- Technical issues Getting to orbit Acceleration
- Practical attempts Project Babylon Super High Altitude Research Project Green Launch
- In fiction
- See also
- References
- External links
A space gun, sometimes called a Verne gun because of its appearance in From the Earth to the Moon by Jules Verne, is a method of launching an object into space using a large gun- or cannonlike structure. Space guns could thus potentially provide a method of non-rocket spacelaunch. It has been conjectured that space guns could place satellites into Earth's orbit (although after-launch propulsion of the satellite would be necessary to achieve a stable orbit), and could also launch spacecraft beyond Earth's gravitational pull and into other parts of the Solar System by exceeding Earth's escape velocity of about 11.2 km/s or {{convert|40320|kph|mph|abbr=on}}. However, these speeds are too far into the hypersonic range for most practical propulsion systems and also would cause most objects to burn up due to aerodynamic heating or be torn apart by aerodynamic drag.
Therefore, a more likely future use of space guns would be to launch objects into near Earth orbit, from where attached rockets could be fired or the objects could be "collected" by maneuverable orbiting satellites.{{cn|date=March 2018}}
In Project HARP, a 1960s joint United States and Canada defence project, a U.S. Navy {{convert|16|in|mm|abbr=on}} 100 caliber gun was used to fire a {{convert|180|kg|lb|abbr=on}} projectile at 3600 m/s or {{convert|12960|kph|mph|abbr=on}}, reaching an apogee of {{convert|180|km|mi|abbr=on}}, hence performing a suborbital spaceflight. However, a space gun has never been successfully used to launch an object into orbit or out of Earth's gravitational pull.
Technical issues
The large g-force likely to be experienced by a ballistic projectile launched in this manner would mean that a space gun would be incapable of safely launching humans or delicate instruments, rather being restricted to freight, fuel or ruggedized satellites.
Getting to orbit
A space gun by itself is not capable of placing objects into stable orbit around the object (planet or otherwise) from which it launches them. The orbit is a parabolic orbit, a hyperbolic orbit, or part of an elliptic orbit which ends at the planet's surface at the point of launch or another point. This means that an uncorrected ballistic payload will always strike the planet within its first orbit unless the velocity was so high as to reach or exceed escape velocity.{{cn|date=May 2018}}. As a result, all payloads intended to reach a closed orbit need at least to perform some sort of course correction to create another orbit that does not intersect the planet's surface.
A rocket can be used for additional boost, as planned in both Project HARP and the Quicklaunch project. The magnitude of such correction may be small; for instance, the StarTram Generation 1 reference design involves a total of 0.6 km/s of rocket burn to raise perigee well above the atmosphere when entering an 8 km/s low Earth orbit.[1]
In a three-body or larger system, a gravity assist trajectory might be available such that a carefully aimed escape velocity projectile would have its trajectory modified by the gravitational fields of other bodies in the system such that the projectile would eventually return to orbit the initial planet using only the launch delta-v.[2][3]
Isaac Newton avoided this objection in his thought experiment by positing an impossibly tall mountain from which his cannon was fired. If in a stable orbit, the projectile would circle the planet and return to the altitude of launch after one orbit (see Newton's cannonball).[4]Acceleration
A space gun with a "gun barrel" of length ( ), and the needed velocity (
), and the needed velocity (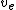 ), the acceleration (
), the acceleration ( ) is provided by the following formula:{{cn|date=May 2018}}
) is provided by the following formula:{{cn|date=May 2018}}
For instance, with a space gun with a vertical "gun barrel" through both the Earth's crust and the troposphere, totalling ~60 km of length ( ), and a velocity (
), and a velocity (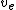 ) enough to escape the Earth's gravity (escape velocity, which is 11.2 km/s on Earth), the acceleration (
