- See also
In type theory, a kind of foundation of mathematics, a quotient type is an algebraic data type that represents a type whose equality relation has been redefined by a given equivalence relation such that the elements of the type are partitioned into a set of equivalence classes whose cardinality is less than or equal to that of the base type. Just as product types and sum types are analogous to the cartesian product and disjoint sum of abstract algebraic structures, quotient types reflect the concept of set-theoretic quotients, sets whose elements are surjectively partitioned into equivalence classes by a given equivalence relation on the set. Algebraic structures whose underlying set is a quotient are also termed quotients. Examples of such quotient structures include quotient sets, groups, rings, categories and, in topology, quotient spaces. For example,  , the rational numbers, is the quotient ring – or "field of fractions" – of
, the rational numbers, is the quotient ring – or "field of fractions" – of 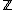 , the integers.
, the integers.
In type theories that lack quotient types, setoids – sets explicitly equipped with an equivalence relation – are often used instead.
See also
- Algebraic data type
- Product type
- Sum type
- Setoid
- 2008-09 OK Liga
- 2008-09 OK Liga Femenina
- 2008-09 Ole Miss Rebels men's basketball team
- 2008-09 Olympiacos B.C. season
- 2008-09 Olympique de Marseille season
- 2008-09 Orszagos Bajnoksag I (men's water polo)
- 2008-09 Országos Bajnokság I (men's water polo)
- 2008-09 Oslo riots
- 2008-09 Pakistan Premier League
- 2008-09 Panionios G.S.S. season
- 2008-09 Papua New Guinea National Soccer League
- 2008-09 Paris Saint-Germain F.C. (Ladies) season
- 2008-09 Paris Saint-Germain F.C. season
- 2008-09 Parma F.C. season
- 2008-09 Pentangular One Day Cup
- 2008-09 Persian Gulf Cup table
- 2008-09 Persib Bandung season
- 2008-09 Perth Glory FC season
- 2008-09 Perth Glory W-League season
- 2008-09 PFC Levski Sofia season
- 2008-09 PlusLiga
- 2008-09 Port Vale FC season
- 2008-09 Port Vale season
- 2008-09 Port Vila Premier League
- 2008-09 Premiership Rugby