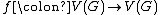- Finite examples
- Properties
- Infinite examples
- See also
- References
- External links
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a vertex-transitive graph is a graph G such that, given any two vertices v1 and v2 of G, there is some automorphism
such that
In other words, a graph is vertex-transitive if its automorphism group acts transitively upon its vertices.[1] A graph is vertex-transitive if and only if its graph complement is, since the group actions are identical.
Every symmetric graph without isolated vertices is vertex-transitive, and every vertex-transitive graph is regular. However, not all vertex-transitive graphs are symmetric (for example, the edges of the truncated tetrahedron), and not all regular graphs are vertex-transitive (for example, the Frucht graph and Tietze's graph).
Finite examples
Finite vertex-transitive graphs include the symmetric graphs (such as the Petersen graph, the Heawood graph and the vertices and edges of the Platonic solids). The finite Cayley graphs (such as cube-connected cycles) are also vertex-transitive, as are the vertices and edges of the Archimedean solids (though only two of these are symmetric). Potočnik, Spiga and Verret have constructed a census of all connected cubic vertex-transitive graphs on at most 1280 vertices.[2]
Although every Cayley graph is vertex-transitive, there exist other vertex-transitive graphs that are not Cayley graphs. The most famous example is the Petersen graph, but others can be constructed including the line graphs of edge-transitive non-bipartite graphs with odd vertex degrees.[3]
Properties
The edge-connectivity of a vertex-transitive graph is equal to the degree d, while the vertex-connectivity will be at least 2(d + 1)/3.[4]
If the degree is 4 or less, or the graph is also edge-transitive, or the graph is a minimal Cayley graph, then the vertex-connectivity will also be equal to d.[5]
Infinite examples
Infinite vertex-transitive graphs include:
- infinite paths (infinite in both directions)
- infinite regular trees, e.g. the Cayley graph of the free group
- graphs of uniform tessellations (see a complete list of planar tessellations), including all tilings by regular polygons
- infinite Cayley graphs
- the Rado graph
Two countable vertex-transitive graphs are called quasi-isometric if the ratio of their distance functions is bounded from below and from above. A well known conjecture stated that every infinite vertex-transitive graph is quasi-isometric to a Cayley graph. A counterexample was proposed by Diestel and Leader in 2001.[6] In 2005, Eskin, Fisher, and Whyte confirmed the counterexample.[7]
See also
- Edge-transitive graph
- Lovász conjecture
- Semi-symmetric graph
- Zero-symmetric graph
References
2. ^{{citation|title=Cubic vertex-transitive graphs on up to 1280 vertices|author1=Potočnik P., Spiga P. |author2=Verret G. |lastauthoramp=yes |journal=Journal of Symbolic Computation |volume = 50 | year = 2013|pages = 465–477|doi=10.1016/j.jsc.2012.09.002|arxiv=1201.5317}}.
3. ^{{citation | last1 = Lauri | first1 = Josef | last2 = Scapellato | first2 = Raffaele | isbn = 0-521-82151-7 | location = Cambridge | mr = 1971819 | page = 44 | publisher = Cambridge University Press | series = London Mathematical Society Student Texts | title = Topics in graph automorphisms and reconstruction | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=hsymFm0E0uIC&pg=PA44 | volume = 54 | year = 2003}}. Lauri and Scapelleto credit this construction to Mark Watkins.
4. ^{{Citation|title=Algebraic Graph Theory|author1=Godsil, C. |author2=Royle, G. |lastauthoramp=yes |year=2001|publisher=Springer Verlag}}
5. ^{{Citation|title=Technical Report TR-94-10|author=Babai, L.|year=1996|publisher=University of Chicago}} {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100611212234/http://www.cs.uchicago.edu/files/tr_authentic/TR-94-10.ps |date=2010-06-11 }}
6. ^{{citation|first1=Reinhard|last1=Diestel|first2=Imre|last2=Leader|authorlink2=Imre Leader|url=http://www.math.uni-hamburg.de/home/diestel/papers/Cayley.pdf|title=A conjecture concerning a limit of non-Cayley graphs|journal=Journal of Algebraic Combinatorics|volume=14|issue=1|year=2001|pages=17–25|doi=10.1023/A:1011257718029}}.
7. ^{{cite arXiv|first1=Alex|last1=Eskin|first2=David|last2=Fisher|first3=Kevin|last3=Whyte|eprint=math.GR/0511647 |title=Quasi-isometries and rigidity of solvable groups|year=2005}}.
External links
- {{MathWorld | urlname=Vertex-TransitiveGraph | title=Vertex-transitive graph }}
- A census of small connected cubic vertex-transitive graphs. Primož Potočnik, Pablo Spiga, Gabriel Verret, 2012.
- Anna Maria Muccioli
- Anna-Maria Nilsson
- Anna Maria of Brandenburg
- Anna Maria of Hesse-Kassel
- Anna Maria of Hohenzollern-Hechingen
- Anna Maria of Solms-Sonnewalde
- Anna Maria of the Palatinate-Neuburg
- Annamaria Orla-Bukowska
- Anna Maria Ortese
- Anna Maria Perez de Taglé
- Anna Maria Picarelli
- Annamaria Pierangeli
- Anna Maria Quaini
- Anna Maria Reed
- Anna Maria Rizzoli
- Annamaria Rizzoli
- Anna Maria Roos
- Anna Maria Rubatto
- Anna Maria Ruttimann-Meyer von Schauensee
- Anna Maria Rüttimann-Meyer von Schauensee
- Anna Maria Schwägel
- Anna Maria Seymour
- Anna Maria Steinbach
- Anna Maria Stricker
- Annamaria Szalai