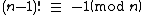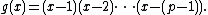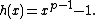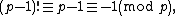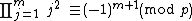- History
- Example
- Proofs Composite modulus Prime modulus
- Applications Primality tests Quadratic residues Formulas for primes p-adic gamma function
- Gauss's generalization
- See also
- Notes
- References
- External links
In number theory, Wilson's theorem states that a natural number n > 1 is a prime number if and only if the product of all the positive integers less than n is one less than a multiple of n. That is (using the notations of modular arithmetic), the factorial 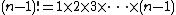 satisfies
satisfies
exactly when n is a prime number.
History
This theorem was stated by Ibn al-Haytham (c. 1000 AD),[1] and, in the 18th century, by John Wilson.[2] Edward Waring announced the theorem in 1770, although neither he nor his student Wilson could prove it. Lagrange gave the first proof in 1771.[3] There is evidence that Leibniz was also aware of the result a century earlier, but he never published it.[4]
Example
For each of the values of n from 2 to 30, the following table shows the number (n − 1)! and the remainder when (n − 1)! is divided by n. (In the notation of modular arithmetic, the remainder when m is divided by n is written m mod n.)
The background color is blue for prime values of n, gold for composite values.
 | {{OEIS>id=A000142 | {{OEIS>id=A061006 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 6 | 2 |
| 5 | 24 | 4 |
| 6 | 120 | 0 |
| 7 | 720 | 6 |
| 8 | 5040 | 0 |
| 9 | 40320 | 0 |
| 10 | 362880 | 0 |
| 11 | 3628800 | 10 |
| 12 | 39916800 | 0 |
| 13 | 479001600 | 12 |
| 14 | 6227020800 | 0 |
| 15 | 87178291200 | 0 |
| 16 | 1307674368000 | 0 |
| 17 | 20922789888000 | 16 |
| 18 | 355687428096000 | 0 |
| 19 | 6402373705728000 | 18 |
| 20 | 121645100408832000 | 0 |
| 21 | 2432902008176640000 | 0 |
| 22 | 51090942171709440000 | 0 |
| 23 | 1124000727777607680000 | 22 |
| 24 | 25852016738884976640000 | 0 |
| 25 | 620448401733239439360000 | 0 |
| 26 | 15511210043330985984000000 | 0 |
| 27 | 403291461126605635584000000 | 0 |
| 28 | 10888869450418352160768000000 | 0 |
| 29 | 304888344611713860501504000000 | 28 |
| 30 | 8841761993739701954543616000000 | 0 |
Proofs
Both of the proofs (for prime moduli)[5] below make use of the fact that the residue classes modulo a prime number are a field—see the article prime field for more details. Lagrange's theorem, which states that in any field a polynomial of degree n has at most n roots, is needed for both proofs.
Composite modulus
If n is composite it is divisible by some prime number q, where {{nowrap|1=2 ≤ q ≤ n − 2}}. If {{nowrap|1=(n − 1)!}} were congruent to {{nowrap|1=−1 (mod n)}} then it would also be congruent to −1 (mod q). But (n − 1)! ≡ 0 (mod q).
In fact, more is true. With the sole exception of 4, where 3! = 6 ≡ 2 (mod 4), if n is composite then (n − 1)! is congruent to 0 (mod n). The proof is divided into two cases: First, if n can be factored as the product of two unequal numbers, {{nowrap|1=n = ab}}, where 2 ≤ a < b ≤ n − 2, then both a and b will appear in the product {{nowrap|1=1 × 2 × ... × (n − 1) = (n − 1)!}} and (n − 1)! will be divisible by n. If n has no such factorization, then it must be the square of some prime q, q > 2. But then 2q < q2 = n, both q and 2q will be factors of (n − 1)!, and again n divides (n − 1)!.
Prime modulus
- Elementary proof
The result is trivial when {{nowrap|1=p = 2}}, so assume p is an odd prime, {{nowrap|1=p ≥ 3}}. Since the residue classes (mod p) are a field, every non-zero a has a unique multiplicative inverse, a−1. Lagrange's theorem implies that the only values of a for which {{nowrap|1=a ≡ a−1 (mod p)}} are {{nowrap|1=a ≡ ±1 (mod p)}} (because the congruence {{nowrap|1=a2 ≡ 1}} can have at most two roots (mod p)). Therefore, with the exception of ±1, the factors of {{nowrap|1=(p − 1)!}} can be arranged in unequal pairs,[6] where the product of each pair is {{nowrap|1=≡ 1 (mod p)}}. This proves Wilson's theorem.
For example, if {{nowrap|1=p = 11}},
- Proof using Fermat's little theorem
Again, the result is trivial for p = 2, so suppose p is an odd prime, {{nowrap|1=p ≥ 3}}. Consider the polynomial
g has degree {{nowrap|1=p − 1}}, leading term {{nowrap|1=xp − 1}}, and constant term {{nowrap|1=(p − 1)!}}. Its {{nowrap|1=p − 1}} roots are 1, 2, ..., {{nowrap|1=p − 1}}.
Now consider
h also has degree {{nowrap|1=p − 1}} and leading term {{nowrap|1=xp − 1}}. Modulo p, Fermat's little theorem says it also has the same {{nowrap|1=p − 1}} roots, 1, 2, ..., {{nowrap|1=p − 1}}.
