- Nomenclature
- Properties
- References
| name = Theta Centauri
}}{{Starbox image
| image =
| caption=Location of θ Centauri (circled)
}}{{Starbox observe
| epoch = J2000.0
| ra = {{RA|14|06|40.94752}}
| dec = {{DEC|–36|22|11.8371}}
| appmag_v = +2.06[3]
| constell = Centaurus
}}{{Starbox character
| class = K0 III[4]
| b-v = +0.99[3]
| u-b = +0.90[3]
| variable =
}}{{Starbox astrometry
| radial_v = +1.3[7]
| prop_mo_ra = –520.53
| prop_mo_dec = –518.06
| parallax = 55.45
| p_error = 0.20
| parallax_footnote =
| absmag_v = 0.87[11]
}}{{Starbox detail
| mass =
| radius = 10.6[12]
| gravity = 2.75[13]
| metal_fe = 0.03[13]
| age_myr =
| luminosity = 60[15]
| temperature = 4,980[13]
| rotational_velocity =
}}{{Starbox catalog
| names = Menkent, 5 Centauri, CD−35° 9260, FK5 520, Gl 539, HD 123139, HIP 68933, HR 5288, LHS 2858, SAO 205188.[17]
}}{{Starbox reference
|Simbad=tet+Cen
}}{{Starbox end}}Theta Centauri (θ Centauri, abbreviated Theta Cen, θ Cen), also named Menkent,[1] is a star in the southern constellation of Centaurus, the centaur. With an apparent visual magnitude of +2.06,[3] it is the fourth-brightest member of the constellation. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is about {{Convert|58.8|ly|pc|abbr=off|lk=on}} distant from the Sun.
Nomenclature
θ Centauri (Latinised to Theta Centauri) is the star's Bayer designation.
It bore the traditional name of Menkent derived from an Arabic word for "shoulder" (of the Centaur) attached to the Latin abbreviation for "kentaurus" (centaur).[15] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[2] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name Menkent for this star on 21 August 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[1]
In Chinese, {{lang|zh|庫樓}} ({{lang|zh-Latn|Kù Lóu}}), meaning arsenal, refers to an asterism consisting of Theta Centauri, Zeta Centauri, Eta Centauri, 2 Centauri, HD 117440, Xi¹ Centauri, Gamma Centauri, Tau Centauri, D Centauri and Sigma Centauri.[3] Consequently, Theta Centauri itself is known as {{lang|zh|庫樓三}} ({{lang|zh-Latn|Kù Lóu sān}}, {{lang-en|the Third Star of Arsenal}}).[4]
Properties
This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III.[4] The interferometry-measured angular diameter of this star, after correcting for limb darkening, is {{nowrap|5.46 ± 0.06 milliarcseconds}},[27] which, at its estimated distance, equates to a physical radius of about 10.6 times the radius of the Sun.[12] The outer envelope has an effective temperature of 4,980 K,[13] giving it the orange-hued glow of a cool, K-type star.[30] Soft X-ray emission has been detected from this star, which has an estimated X-ray luminosity of {{nowrap|1.4 × 1027 erg s−1}}.[31]
References
1. ^1 {{cite web | url=https://www.iau.org/public/themes/naming_stars/ | title=Naming Stars |publisher=IAU.org |accessdate=18 June 2018}}
2. ^{{cite web | url=https://www.iau.org/science/scientific_bodies/working_groups/280/ | title=IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)|accessdate=22 May 2016}}
3. ^{{zh icon}} 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, {{ISBN|978-986-7332-25-7}}.
