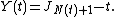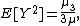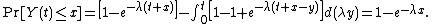- Formal definition
- Probability distribution of the residual time Waiting time paradox Special case: Markovian holding times
- Related notions
- References
In the theory of renewal processes, a part of the mathematical theory of probability, the residual time or the forward recurrence time is the time between any given time  and the next epoch of the renewal process under consideration. In the context of random walks, it is also known as overshoot. Another way to phrase residual time is "how much more time is there to wait?".
and the next epoch of the renewal process under consideration. In the context of random walks, it is also known as overshoot. Another way to phrase residual time is "how much more time is there to wait?".
The residual time is very important in most of the practical applications of renewal processes:
- In queueing theory, it determines the remaining time, that a newly arriving customer to a non-empty queue has to wait until being served.[1]
- In wireless networking, it determines, for example, the remaining lifetime of a wireless link on arrival of a new packet.
- In dependability studies, it models the remaining lifetime of a component.
- etc.
Formal definition
Consider a renewal process  , with holding times
, with holding times 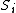 and jump times (or renewal epochs)
and jump times (or renewal epochs)  , and
, and  . The holding times
. The holding times 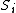 are non-negative, independent, identically distributed random variables and the renewal process is defined as
are non-negative, independent, identically distributed random variables and the renewal process is defined as  . Then, to a given time
. Then, to a given time  , there corresponds uniquely an
, there corresponds uniquely an 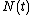 , such that:
, such that:
The residual time (or excess time) is given by the time  from
from  to the next renewal epoch.
to the next renewal epoch.
Probability distribution of the residual time
Let the cumulative distribution function of the holding times 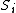 be
be  and recall that the renewal function of a process is
and recall that the renewal function of a process is  . Then, for a given time
. Then, for a given time  , the cumulative distribution function of
, the cumulative distribution function of  is calculated as:[2]
is calculated as:[2]
Differentiating with respect to  , the probability density function can be written as
, the probability density function can be written as
where we have substituted  From elementary renewal theorem
From elementary renewal theorem 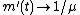 as
as  . If we consider the limiting distribution as
. If we consider the limiting distribution as  , assuming that
, assuming that  as
as  , we have the limiting pdf as
, we have the limiting pdf as
where  is the mean of the distribution
is the mean of the distribution  . Likewise, the cumulative distribution of the residual time is
. Likewise, the cumulative distribution of the residual time is
For large  , the distribution is independent of
, the distribution is independent of  , making it a stationary distribution. An interesting fact is that the limiting distribution of forward recurrence time (or residual time) has the same form as the limiting distribution of the backward recurrence time (or age). This distribution is always J-shaped, with mode at zero.
, making it a stationary distribution. An interesting fact is that the limiting distribution of forward recurrence time (or residual time) has the same form as the limiting distribution of the backward recurrence time (or age). This distribution is always J-shaped, with mode at zero.
The first two moments of this limiting distribution  are:
are:
where  is the variance of
is the variance of  and
and  and
and  are its second and third moments.
are its second and third moments.
Waiting time paradox
The fact that  is also known variously as the waiting time paradox, inspection paradox, or the paradox of renewal theory. The paradox arises from the fact that the average waiting time for to the next renewal, assuming that the reference time point
is also known variously as the waiting time paradox, inspection paradox, or the paradox of renewal theory. The paradox arises from the fact that the average waiting time for to the next renewal, assuming that the reference time point  is uniform randomly selected within the inter-renewal interval, is larger than the average inter-renewal interval
is uniform randomly selected within the inter-renewal interval, is larger than the average inter-renewal interval  . The average waiting is
. The average waiting is  only when
only when 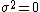 , that is when the renewals are always punctual or deterministic.
, that is when the renewals are always punctual or deterministic.
Special case: Markovian holding times
When the holding times 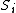 are exponentially distributed with
are exponentially distributed with  , the residual times are also exponentially distributed. That is because
, the residual times are also exponentially distributed. That is because  and:
and:
This is a known characteristic of the exponential distribution, i.e., its memoryless property. Intuitively, this means that it does not matter how long it has been since the last renewal epoch, the remaining time is still probabilistically the same as in the beginning of the holding time interval.
Related notions
Renewal theory texts usually also define the spent time or the backward recurrence time (or the current lifetime) as  . Its distribution can be calculated in a similar way to that of the residual time. Likewise, the total life time is the sum of backward recurrence time and forward recurrence time.
. Its distribution can be calculated in a similar way to that of the residual time. Likewise, the total life time is the sum of backward recurrence time and forward recurrence time.
References
2. ^Jyotiprasad Medhi, "Stochastic processes", New Age International, 1994, {{ISBN|81-224-0549-5}}, 9788122405491
- Terapixel
- Terapixel image
- Terapon theraps
- Tera Pukhri
- Tera Pyaar Meri Zindagi
- Tera Pyar Nahi Bhoole
- Teraqechi Kola
- Teraqichi Kola
- Teraran
- Teraria
- TERA Rising
- Terarria
- TERAS
- Teras
- Teras abjectana
- Teras aenea
- Teras affinatana
- Terasaki
- Teras albaniana
- Teras albiscapulana
- Teras algoana
- Teras americana
- Teras arcticana
- Teras articana
- Teras aspersana