) enough to escape the Earth's gravity (escape velocity, which is 11.2 km/s on Earth), the acceleration ( ) would theoretically be more than 1000 m/s2, which is more than 100 g-forces, which is about 3 times the human tolerance to g-forces of maximum 20 to 35 g[5] during the ~10 seconds such a firing would take. Theoretically, a space gun with a circular (ring shaped) track could utilize much lower accelerations because its effective track length is infinite (with the object going around the ring numerous times), though the centripetal acceleration could be enormous as the payload neared escape velocity, depending on the track size.{{cn|date=May 2018}}
) would theoretically be more than 1000 m/s2, which is more than 100 g-forces, which is about 3 times the human tolerance to g-forces of maximum 20 to 35 g[5] during the ~10 seconds such a firing would take. Theoretically, a space gun with a circular (ring shaped) track could utilize much lower accelerations because its effective track length is infinite (with the object going around the ring numerous times), though the centripetal acceleration could be enormous as the payload neared escape velocity, depending on the track size.{{cn|date=May 2018}}
Practical attempts
The German V-3 cannon program (less well known than the V-2 rocket or V-1 flying bomb), during the Second World War was an attempt to build something approaching a space gun. Based in the Pas-de-Calais area of France it was planned to be more devastating than the other Nazi 'Vengeance weapons'. The cannon was capable of launching 140 kg, 15 cm diameter shells over a distance of 88 km. It was destroyed by RAF bombing using Tallboy blockbuster bombs in July 1944.[6] The V-3 cannon used staged propulsion, which gave it a far greater range.[7]
Project Babylon
The most prominent recent attempt to make a space gun was artillery engineer Gerald Bull's Project Babylon, which was also known as the 'Iraqi supergun' by the media. During Project Babylon, Bull used his experience from Project HARP to build a massive cannon for Saddam Hussein, leader of Ba'athist Iraq. Bull was assassinated before the project was completed.[8]
Super High Altitude Research Project
Since Bull's death, few have seriously attempted to build a space gun. Perhaps most promisingly, the US Ballistic Missile Defense program sponsored the Super High Altitude Research Project (SHARP) in the 1980s. Developed at Lawrence Livermore Laboratory, it is a light-gas gun and has been used to test fire objects at Mach 9.
Green Launch
After cancellation of SHARP, lead developer John Hunter founded the Jules Verne Launcher Company in 1996 and the, currently inactive, Quicklaunch company. As of January 2017, Hunter's Green Launch is striving to surpass the ballistic altitude world record set by HARP in 1966.
Ram accelerators have also been proposed as an alternative to light-gas guns. Other proposals use electromagnetic techniques for accelerating the payload, such as coilguns and railguns.{{cn|date=May 2018}}
In fiction
The first publication of the concept may be Newton's cannonball in the 1728 book A Treatise of the System of the World, although it was primarily used as a thought experiment regarding gravity.[9]
Perhaps the most famous representation of a space gun is in Jules Verne's novels From the Earth to the Moon and Around the Moon (loosely interpreted into the early film Le Voyage dans la Lune), in which astronauts fly to the moon aboard a ship launched from a cannon. Another famous example is the hydrogen accelerator cannon used by the Martians to launch their invasion in H. G. Wells' book The War of the Worlds. Wells also used the concept in the climax of the 1936 movie Things to Come. The device was featured in films as late as 1967, such as Jules Verne's Rocket to the Moon.
In the video game Worlds of Adventure 2: Martian Dreams, Percival Lowell builds a space gun to send a spacecraft to Mars.
The video game Steel Empire, a shoot 'em up with steampunk aesthetics, features a space gun in its seventh level that is used by the main villain General Styron to launch himself to the Moon.
In Hannu Rajaniemi's 2012 novel The Fractal Prince, a space gun at the "Jannah-of-the-cannon", powered by a 150-kiloton nuclear bomb, is used to launch a spaceship from Earth.
The 2015 video game SOMA features a space gun used to launch satellites.
Gerald Bull's assassination and the Project Babylon gun were also the starting point for Frederick Forsyth's 1994 novel The Fist of God. In Larry Bond's 2001 novella and 2015 novel Lash-Up, China uses a space gun to destroy American GPS satellites.
