- References
- Further reading
In mathematics, the Banach game is a topological game introduced by Stefan Banach in 1935 in the second addendum to problem 43 of the Scottish book as a variation of the Banach–Mazur game.[1]
Given a subset 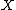 of real numbers, two players alternatively write down arbitrary (not necessarily in
of real numbers, two players alternatively write down arbitrary (not necessarily in 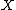 ) positive real numbers
) positive real numbers  such that
such that 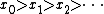 Player one wins if and only if
Player one wins if and only if  exists and is in
exists and is in 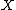 .[2]
.[2]
One observation about the game is that if 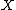 is a countable set, then either of the players can cause the final sum to avoid the set.{{sfn|Mauldin|1981|p=116}} Thus in this situation the second player can win.
is a countable set, then either of the players can cause the final sum to avoid the set.{{sfn|Mauldin|1981|p=116}} Thus in this situation the second player can win.
References
1. ^{{cite book|last1=Mauldin|first1=R. Daniel|title=The Scottish Book: Mathematics from the Scottish Cafe|date=April 1981|publisher=Birkhäuser|isbn=978-3-7643-3045-3|page=113|edition=1|url=http://users.auth.gr/siskakis/The%20Scottish%20book.pdf}}
2. ^{{cite journal|last1=Telgársky|first1=Rastislav|title=Topological Games: On the 50th Anniversary of the Banach–Mazur Game|journal=Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics|date=Spring 1987|volume=17|issue=2|pages=227–276|url=http://www.telgarsky.com/1987-RMJM-Telgarsky-Topological-Games.pdf}} at 242.
2. ^{{cite journal|last1=Telgársky|first1=Rastislav|title=Topological Games: On the 50th Anniversary of the Banach–Mazur Game|journal=Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics|date=Spring 1987|volume=17|issue=2|pages=227–276|url=http://www.telgarsky.com/1987-RMJM-Telgarsky-Topological-Games.pdf}} at 242.
Further reading
- {{cite journal|last1=Moran|first1=Gadi|title=Existence of nondetermined sets for some two person games over reals|journal=Israel Journal of Mathematics|date=September 1971|volume=9|issue=3|pages=316–329|doi=10.1007/BF02771682}}
1 : Topological games
- Luis Rodríguez
- Luis Romano de Madeira Melo
- Luis Roman Rolon
- Luis Román Rolón
- Luis Rosas
- Luis Rosendo Ramos
- Luis Rossi
- Luis Rubiales
- Luis Russell and His Orchestra
- Luis R Vera
- Luis R. Vera
- LUISS
- Luis Saenz Pena Davila
- Luis Saenz Peña
- Luis Sales
- Luis Sanchez Gil
- Luis Sandrini
- Luis Santaigo
- Luis Santalo
- Luis Santaló
- Luis Santamaría
- Luis Santana
- Luis Santibanez
- Luis Santibáñez
- Luis Sapag