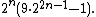- Properties
- Connection with amicable numbers
- Generalization
- References
- External links
| name = Thabit prime
| named_after = Thābit ibn Qurra
| terms_number = 62
| con_number = Infinite
| parentsequence = Thabit numbers
| first_terms = 2, 5, 11, 23, 47, 191, 383, 6143, 786431
| largest_known_term = {{nowrap|3×211,895,718 − 1}}
| OEIS = A007505
}}
In number theory, a Thabit number, Thâbit ibn Kurrah number, or 321 number is an integer of the form  for a non-negative integer n.
for a non-negative integer n.
The first few Thabit numbers are:
2, 5, 11, 23, 47, 95, 191, 383, 767, 1535, 3071, 6143, 12287, 24575, 49151, 98303, 196607, 393215, 786431, 1572863, ... {{OEIS|id=A055010}}
The 9th Century mathematician, physician, astronomer and translator Thābit ibn Qurra is credited as the first to study these numbers and their relation to amicable numbers.[1]
Properties
The binary representation of the Thabit number 3·2n−1 is n+2 digits long, consisting of "10" followed by n 1s.
The first few Thabit numbers that are prime (also known as Thabit primes or 321 primes):
2, 5, 11, 23, 47, 191, 383, 6143, 786431, 51539607551, 824633720831, ... {{OEIS|id=A007505}}{{As of|2015|10}}, there are 62 known prime Thabit numbers. Their n values are :[2][3][4]
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 11, 18, 34, 38, 43, 55, 64, 76, 94, 103, 143, 206, 216, 306, 324, 391, 458, 470, 827, 1274, 3276, 4204, 5134, 7559, 12676, 14898, 18123, 18819, 25690, 26459, 41628, 51387, 71783, 80330, 85687, 88171, 97063, 123630, 155930, 164987, 234760, 414840, 584995, 702038, 727699, 992700, 1201046, 1232255, 2312734, 3136255, 4235414, 6090515, 11484018, 11731850, 11895718, ... {{OEIS|id=A002235}}
The primes for n≥234760 were found by the distributed computing project 321 search.[5] The largest of these, 3·211895718−1, has 3580969 digits and was found in June 2015.
In 2008, Primegrid took over the search for Thabit primes.[6] It is still searching and has already found all currently known Thabit primes with n ≥ 4235414.[7] It is also searching for primes of the form 3·2n+1, such primes are called Thabit primes of the second kind or 321 primes of the second kind.
The first few Thabit numbers of the second kind are:
4, 7, 13, 25, 49, 97, 193, 385, 769, 1537, 3073, 6145, 12289, 24577, 49153, 98305, 196609, 393217, 786433, 1572865, ... {{OEIS|id=A181565}}
The first few Thabit primes of the second kind are:
7, 13, 97, 193, 769, 12289, 786433, 3221225473, 206158430209, 6597069766657, 221360928884514619393, ... {{OEIS|id=A039687}}
Their n values are:
1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 12, 18, 30, 36, 41, 66, 189, 201, 209, 276, 353, 408, 438, 534, 2208, 2816, 3168, 3189, 3912, 20909, 34350, 42294, 42665, 44685, 48150, 54792, 55182, 59973, 80190, 157169, 213321, 303093, 362765, 382449, 709968, 801978, 916773, 1832496, 2145353, 2291610, 2478785, 5082306, 7033641, 10829346, ... {{OEIS|id=A002253}}
Connection with amicable numbers
When both n and n−1 yield Thabit primes (of the first kind), and  is also prime, a pair of amicable numbers can be calculated as follows:
is also prime, a pair of amicable numbers can be calculated as follows:
and
For example, n = 2 gives the Thabit prime 11, and n−1 = 1 gives the Thabit prime 5, and our third term is 71. Then, 22=4, multiplied by 5 and 11 results in 220, whose divisors add up to 284, and 4 times 71 is 284, whose divisors add up to 220.
The only known n satisfying these conditions are 2, 4 and 7, corresponding to the Thabit primes 11, 47 and 383 given by n, the Thabit primes 5, 23 and 191 given by n−1, and our third terms are 71, 1151 and 73727. (The corresponding amicable pairs are (220, 284), (17296, 18416) and (9363584, 9437056))
Generalization
For integer b ≥ 2, a Thabit number base b is a number of the form (b+1)·bn − 1 for a non-negative integer n. Also, for integer b ≥ 2, a Thabit number of the second kind base b is a number of the form (b+1)·bn + 1 for a non-negative integer n.
