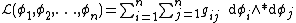- Overview
- References
In physics, a sigma model is a physical system that is described by a Lagrangian density of the form:
Depending on the scalars in {{math|gij}}, it is either a linear sigma model or a non-linear sigma model. The fields {{math|ϕi}}, in general, provide a map from a base manifold called the worldsheet to a target Riemannian manifold of the scalars linked together by internal symmetries. (In string theory, however, that is often understood to be the actual spacetime.)
Overview
The sigma model was introduced by {{harvtxt|Gell-Mann|Lévy|1960|loc=section 5}}; the name σ-model comes from a field in their model corresponding to a spinless meson called {{mvar|σ}}, a scalar meson introduced earlier by Julian Schwinger.[1] The model served as the dominant prototype of spontaneous symmetry breaking of O(4) down to O(3): the three axial generators broken are the simplest manifestation of chiral symmetry breaking, the surviving unbroken O(3) representing isospin.
A basic example is provided by quantum mechanics which is a quantum field theory in one dimension. It's a sigma model with a base manifold given by the real line parameterizing the time (or an interval, or the circle, etc.) and a target space that is the real line.
The model may be augmented by a torsion term to yield the Wess–Zumino–Witten model.
References
- {{Citation
| last1=Gell-Mann | first1=M.
| last2=Lévy | first2=M.
| year=1960
| title=The axial vector current in beta decay
| journal=Il Nuovo Cimento
| volume=16 | pages=705–726
| doi=10.1007/BF02859738
| bibcode=1960NCim...16..705G}} online copy