4. ^{{zh icon}} 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表 {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110130063012/http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/Research/StarName/c_research_chinengstars_m.htm |date=2011-01-30 }}, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
5. ^1 2 3 4 {{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Jones | first1=K. L. | last2=Robinson | first2=R. D. | last3=Slee | first3=O. B. | last4=Stewart | first4=R. T. | title=Spectroscopic investigation of cool giants and the authenticity of their reported microwave emission | journal=Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | volume=256 | issue=3 | pages=535–544 |date=June 1992 | bibcode=1992MNRAS.256..535J | doi=10.1093/mnras/256.3.535}}
6. ^1 2 {{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Gray | first1=R. O. | first2=C. J. | last2=Corbally | first3=R. F. | last3=Garrison | first4=M. T. | last4=McFadden | first5=P. E. | last5=Robinson | title=Contributions to the Nearby Stars (NStars) Project: Spectroscopy of Stars Earlier than M0 within 40 parsecs: The Northern Sample I | journal=The Astronomical Journal | volume=132 | issue=1 | pages=161–170 |date=July 2006 | doi=10.1086/504637 | bibcode=2006AJ....132..161G |arxiv = astro-ph/0603770 }}
7. ^1 {{citation | display-authors=1 | title=Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions | journal=Veröff. Astron. Rechen-Inst. Heidelb | volume=35 | last1=Wielen | first1=R. | last2=Schwan | first2=H. | last3=Dettbarn | first3=C. | last4=Lenhardt | first4=H. | last5=Jahreiß | first5=H. | last6=Jährling | first6=R. | publisher=Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg | issue=35 | date=1999 | bibcode=1999VeARI..35....1W }}
8. ^1 2 3 4 {{cite journal | display-authors=1 | last1=Johnson | first1=H. L. | last2=Iriarte | first2=B. | last3=Mitchell | first3=R. I. | last4=Wisniewskj | first4=W. Z. | title=UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars | journal=Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory | volume=4 | issue=99 | pages=99 | date=1966 | bibcode=1966CoLPL...4...99J }}
9. ^1 {{citation | last1=Richichi | first1=A. | last2=Percheron | first2=I. | last3=Khristoforova | first3=M. | title=CHARM2: An updated Catalog of High Angular Resolution Measurements | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=431 | issue=2 | pages=773–777 |date=February 2005 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20042039 | bibcode=2005A&A...431..773R }}
10. ^1 2 {{citation | first1=Kenneth R. | last1=Lang | title=Astrophysical formulae | volume=1 | series=Astronomy and astrophysics library | edition=3rd | publisher=Birkhäuser | date=2006 | isbn=3-540-29692-1 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OvTjLcQ4MCQC&pg=PA41 }}. The radius (R*) is given by::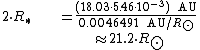
11. ^1 {{citation | last1=Schroeder | first1=K.-P. | last2=Huensch | first2=M. | last3=Schmitt | first3=J. H. M. M. | title=X-ray activity and evolutionary status of late-type giants | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=335 | pages=591–595 |date=July 1998 | bibcode=1998A&A...335..591S }}
12. ^1 {{cite simbad | title=tet Cen | accessdate=2012-03-01 }}
13. ^1 {{citation | title=The Colour of Stars | date=December 21, 2004 | work=Australia Telescope, Outreach and Education | publisher=Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation | url=http://outreach.atnf.csiro.au/education/senior/astrophysics/photometry_colour.html | accessdate=2012-01-16 }}
14. ^1 2 {{citation | first1=James B. | last1=Kaler | title=MENKENT (Theta Centauri) | work=Stars | publisher=University of Illinois | url=http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/menkent.html | accessdate=2012-03-01 }}
15. ^1 {{citation | last1=Elgarøy | first1=Øystein | last2=Engvold | first2=Oddbjørn | last3=Lund | first3=Niels | title=The Wilson-Bappu effect of the MgII K line - dependence on stellar temperature, activity and metallicity | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=343 | pages=222–228 |date=March 1999 | bibcode=1999A&A...343..222E }}
[5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15]2. ^{{cite web | url=https://www.iau.org/science/scientific_bodies/working_groups/280/ | title=IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)|accessdate=22 May 2016}}
3. ^{{zh icon}} 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, {{ISBN|978-986-7332-25-7}}.