The Williams numbers are also a generalization of Thabit numbers. For integer b ≥ 2, a Williams number base b is a number of the form (b−1)·bn − 1 for a non-negative integer n.[8] Also, for integer b ≥ 2, a Williams number of the second kind base b is a number of the form (b−1)·bn + 1 for a non-negative integer n.
For integer b ≥ 2, a Thabit prime base b is a Thabit number base b that is also prime. Similarly, for integer b ≥ 2, a Williams prime base b is a Williams number base b that is also prime.
Every prime p is a Thabit prime of the first kind base p, a Williams prime of the first kind base p+2, and a Williams prime of the second kind base p; if p ≥ 5, then p is also a Thabit prime of the second kind base p−2.
It is a conjecture that for every integer b ≥ 2, there are infinitely many Thabit primes of the first kind base b, infinitely many Williams primes of the first kind base b, and infinitely many Williams primes of the second kind base b; also, for every integer b ≥ 2 that is not congruent to 1 modulo 3, there are infinitely many Thabit primes of the second kind base b. (If the base b is congruent to 1 modulo 3, then all Thabit numbers of the second kind base b are divisible by 3 (and greater than 3, since b ≥ 2), so there are no Thabit primes of the second kind base b.)
The exponent of Thabit primes of the second kind cannot congruent to 1 mod 3 (except 1 itself), the exponent of Williams primes of the first kind cannot congruent to 4 mod 6, and the exponent of Williams primes of the second kind cannot congruent to 1 mod 6 (except 1 itself), since the corresponding polynomial to b is a reducible polynomial. (If n ≡ 1 mod 3, then (b+1)·bn + 1 is divisible by b2 + b + 1; if n ≡ 4 mod 6, then (b−1)·bn − 1 is divisible by b2 − b + 1; and if n ≡ 1 mod 6, then (b−1)·bn + 1 is divisible by b2 − b + 1) Otherwise, the corresponding polynomial to b is an irreducible polynomial, so if Bunyakovsky conjecture is true, then there are infinitely many bases b such that the corresponding number (for fixed exponent n satisfying the condition) is prime. ((b+1)·bn − 1 is irreducible for all nonnegative integer n, so if Bunyakovsky conjecture is true, then there are infinitely many bases b such that the corresponding number (for fixed exponent n) is prime)
| b | numbers n such that (b+1)·bn − 1 is prime (Thabit primes of the first kind base b) | numbers n such that (b+1)·bn + 1 is prime (Thabit primes of the second kind base b) | numbers n such that (b−1)·bn − 1 is prime (Williams primes of the first kind base b) | numbers n such that (b−1)·bn + 1 is prime (Williams primes of the second kind base b) |
| 2 | id=A002235}} | id=A002253}} | id=A000043}} | 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, ... (see Fermat prime) |
| 3 | id=A005540}} | id=A005537}} | id=A003307}} | id=A003306}} |
| 4 | 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 16, 24, 27, 36, 74, 92, 124, 135, 137, 210, ... | (none) | id=A272057}} | 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, 15, 18, 33, 138, 204, 219, 267, ... |
| 5 | id=A257790}} | id=A143279}} | id=A046865}} | id=A204322}} |
| 6 | 1, 2, 3, 13, 21, 28, 30, 32, 36, 48, 52, 76, ... | 1, 6, 17, 38, 50, 80, 207, 236, 264, ... | id=A079906}} | id=A247260}} |
| 7 | 0, 4, 7, 10, 14, 23, 59, ... | (none) | id=A046866}} | id=A245241}} |
| 8 | 1, 5, 7, 21, 33, 53, 103, ... | 1, 2, 11, 14, 21, 27, 54, 122, 221, ... | id=A268061}} | id=A269544}} |
| 9 | 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 10, 11, 13, 15, 19, 27, 29, 35, 42, 51, 70, 112, 164, 179, 180, 242, ... | 0, 2, 6, 9, 11, 51, 56, 81, ... | id=A268356}} | id=A056799}} |
| 10 | id=A111391}} | (none) | id=A056725}} | id=A056797}} |
| 11 | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 11, 13, 22, 27, 48, 51, 103, 147, 280, ... | 0, 2, 3, 6, 8, 138, 149, 222, ... | id=A046867}} | id=A057462}} |
| 12 | 2, 6, 11, 66, 196, ... | 1, 2, 8, 9, 17, 26, 62, 86, 152, ... | id=A079907}} | id=A251259}} |
Least k ≥ 1 such that (n+1)·nk − 1 is prime are: (start with n = 2)
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 4, 3, 1, 1, 1, 2, 7, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 4, 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 8, 3, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 5, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 5, 2, 1483, 1, 1, 1, 24, 1, 2, 1, 2, 6, 3, 3, 36, 1, 10, 8, 3, 7, 2, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 7, 1704, 1, 3, 9, 4, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 24, 25, 1, ...
