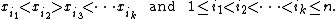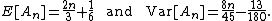- Efficient algorithms
- Distributional results
- Online algorithms
- See also
- References
In combinatorial mathematics, probability, and computer science, in the longest alternating subsequence problem, one wants to find a subsequence of a given sequence in which the elements are in alternating order, and in which the sequence is as long as possible.
Formally, if name="Stanleybook">{{citation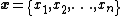 is a sequence of distinct real numbers, then the subsequence
is a sequence of distinct real numbers, then the subsequence 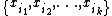 is alternating
is alternating
|first=Richard P.
|last=Stanley
|author-link=Richard P. Stanley
|title=Enumerative Combinatorics, Volume I, second edition
|publisher=Cambridge University Press
|year=2011}} (or zigzag or down-up)if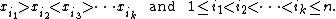
Similarly,  is reverse alternating (or up-down) if
is reverse alternating (or up-down) if
Let 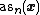 denote the length (number of terms) of the longest alternating subsequence of
denote the length (number of terms) of the longest alternating subsequence of  . For example, if we consider some of the permutations of the integers 1,2,3,4,5, we have that
. For example, if we consider some of the permutations of the integers 1,2,3,4,5, we have that
-
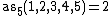 ; because any sequence of 2 distinct digits are (by definition) alternating. (for example 1,2 or 1,4 or 3,5)
; because any sequence of 2 distinct digits are (by definition) alternating. (for example 1,2 or 1,4 or 3,5) -
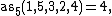 because 1,5,3,4 and 1,5,2,4 and 1,3,2,4 are all alternating, and there is no alternating subsequence with more elements;
because 1,5,3,4 and 1,5,2,4 and 1,3,2,4 are all alternating, and there is no alternating subsequence with more elements; -
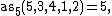 because 5,3,4,1,2 is itself alternating.
because 5,3,4,1,2 is itself alternating.
Efficient algorithms
The longest alternating subsequence problem is solvable in time 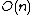 , where
, where  is the length of the original sequence.{{Citation needed|date=October 2016}}
is the length of the original sequence.{{Citation needed|date=October 2016}}
Distributional results
If name="widom">{{citation is a random permutation of the integers
is a random permutation of the integers 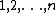 and
and 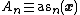 , then it is possible to show
, then it is possible to show
| url = http://www.combinatorics.org/Volume_13/Abstracts/v13i1r25.html
| last1 = Widom | first1 = Harold
| journal = Electron. J. Combin.
| pages = Research Paper 25, 7
| title = On the limiting distribution for the length of the longest alternating sequence in a random permutation
| volume = 13
| year = 2006}}
| doi = 10.1307/mmj/1220879431
| last1 = Stanley | first1 = Richard P. | author1-link = Richard_P._Stanley
| journal = Michigan Math. J.
| pages = 675–687
| title = Longest alternating subsequences of permutations
| volume = 57
| year = 2008| arxiv = math/0511419}}
| url = http://www.combinatorics.org/Volume_17/Abstracts/v17i1r168.html
| last1 = Houdré | first1 = Christian
| last2 = Restrepo | first2 = Ricardo
| journal = Electron. J. Combin.
| title = A probabilistic approach to the asymptotics of the length of the longest alternating subsequence
| volume = 17
| pages = Research Paper 168, 19
| year = 2010}}
that
Moreover, as  , the random variable
, the random variable  , appropriately centered and scaled, converges to a standard normal distribution.
, appropriately centered and scaled, converges to a standard normal distribution.
Online algorithms
The longest alternating subsequence problem has also been studied in the setting of online algorithms, in which the elements of  are presented in an online fashion, and a decision maker needs to decide whether to include or exclude each element at the time it is first presented, without any knowledge of the elements that will be presented in the future,
are presented in an online fashion, and a decision maker needs to decide whether to include or exclude each element at the time it is first presented, without any knowledge of the elements that will be presented in the future,
and without the possibility of recalling on preceding observations.
Given a sequence 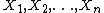 of independent random variables with common continuous distribution
of independent random variables with common continuous distribution  , it is possible to construct a selection procedure that maximizes the expected number of alternating selections.
, it is possible to construct a selection procedure that maximizes the expected number of alternating selections.
Such expected values can be tightly estimated, and it equals 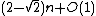 .[1]
.[1]
As  , the optimal number of online alternating selections appropriately centered and scaled converges to a normal distribution.[2]
, the optimal number of online alternating selections appropriately centered and scaled converges to a normal distribution.[2]
See also
- Alternating permutation
- Permutation pattern and pattern avoidance
- Counting local maxima and/or local minima in a given sequence
- Turning point tests for testing statistical independence of
 observations
observations - Number of alternating runs
- Longest increasing subsequence
- Longest common subsequence problem
References
2. ^{{citation | doi = 10.1239/aap/1401369706 | last1 = Arlotto | first1 = Alessandro | last2 = Steele | first2 = J. Michael | author2-link = J._Michael_Steele | journal = Adv. Appl. Probab. | pages = 536–559 | title = Optimal online selection of an alternating subsequence: a central limit theorem | volume = 46 | issue = 2 | year = 2014}}
- Read in
- Readin' and Writin'
- Readin and Writin
- Read India
- Reading
- Reading 20K
- Reading Abbey Gateway
- Reading Abbey R F C
- Reading Abbey R. F. C.
- Reading abbey ruins
- Reading a book
- Reading Aces
- Reading Airport Authority
- Reading Airport, Pennsylvania
- Reading aloud
- Reading Amateur Regatta
- Reading and Leeds Festival 2011
- Reading and Northern Railroad.
- Reading and writing
- Reading Army Airfield
- Readingas
- Reading Athletic Club
- Reading & Bates
- Reading & Bates Drilling Co.
- Reading Bluecoat School