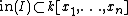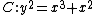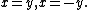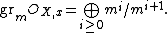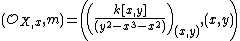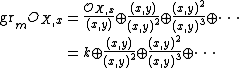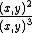- Definitions in nonlinear analysis
- Definition in convex geometry
- Definition in algebraic geometry
- See also
- References
In geometry, the tangent cone is a generalization of the notion of the tangent space to a manifold to the case of certain spaces with singularities.
Definitions in nonlinear analysis
In nonlinear analysis, there are many definitions for a tangent cone, including the adjacent cone, Bouligand's contingent cone, and the Clarke tangent cone. These three cones coincide for a convex set, but they can differ on more general sets.
Definition in convex geometry
Let K be a closed convex subset of a real vector space V and ∂K be the boundary of K. The solid tangent cone to K at a point x ∈ ∂K is the closure of the cone formed by all half-lines (or rays) emanating from x and intersecting K in at least one point y distinct from x. It is a convex cone in V and can also be defined as the intersection of the closed half-spaces of V containing K and bounded by the supporting hyperplanes of K at x. The boundary TK of the solid tangent cone is the tangent cone to K and ∂K at x. If this is an affine subspace of V then the point x is called a smooth point of ∂K and ∂K is said to be differentiable at x and TK is the ordinary tangent space to ∂K at x.
Definition in algebraic geometry
Let X be an affine algebraic variety embedded into the affine space  , with defining ideal
, with defining ideal 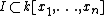 . For any polynomial f, let
. For any polynomial f, let 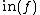 be the homogeneous component of f of the lowest degree, the initial term of f, and let
be the homogeneous component of f of the lowest degree, the initial term of f, and let
be the homogeneous ideal which is formed by the initial terms 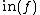 for all
for all 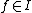 , the initial ideal of I. The tangent cone to X at the origin is the Zariski closed subset of
, the initial ideal of I. The tangent cone to X at the origin is the Zariski closed subset of  defined by the ideal
defined by the ideal 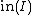 . By shifting the coordinate system, this definition extends to an arbitrary point of
. By shifting the coordinate system, this definition extends to an arbitrary point of  in place of the origin. The tangent cone serves as the extension of the notion of the tangent space to X at a regular point, where X most closely resembles a differentiable manifold, to all of X. (The tangent cone at a point of
in place of the origin. The tangent cone serves as the extension of the notion of the tangent space to X at a regular point, where X most closely resembles a differentiable manifold, to all of X. (The tangent cone at a point of  that is not contained in X is empty.)
that is not contained in X is empty.)
For example, the nodal curve
is singular at the origin, because both partial derivatives of f(x, y) = y2 − x3 − x2 vanish at (0, 0). Thus the Zariski tangent space to C at the origin is the whole plane, and has higher dimension than the curve itself (two versus one). On the other hand, the tangent cone is the union of the tangent lines to the two branches of C at the origin,
Its defining ideal is the principal ideal of k[x] generated by the initial term of f, namely y2 − x2 = 0.
The definition of the tangent cone can be extended to abstract algebraic varieties, and even to general Noetherian schemes. Let X be an algebraic variety, x a point of X, and (OX,x, m) be the local ring of X at x. Then the tangent cone to X at x is the spectrum of the associated graded ring of OX,x with respect to the m-adic filtration:
If we look at our previous example, then we can see that graded pieces contain the same information. So let
then if we expand out the associated graded ring
we can see that the polynomial defining our variety
in
See also
- Cone
- Monge cone
- Normal cone
References
- {{Springer|title=Tangent cone|id=T/t092120|author=M. I. Voitsekhovskii}}
- Chinese wall (disambiguation)
- Chinese Wall (Mad Men)
- Chinese Walter
- "Chinese" Walter
- Chinese warlord
- Chinese water snake
- Chinese wealth fund
- Chinese weather fish
- Chinese weatherfish
- Chinese weatherloach
- Chinese weather loach
- Chinese week
- Chinese White
- Chinese White Dolphin
- Chinese white pear
- Chinese Wikepedia
- Chinese Wiki
- Chinese wikipedia
- Chinese Willow
- Chinesewilson
- Chinese windlass
- Chinese windmill
- Chinese wine
- Chinese Witch Hazel
- Chinese witch hazel