Least k ≥ 1 such that (n+1)·nk + 1 is prime are: (start with n = 2, 0 if no such k exists)
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 9, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 5, 2, 0, 5, 1, 0, 2, 3, 0, 1, 3, 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 2, 6, 0, 1, 183, 0, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 21, 0, 1, 185, 0, 3, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 120, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 8, 0, 5, 9, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, 3, 0, 9, 14, 0, 3, 1, 0, ...
Least k ≥ 1 such that (n−1)·nk − 1 is prime are: (start with n = 2)
2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 14, 1, 1, 2, 6, 1, 1, 1, 55, 12, 1, 133, 1, 20, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 15, 3, 1, 7, 136211, 1, 1, 7, 1, 7, 7, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 25, 1, 5, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 1, 1, 899, 3, 11, 1, 1, 1, 63, 1, 13, 1, 25, 8, 3, 2, 7, 1, 44, 2, 11, 3, 81, 21495, 1, 2, 1, 1, 3, 25, 1, 519, 77, 476, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4983, 2, 2, ...
Least k ≥ 1 such that (n−1)·nk + 1 is prime are: (start with n = 2)
1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 3, 10, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 4, 1, 29, 14, 1, 1, 14, 2, 1, 2, 4, 1, 2, 4, 5, 12, 2, 1, 2, 2, 9, 16, 1, 2, 80, 1, 2, 4, 2, 3, 16, 2, 2, 2, 1, 15, 960, 15, 1, 4, 3, 1, 14, 1, 6, 20, 1, 3, 946, 6, 1, 18, 10, 1, 4, 1, 5, 42, 4, 1, 828, 1, 1, 2, 1, 12, 2, 6, 4, 30, 3, 3022, 2, 1, 1, 8, 2, 4, 4, 2, 11, 8, 2, 1, ...
References
2. ^
3. ^
4. ^
5. ^
6. ^
7. ^
8. ^List of Williams primes (of the first kind) base 3 to 2049 (for exponent ≥ 1)
External links
- {{MathWorld|title=Thâbit ibn Kurrah Number|urlname=ThabitibnKurrahNumber}}
- {{MathWorld|title=Thâbit ibn Kurrah Prime|urlname=ThabitibnKurrahPrime}}
- Chris Caldwell, The Largest Known Primes Database at The Prime Pages
- A Thabit prime of the first kind base 2: (2+1)·211895718 − 1
- A Thabit prime of the second kind base 2: (2+1)·210829346 + 1
- A Williams prime of the first kind base 2: (2−1)·274207281 − 1
- A Williams prime of the first kind base 3: (3−1)·31360104 − 1
- A Williams prime of the second kind base 3: (3−1)·31175232 + 1
- A Williams prime of the first kind base 10: (10−1)·10383643 − 1
- A Williams prime of the first kind base 113: (113−1)·113286643 − 1
- [https://docs.google.com/document/d/e/2PACX-1vTLI9TAODTtBE9j0kQmMSR9y5YDuN_wI5cdgJZn25snYSAgyR07bLW89vxzhCypiK70YgEqschbavf-/pub List of Williams primes]
- PrimeGrid’s 321 Prime Search, about the discovery of the Thabit prime of the first kind base 2: (2+1)·26090515 − 1
- Mopani/Redpath Zambia Open
- Mopani Zambia Open
- Mopan Maya language
- Mop bucket cart
- MOPC
- Mop cart
- MOP, Chile
- Mo'pe-choko-pa
- Mopechucope
- Moped Operandi
- Mopelia
- Mopertingen
- Mopeseano language
- Mop fair
- MOP-Gate case
- MOP-Gate Case
- MOPH
- Mopha language
- Mophane worm
- Mophato Monyake
- Mopidevi Venkataramana
- Mopidevi Venkata Ramana
- Mopi language
- Mopin
- M-Opioid