4. ^{{zh icon}} 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表 {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110130063012/http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/Research/StarName/c_research_chinengstars_m.htm |date=2011-01-30 }}, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
5. ^1 2 3 4 {{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Jones | first1=K. L. | last2=Robinson | first2=R. D. | last3=Slee | first3=O. B. | last4=Stewart | first4=R. T. | title=Spectroscopic investigation of cool giants and the authenticity of their reported microwave emission | journal=Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | volume=256 | issue=3 | pages=535–544 |date=June 1992 | bibcode=1992MNRAS.256..535J | doi=10.1093/mnras/256.3.535}}
6. ^1 2 {{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Gray | first1=R. O. | first2=C. J. | last2=Corbally | first3=R. F. | last3=Garrison | first4=M. T. | last4=McFadden | first5=P. E. | last5=Robinson | title=Contributions to the Nearby Stars (NStars) Project: Spectroscopy of Stars Earlier than M0 within 40 parsecs: The Northern Sample I | journal=The Astronomical Journal | volume=132 | issue=1 | pages=161–170 |date=July 2006 | doi=10.1086/504637 | bibcode=2006AJ....132..161G |arxiv = astro-ph/0603770 }}
7. ^1 {{citation | display-authors=1 | title=Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions | journal=Veröff. Astron. Rechen-Inst. Heidelb | volume=35 | last1=Wielen | first1=R. | last2=Schwan | first2=H. | last3=Dettbarn | first3=C. | last4=Lenhardt | first4=H. | last5=Jahreiß | first5=H. | last6=Jährling | first6=R. | publisher=Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg | issue=35 | date=1999 | bibcode=1999VeARI..35....1W }}
8. ^1 2 3 4 {{cite journal | display-authors=1 | last1=Johnson | first1=H. L. | last2=Iriarte | first2=B. | last3=Mitchell | first3=R. I. | last4=Wisniewskj | first4=W. Z. | title=UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars | journal=Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory | volume=4 | issue=99 | pages=99 | date=1966 | bibcode=1966CoLPL...4...99J }}
9. ^1 {{citation | last1=Richichi | first1=A. | last2=Percheron | first2=I. | last3=Khristoforova | first3=M. | title=CHARM2: An updated Catalog of High Angular Resolution Measurements | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=431 | issue=2 | pages=773–777 |date=February 2005 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20042039 | bibcode=2005A&A...431..773R }}
10. ^1 2 {{citation | first1=Kenneth R. | last1=Lang | title=Astrophysical formulae | volume=1 | series=Astronomy and astrophysics library | edition=3rd | publisher=Birkhäuser | date=2006 | isbn=3-540-29692-1 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OvTjLcQ4MCQC&pg=PA41 }}. The radius (R*) is given by::
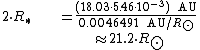
11. ^1 {{citation | last1=Schroeder | first1=K.-P. | last2=Huensch | first2=M. | last3=Schmitt | first3=J. H. M. M. | title=X-ray activity and evolutionary status of late-type giants | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=335 | pages=591–595 |date=July 1998 | bibcode=1998A&A...335..591S }}
12. ^1 {{cite simbad | title=tet Cen | accessdate=2012-03-01 }}
13. ^1 {{citation | title=The Colour of Stars | date=December 21, 2004 | work=Australia Telescope, Outreach and Education | publisher=Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation | url=http://outreach.atnf.csiro.au/education/senior/astrophysics/photometry_colour.html | accessdate=2012-01-16 }}
14. ^1 2 {{citation | first1=James B. | last1=Kaler | title=MENKENT (Theta Centauri) | work=Stars | publisher=University of Illinois | url=http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/menkent.html | accessdate=2012-03-01 }}
15. ^1 {{citation | last1=Elgarøy | first1=Øystein | last2=Engvold | first2=Oddbjørn | last3=Lund | first3=Niels | title=The Wilson-Bappu effect of the MgII K line - dependence on stellar temperature, activity and metallicity | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=343 | pages=222–228 |date=March 1999 | bibcode=1999A&A...343..222E }}
}}{{Stars of Centaurus}}
10 : Bayer objects|Flamsteed objects|Centaurus (constellation)|K-type giants|Stars with proper names|Hipparcos objects|HR objects|Henry Draper Catalogue objects|Durchmusterung objects|Gliese and GJ objects
- Vacuus Viator
- Vacy Bridge over Paterson River
- Vacłaŭ Łastoŭski
- Vada Azeem
- Vadade
- Vadadustat
- Vada (food)
- Vadagam
- Vadagupatti Maapillai
- Vadakannikaapuram railway station
- Vadakara (Lok Sabha constituency)
- Vadakara Lok sabha constituency
- Vadakkadathukavu
- Vadakkangara
- Vadakkan Koyikkal Devi Temple Puthiyavila
- Vadakke Koottala Narayanankutty
- Vadakkumkara (Mukundapuram, Thrissur)
- Vadakku Nokki Yandhram
- Vadakku nokki yandram
- Vadakste parish
- Vadal
- Vadal Alexander
- Vadal (disambiguation)
- Vadal, Gujarat
- Vadali