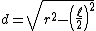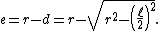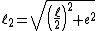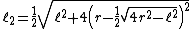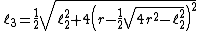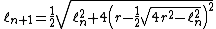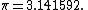- Algorithm
- See also
- References
Zhao Youqin's {{pi}} algorithm was an algorithm devised by Yuan dynasty Chinese astronomer and mathematician Zhao Youqin ({{lang|zh|赵友钦}}, ? – 1330) to calculate the value of {{pi}} in his book Ge Xiang Xin Shu ({{lang|zh|革象新书}}).
Algorithm
Zhao Youqin started with an inscribed square in a circle with radius r.[1]
If  denotes the length of a side of the square, draw a perpendicular line d from the center of the circle to side l. Let e denotes r − d. Then from the diagram:
denotes the length of a side of the square, draw a perpendicular line d from the center of the circle to side l. Let e denotes r − d. Then from the diagram:
Extend the perpendicular line d to dissect the circle into an octagon;  denotes the length of one side of octagon.
denotes the length of one side of octagon.
Let  denotes the length of a side of hexadecagon
denotes the length of a side of hexadecagon
similarly
Proceeding in this way, he at last calculated the side of a 16384-gon, multiplying it by 16384 to obtain 3141.592 for a circle with diameter = 1000 units, or
He multiplied this number by 113 and obtained 355. From this he deduced that of the traditional values of {{pi}}, that is 3, 3.14, {{sfrac|22|7}} and {{sfrac|355|113}}, the last is the most exact.[2]
See also
- Liu Hui's {{pi}} algorithm
References
2. ^Yoshio Mikami, p136
- Khareh-ye Aghlan
- Khareh-ye Chaki
- Kharej Gil
- Kharem
- Khareng
- Kharengan
- Kharengun
- Khar Eshgaft
- Khareshk
- Khar Eshkaft
- Khareshtom
- Kharestan
- Kharestan-e Bala
- Kharestan-e Bala, Fars
- Kharestan-e Olya
- Kharestan-e Olya (disambiguation)
- Kharestan-e Olya, Fars
- Kharestan-e Olya, Khuzestan
- Kharestan-e Paeen
- Kharestan-e Pa'in
- Kharestan-e Pain
- Kharestan-e Pain, Fars
- Kharestan-e Sofla
- Kharestan-e Sofla (disambiguation)
- Kharestan-e Sofla, Fars