- Performance
- Airspeed sensing errors
- Use in navigation calculations
- Calculating true airspeed Low-speed flight High-speed flight
- See also
- Notes
- References
- External links
The true airspeed (TAS; also KTAS, for knots true airspeed) of an aircraft is the speed of the aircraft relative to the airmass in which it is flying. The true airspeed is important information for accurate navigation of an aircraft. Traditionally it is measured using an analogue TAS indicator, but as the Global Positioning System has become available for civilian use, the importance of such analogue instruments has decreased. Since indicated airspeed is a better indicator of power used and lift available, True airspeed is not used for controlling the aircraft during taxiing, takeoff, climb, descent, approach or landing; for these purposes the Indicated airspeed – IAS or KIAS (knots indicated airspeed) – is used. However, since indicated airspeed only shows true speed through the air at standard sea level pressure and temperature, a TAS meter is necessary for navigation purposes at cruising altitude in less dense air. The IAS meter reads very nearly the TAS at lower altitude and at lower speed. On jet airliners the TAS meter is usually hidden at speeds below {{convert|200|kn|km/h}}. Neither provides for accurate speed over the ground, since surface winds or winds aloft are not taken into account.
Performance
TAS is the true measure of aircraft performance in cruise, thus it is the speed listed in aircraft specifications, manuals, performance comparisons, pilot reports, and every situation when cruise or endurance performance needs to be measured.
It is the speed normally listed on the flight plan, also used in flight planning, before considering the effects of wind.
Airspeed sensing errors
The airspeed indicator (ASI), driven by ram air into a Pitot tube and still air into a barometric static port, and shows what is called indicated airspeed (IAS). The differential pressure is affected by air density. The ratio between the two measurements is temperature-dependent and pressure-dependent, according to the ideal gas law.
At sea level in the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) and at low speeds where air compressibility is negligible (i.e., assuming a constant air density), IAS corresponds to TAS. When the air density or temperature around the aircraft differs from standard sea level conditions, IAS will no longer correspond to TAS, thus it will no longer reflect aircraft performance. The ASI will indicate less than TAS when the air density decreases due to a change in altitude or air temperature. For this reason, TAS cannot be measured directly. In flight, it can be calculated either by using an E6B flight calculator or its equivalent.
For low speeds, the data required are static air temperature, pressure altitude and IAS (or CAS for more precision). Above approximately {{convert|100|kn|km/h}}, the compressibility error rises significantly and TAS must be calculated by the Mach speed. Mach incorporates the above data including the compressibility factor.
Modern aircraft instrumentation use an Air Data Computer to perform this calculation in real time and display the TAS reading directly on the EFIS.
Since temperature variations are of a smaller influence, the ASI error can be roughly estimated as indicating about 2% less than TAS per {{convert|1000|ft|m|sigfig=1}} of altitude above sea level. For example, an aircraft flying at {{convert|15000|ft|m}} in the international standard atmosphere with an IAS of {{convert|100|kn|km/h}}, is actually flying at {{convert|126|kn|km/h}} TAS.
Use in navigation calculations
To maintain a desired ground track whilst flying in the moving airmass, the pilot of an aircraft must use knowledge of wind speed, wind direction, and true air speed to determine the required heading. See also wind triangle.
Calculating true airspeed
Low-speed flight
At low speeds and altitudes, IAS and CAS are close to equivalent airspeed (EAS). TAS can be calculated as a function of EAS and air density:[1]
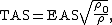
where
is true airspeed,
is equivalent airspeed,
is the air density at sea level in the International Standard Atmosphere (15 °C and 1013.25 hectopascals, corresponding to a density of 1.225 kg/m3),
is the density of the air in which the aircraft is flying.
High-speed flight
TAS can be calculated as a function of Mach number and static air temperature:

where
is the speed of sound at standard sea level ({{convert|661.47|kn|km/h m/s}}),
is Mach number,
is static air temperature in kelvins,
is the temperature at standard sea level (288.15 K).
For manual calculation of TAS in knots, where Mach number and static air temperature are known, the expression may be simplified to
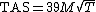
(remembering temperature is in kelvins).
Combining the above with the expression for Mach number gives an expression for TAS as a function of impact pressure, static pressure and static air temperature (valid for subsonic flow):

where:
is impact pressure,
is static pressure.
Electronic flight instrument systems (EFIS) contain an air data computer with inputs of impact pressure, static pressure and total air temperature. In order to compute TAS, the air data computer must convert total air temperature to static air temperature. This is also a function of Mach number:

where
total air temperature.
In simple aircraft, without an air data computer or Machmeter, true airspeed can be calculated as a function of calibrated airspeed and local air density (or static air temperature and pressure altitude, which determine density). Some airspeed indicators incorporate a slide rule mechanism to perform this calculation. Otherwise, it can be performed using this applet or a device such as the E6B (a handheld circular slide rule).
See also
- Equivalent airspeed
- Indicated airspeed
- Calibrated airspeed
- Flight planning
Notes
References
- {{cite book | date=1 December 1989 | title=Air Navigation |publisher=Department of the Air Force| id=AFM 51-40 }}
- Clancy, L.J.(1975), Aerodynamics, Chapter 3. Pitman Publishing Limited, London. {{ISBN|0-273-01120-0}}
- Kermode, A.C., Mechanics of Flight, Chapter 2. (Eighth edition 1972) Pitman Publishing Limited, London. {{ISBN|0-273-31623-0}}
- Gracey, William (1980), "Measurement of Aircraft Speed and Altitude" (11 MB), NASA Reference Publication 1046.
External links
- [https://sites.google.com/site/maltapplication/home A free windows calculator which converts between various airspeeds (true / equivalent / calibrated) according to the appropriate atmospheric (standard and not standard!) conditions]
- [https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=malta.aeroCalc Android application for airspeed conversion in different atmospheric conditions]
- True, Equivalent, and Calibrated Airspeed at MathPages
- Newbyte airspeed converter, [https://archive.is/20121209064246/http://market.android.com/details?id=appinventor.ai_barkan86.AtmosCalculatorFree Android Version]
- [https://web.archive.org/web/20110201094502/http://avc.obsment.com/ avc.obsment.com] - True airspeed calculator.
- Calculate True Airspeed, Mach, Pitot Tube Impact Air Pressure and more at luizmonteiro.com
- Turkish senate elections, 1977
- Turkish senate elections, 1979
- Turkish-Serbian War (disambiguation)
- Turkish skirmish at the White House
- Turkish Society for Electron Microscopy
- Turkish sociology
- Turkish soup
- Turkish Space Agency
- Turkish Special Forces
- Turkish special forces
- Turkish Staff College
- Turkish State Highway System
- Turkish State Mint
- Turkish State Railway
- Turkish Stream
- Turkish strikes on Sinjar (2018)
- Turkish style pizza
- Turkish Style Pizza
- Turkish sultan
- Turkish Sultanate
- Turkish Super Cup Basketball
- Turkish-Syrian border aerial dispute
- Turkish tea
- Turkish Time
- Turkish towel seaweed