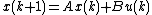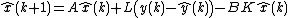- Typical observer model Discrete-time case Continuous-time case Peaking and other observer methods
- State observers for nonlinear systems Linearizable error dynamics Sliding mode observer
- Multi Observer
- Bounding observers
- See also
- References
In control theory, a state observer is a system that provides an estimate of the internal state of a given real system, from measurements of the input and output of the real system. It is typically computer-implemented, and provides the basis of many practical applications.
Knowing the system state is necessary to solve many control theory problems; for example, stabilizing a system using state feedback. In most practical cases, the physical state of the system cannot be determined by direct observation. Instead, indirect effects of the internal state are observed by way of the system outputs. A simple example is that of vehicles in a tunnel: the rates and velocities at which vehicles enter and leave the tunnel can be observed directly, but the exact state inside the tunnel can only be estimated. If a system is observable, it is possible to fully reconstruct the system state from its output measurements using the state observer.
Typical observer model
Discrete-time case
The state of a linear, time-invariant physical discrete-time system is assumed to satisfy
where, at time  ,
,  is the plant's state;
is the plant's state;  is its inputs; and
is its inputs; and  is its outputs. These equations simply say that the plant's current outputs and its future state are both determined solely by its current states and the current inputs. (Although these equations are expressed in terms of discrete time steps, very similar equations hold for continuous systems). If this system is observable then the output of the plant,
is its outputs. These equations simply say that the plant's current outputs and its future state are both determined solely by its current states and the current inputs. (Although these equations are expressed in terms of discrete time steps, very similar equations hold for continuous systems). If this system is observable then the output of the plant,  , can be used to steer the state of the state observer.
, can be used to steer the state of the state observer.
The observer model of the physical system is then typically derived from the above equations. Additional terms may be included in order to ensure that, on receiving successive measured values of the plant's inputs and outputs, the model's state converges to that of the plant. In particular, the output of the observer may be subtracted from the output of the plant and then multiplied by a matrix  ; this is then added to the equations for the state of the observer to produce a so-called Luenberger observer, defined by the equations below. Note that the variables of a state observer are commonly denoted by a "hat":
; this is then added to the equations for the state of the observer to produce a so-called Luenberger observer, defined by the equations below. Note that the variables of a state observer are commonly denoted by a "hat":  and
and 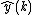 to distinguish them from the variables of the equations satisfied by the physical system.
to distinguish them from the variables of the equations satisfied by the physical system.
The observer is called asymptotically stable if the observer error  converges to zero when
converges to zero when  . For a Luenberger observer, the observer error satisfies
. For a Luenberger observer, the observer error satisfies 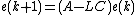 . The Luenberger observer for this discrete-time system is therefore asymptotically stable when the matrix
. The Luenberger observer for this discrete-time system is therefore asymptotically stable when the matrix  has all the eigenvalues inside the unit circle.
has all the eigenvalues inside the unit circle.
For control purposes the output of the observer system is fed back to the input of both the observer and the plant through the gains matrix  .
.
The observer equations then become:
or, more simply,