dimensions |  where the position of the particle is r = (x, y, z). |  where the position of particle n is r n = (xn, yn, zn), and the Laplacian for particle n using the corresponding position coordinates is  |
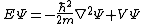 |  | |
 |  for non-interacting particles  |
Non-relativistic time-dependent Schrödinger equation
Again, summarized below are the various forms the Hamiltonian takes, with the corresponding Schrödinger equations and forms of solutions.
| One particle | N particles | |
| One dimension | 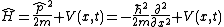 | 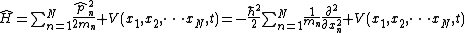 where the position of particle n is xn. |
 |  | |
 |  | |
| Three dimensions |  | 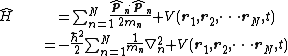 |
 |  This last equation is in a very high dimension,[2] so the solutions are not easy to visualize. | |
 |  |
Photoemission
| Property/Effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Photoelectric equation |
|  |
| Threshold frequency and |
| Can only be found by experiment. The De Broglie relations give the relation between them:  |
| Photon momentum |
The De Broglie relations give:  | |
Quantum uncertainty
| Property or effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Heisenberg's uncertainty principles |
| Position-momentum Energy-time  Number-phase  |
| Dispersion of observable |
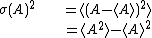 | |
| General uncertainty relation |
|  |
| Property or effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Density of states | 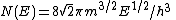 | |
| Fermi–Dirac distribution (fermions) |
|  |
| Bose–Einstein distribution (bosons) |  | |
Angular momentum
{{main|angular momentum operator|quantum number}}| Property or effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Angular momentum quantum numbers |
| Spin projection: Orbital:   Total:  |
| Angular momentum magnitudes | angular momementa:
| Spin magnitude: Orbital magnitude: 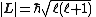 Total magnitude:   |
| Angular momentum components | Spin: Orbital:  | |
- Magnetic moments
In what follows, B is an applied external magnetic field and the quantum numbers above are used.
| Property or effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| orbital magnetic dipole moment |
|  z-component:  |
| spin magnetic dipole moment |
|  z-component:  |
| dipole moment potential |
|  |
The Hydrogen atom
{{main|Hydrogen atom}}| Property or effect | Nomenclature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Energy level :p≈ |
|  |
| Spectrum | λ = wavelength of emitted photon, during electronic transition from Ei to Ej | 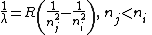 |
See also
- Defining equation (physical chemistry)
- List of electromagnetism equations
- List of equations in classical mechanics
- List of equations in fluid mechanics
- List of equations in gravitation
- List of equations in nuclear and particle physics
- List of equations in wave theory
- List of photonics equations
- List of relativistic equations
Footnotes
2. ^{{cite book |last=Shankar |first=R. |year=1994 |title=Principles of Quantum Mechanics |page=141 |publisher=Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers |isbn=978-0-306-44790-7}}
Sources
- {{cite book|author1=P.M. Whelan |author2=M.J. Hodgeson | title=Essential Principles of Physics| publisher=John Murray|edition=2nd| year=1978 | isbn=0-7195-3382-1}}
- {{cite book| author=G. Woan| title=The Cambridge Handbook of Physics Formulas| publisher=Cambridge University Press|edition=| year=2010| isbn=978-0-521-57507-2}}
- {{cite book| author=A. Halpern| title=3000 Solved Problems in Physics, Schaum Series| publisher=Mc Graw Hill|edition=| year=1988| isbn=978-0-07-025734-4}}
- {{cite book|pages=12–13|author1=R. G. Lerner |author2=G. L. Trigg | title=Encyclopaedia of Physics| publisher=VHC Publishers, Hans Warlimont, Springer|edition=2nd| year=2005| isbn=978-0-07-025734-4}}
- {{cite book|page=| author=C. B. Parker| title=McGraw Hill Encyclopaedia of Physics| publisher=McGraw Hill|edition=2nd| year=1994| isbn=0-07-051400-3}}
- {{cite book|page=|author1=P. A. Tipler |author2=G. Mosca | title=Physics for Scientists and Engineers: With Modern Physics| publisher=W. H. Freeman and Co|edition=6th| year=2008| isbn=978-1-4292-0265-7}}
- {{cite book|title=Analytical Mechanics|author1=L.N. Hand |author2=J. D. Finch |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2008|isbn=978-0-521-57572-0}}
- {{cite book|title=Mechanics, Vibrations and Waves|author1=T. B. Arkill |author2=C. J. Millar |publisher=John Murray |year=1974|isbn=0-7195-2882-8}}
- {{cite book|title=The Physics of Vibrations and Waves|edition=3rd|author=H.J. Pain|publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=1983|isbn=0-471-90182-2}}
- {{cite book|title=Dynamics and Relativity|author1=J. R. Forshaw |author2=A. G. Smith |publisher=Wiley |year=2009|isbn=978-0-470-01460-8}}
- {{cite book|title=Electricity and Modern Physics |edition=2nd|author=G. A. G. Bennet|publisher=Edward Arnold (UK)|year=1974|isbn=0-7131-2459-8}}
- {{cite book|title=Electromagnetism (2nd Edition)|author1=I. S. Grant |author2=W. R. Phillips |author3=Manchester Physics |publisher=John Wiley & Sons|year=2008|isbn=978-0-471-92712-9}}
- {{cite book|title=Introduction to Electrodynamics|edition=3rd |author=D.J. Griffiths|publisher=Pearson Education, Dorling Kindersley |year=2007|isbn=81-7758-293-3}}
Further reading
- {{cite book|title=Physics with Modern Applications|author=L. H. Greenberg|publisher=Holt-Saunders International W. B. Saunders and Co|year=1978|isbn=0-7216-4247-0}}
- {{cite book|title=Principles of Physics|author1=J. B. Marion |author2=W. F. Hornyak |publisher=Holt-Saunders International Saunders College|year=1984|isbn=4-8337-0195-2}}
- {{cite book|title=Concepts of Modern Physics|edition=4th|author=A. Beiser|publisher=McGraw-Hill (International)|year=1987|isbn=0-07-100144-1}}
- {{cite book|title=University Physics – With Modern Physics|edition=12th|author1=H. D. Young |author2=R. A. Freedman |publisher=Addison-Wesley (Pearson International)|year=2008|isbn=0-321-50130-6}}
- Primitive tribal group
- Primitivo (album)
- Primitivo (disambiguation)
- Primitivo Martinez
- Primitivo Martínez
- Primitivo Ríos Vázquez
- Primitivo Soul!
- Primitivo Viray
- Primkenau
- Primmer
- Primmi language
- Primm, Nevada, USA
- Primmore's Pride
- Primm Springs, Tennessee
- Prim (Neckar)
- Primnoa
- Primnoa pacifica
- Primnoa wingi
- Primnoidae
- Primo (2005 film)
- Primo amore
- Primo amore (1941 film)
- Primo amore (2004 film)
- Primo amore (disambiguation)
- Primo and Epico
 denotes the average
denotes the average