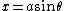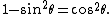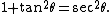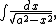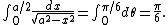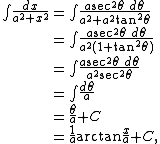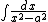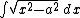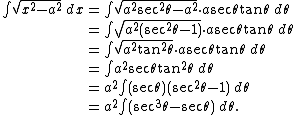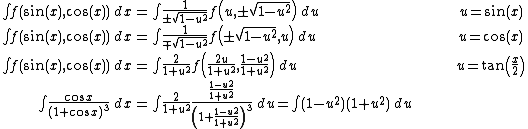- Examples Integrals containing a2 − x2 Integrals containing a2 + x2 Integrals containing x2 − a2
- Substitutions that eliminate trigonometric functions
- Hyperbolic substitution
- See also
- References
In mathematics, trigonometric substitution is the substitution of trigonometric functions for other expressions. One may use the trigonometric identities to simplify certain integrals containing radical expressions:[1][2]
Substitution 1. If the integrand contains a2 − x2, letand use the identity
Substitution 2. If the integrand contains a2 + x2, letand use the identity
Substitution 3. If the integrand contains x2 − a2, letand use the identity
Examples
Integrals containing a2 − x2
In the integral
we may use
Then,
The above step requires that {{math|a > 0}} and {{math|cos(θ) > 0}}; we can choose {{mvar|a}} to be the positive square root of {{math|a2}}, and we impose the restriction {{math|−π/2 < θ < π/2}} on {{mvar|θ}} by using the arcsin function.
For a definite integral, one must figure out how the bounds of integration change. For example, as {{mvar|x}} goes from 0 to {{math|a/2}}, then {{math|sin θ}} goes from 0 to 1/2, so {{mvar|θ}} goes from 0 to {{math|π/6}}. Then,
Some care is needed when picking the bounds. The integration above requires that {{math|−π/2 < θ < π/2}}, so {{mvar|θ}} going from 0 to π/6 is the only choice. Neglecting this restriction, one might have picked {{mvar|θ}} to go from {{mvar|π}} to {{math|5π/6}}, which would have resulted in the negative of the actual value.
Integrals containing a2 + x2
In the integral
we may write
so that the integral becomes
provided {{math|a ≠ 0}}.
Integrals containing x2 − a2
Integrals like
can also be evaluated by partial fractions rather than trigonometric substitutions. However, the integral
cannot. In this case, an appropriate substitution is:
Then,
We can then solve this using the formula for the integral of secant cubed.
Substitutions that eliminate trigonometric functions
Substitution can be used to remove trigonometric functions. In particular, see Tangent half-angle substitution.
For instance,
Hyperbolic substitution
Substitutions of hyperbolic functions can also be used to simplify integrals.[3]
In the integral  , make the substitution
, make the substitution 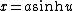 ,
, 
Then, using the identities 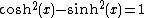 and
and 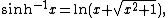

See also
{{Portal|Mathematics}}{{Wikiversity|Trigonometric Substitutions}}{{Wikibooks|Calculus/Integration techniques/Trigonometric Substitution}}- Tangent half-angle substitution
References
2. ^{{cite book | last1 = Thomas | first1 = George B. | last2=Weir | first2= Maurice D. | last3=Hass | first3=Joel | author3-link = Joel Hass | authorlink=George B. Thomas | title=Thomas' Calculus: Early Transcendentals | publisher=Addison-Wesley | year=2010 | edition=12th | isbn=0-321-58876-2}}
3. ^{{cite web|last=Boyadzhiev|first=Khristo N.|title=Hyperbolic Substitutions for Integrals|url=http://www2.onu.edu/~m-caragiu.1/bonus_files/HYPERSUB.pdf|accessdate=4 March 2013}}
- Zero Patrol
- Zerophilia
- Zerophilia Disease
- Zero-phonon line and phonon sideband
- Zero player game
- Zero plural marking
- Zero point
- Zero Point 1972
- Zero Point Field
- Zero point field
- Zero Point of Longitude
- Zero polynomial
- Zero population
- Zero possessive marking
- Zero power critical
- Zero Power Physics Reactor
- Zero power zero
- Zero price
- Zero-product property
- Zero-Product Property
- Zero product property
- Zero product rule
- Zero-product rule
- Zero-profit condition
- Zero qb rating