In The Thousand-Year Door, a village of Bob-ombs operates a space gun to send Paper Mario and company to the X-Naut's base on the moon.
See also
{{Portal| Spaceflight }}- Geostationary orbit: circular orbit 35,786 kilometres (22,236 mi) above the Earth used by communications satellites
- Newton's cannonball
- SHARP
- Quicklaunch
- StarTram
- Mass driver
- Space elevator
- Launch loop
- Lightcraft
- Space fountain
- Tether propulsion
- Non-rocket spacelaunch
References
2. ^{{cite journal|last=Clarke|first=Victor C., Jr.|title=An Essay On the Application and Principle of Gravity-Assist Trajectories For Space Flight|page=7|date=1970-04-10|url=http://gravityresearchfoundation.org/pdf/awarded/1970/clarke.pdf|accessdate=2013-08-13|publisher=Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology|quote=By induction then, it is obvious that the process of diverting a spacecraft from one planet to another might be continued indefinitely, if the planets were in favorable positions.|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160418190308/http://www.gravityresearchfoundation.org/pdf/awarded/1970/clarke.pdf|archivedate=2016-04-18|df=}}
3. ^{{cite journal|last=Minovitch|first=Michael|title=A Method For Determining Interplanetary Free-Fall Reconnaissance Trajectories|series=Jet Propulsion Laboratory Technical Memos|number=TM-312-130|pages=38–44|date=August 23, 1961|url=http://www.gravityassist.com/Letters/LD-1.pdf#page=24}}
4. ^{{cite book|last=Newton|first=Isaac|title=A Treatise of the System of the World|year=1728|publisher=F. Fayram|pages=6–12|url=https://play.google.com/books/reader?id=rEYUAAAAQAAJ&printsec=frontcover&output=reader&authuser=0&hl=en&pg=GBS.PA4}}
5. ^{{cite web| author=Anton Sukup| title=David PURLEY Silverstone crash| year=1977| url=http://www.asag.sk/bio/purley.htm| accessdate=July 31, 2006}}
6. ^{{cite web|author=RAF staff |date=6 April 2005 |url=http://www.raf.mod.uk/bombercommand/diary.html |work=Bomber Command: Campaign Diary |title=RAF History - Bomber Command 60th Anniversary |publisher=RAF |archiveurl=http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20070706011932/http://www.raf.mod.uk/bombercommand/jul44.html |archivedate=6 July 2007|accessdate=23 October 2013}}
7. ^{{cite web|url=http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-3330715/Building-Hitler-s-SUPERGUN-Researcher-reveals-megaweapon-carved-French-hillside-worked.html|title=Researcher reveals how Hitler’s SUPERGUN worked|website=Dailymail.co.uk|accessdate=20 August 2017}}
8. ^William Lowther, Arms and the Man: Dr. Gerald Bull, Iraq, and the Supergun (Presidio, Novato, 1991)
9. ^vectorsite.net > [4.0] Space Guns v1.1.4 / chapter 4 of 7 / 01 jun 08 / greg goebel / public domain
External links
- FAS space gun page
- The 150 Kiloton Nuclear Verne Gun
- Gerard George Shelley
- Gerard (Gerry) Sarnat
- Gerard Gibbons
- Gerard Gramse
- Gerard Granollers-Pujol
- Gerard Gropaiz
- Gerard Grouve
- Gerard Guazzini
- Gerard Gumbau
- Gerard Gumbau Garriga
- Gerard Hall Lloyd Fitzwilliams
- Gerard Heath Lander
- Gerard Hernandez
- Gerard Herold
- Gerard Hewson
- Gerard Higny
- Gerard H. L. Fitzwilliams
- Gerard Hoet the elder
- Gerard Hoey
- Gerard Holtz
- Gerard Hornebolt
- Gerard Houlton
- Gerard H U Noel
- Gerard I
- Gerard I (bishop of Cambrai)