Finally, consider
f has degree at most p − 2 (since the leading terms cancel), and modulo p also has the {{nowrap|1=p − 1}} roots 1, 2, ..., {{nowrap|1=p − 1}}. But Lagrange's theorem says it cannot have more than p − 2 roots. Therefore, f must be identically zero (mod p), so its constant term {{nowrap|1=(p − 1)! + 1 ≡ 0 (mod p)}}. This is Wilson's theorem.
- Proof using the Sylow theorems
It is possible to deduce Wilson's theorem from a particular application of the Sylow theorems. Let p be a prime. It is immediate to deduce that the symmetric group  has exactly
has exactly  elements of order p, namely the p-cycles
elements of order p, namely the p-cycles  . On the other hand, each Sylow p-subgroup in
. On the other hand, each Sylow p-subgroup in  is a copy of
is a copy of  . Hence it follows that the number of Sylow p-subgroups is
. Hence it follows that the number of Sylow p-subgroups is  . The third Sylow theorem implies
. The third Sylow theorem implies
Multiplying both sides by {{nowrap|1=(p − 1)}} gives
that is, the result.
Applications
Primality tests
In practice, Wilson's theorem is useless as a primality test because computing (n − 1)! modulo n for large n is computationally complex, and much faster primality tests are known (indeed, even trial division is considerably more efficient).
Quadratic residues
Using Wilson's Theorem, for any odd prime {{nowrap|1=p = 2m + 1}}, we can rearrange the left hand side of
to obtain the equality
This becomes
or
We can use this fact to prove part of a famous result: for any prime p such that p ≡ 1 (mod 4), the number (−1) is a square (quadratic residue) mod p. For suppose p = 4k + 1 for some integer k. Then we can take m = 2k above, and we conclude that (m!)2 is congruent to (−1).
Formulas for primes
Wilson's theorem has been used to construct formulas for primes, but they are too slow to have practical value.
p-adic gamma function
Wilson's theorem allows one to define the p-adic gamma function.
Gauss's generalization
Gauss proved that[7]where p represents an odd prime and  a positive integer. The values of m for which the product is −1 are precisely the ones where there is a primitive root modulo m.
a positive integer. The values of m for which the product is −1 are precisely the ones where there is a primitive root modulo m.
This further generalizes to the fact that in any finite abelian group, either the product of all elements is the identity, or there is precisely one element a of order 2 (but not both). In the latter case, the product of all elements equals a.
See also
- Wilson prime
- Table of congruences
Notes
2. ^Edward Waring, Meditationes Algebraicae (Cambridge, England: 1770), page 218 (in Latin). In the third (1782) edition of Waring's Meditationes Algebraicae, Wilson's theorem appears as problem 5 on [https://books.google.com/books?id=1MNbAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA380#v=onepage&f=false page 380]. On that page, Waring states: "Hanc maxime elegantem primorum numerorum proprietatem invenit vir clarissimus, rerumque mathematicarum peritissimus Joannes Wilson Armiger." (A man most illustrious and most skilled in mathematics, Squire John Wilson, found this most elegant property of prime numbers.)
3. ^Joseph Louis Lagrange, [https://books.google.com/books?id=_-U_AAAAYAAJ&pg=PA125#v=onepage&q&f=false "Demonstration d'un théorème nouveau concernant les nombres premiers"] (Proof of a new theorem concerning prime numbers), Nouveaux Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences et Belles-Lettres (Berlin), vol. 2, pages 125–137 (1771).
4. ^Giovanni Vacca (1899) "Sui manoscritti inediti di Leibniz" (On unpublished manuscripts of Leibniz),Bollettino di bibliografia e storia delle scienze matematiche ... (Bulletin of the bibliography and history of mathematics), vol. 2, pages 113–116; see [https://books.google.com/books?id=vqwSAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA114#v=onepage&q&f=false page 114] (in Italian). Vacca quotes from Leibniz's mathematical manuscripts kept at the Royal Public Library in Hanover (Germany), vol. 3 B, bundle 11, page 10:
Original : Inoltre egli intravide anche il teorema di Wilson, come risulta dall'enunciato seguente:
"Productus continuorum usque ad numerum qui antepraecedit datum divisus per datum relinquit 1 (vel complementum ad unum?) si datus sit primitivus. Si datus sit derivativus relinquet numerum qui cum dato habeat communem mensuram unitate majorem."
Egli non giunse pero a dimostrarlo.
Translation : In addition, he [Leibniz] also glimpsed Wilson's theorem, as shown in the following statement:See also: Giuseppe Peano, ed., Formulaire de mathématiques, vol. 2, no. 3, [https://books.google.com/books?id=bfDuAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA85#v=onepage&q&f=false page 85] (1897).
"The product of all integers preceding the given integer, when divided by the given integer, leaves 1 (or the complement of 1?) if the given integer be prime. If the given integer be composite, it leaves a number which has a common factor with the given integer [which is] greater than one."
However, he didn't succeed in proving it.
5. ^Landau, two proofs of thm. 78
6. ^When n = 3, the only factors are ±1
7. ^Gauss, DA, art. 78
References
{{refbegin}}The Disquisitiones Arithmeticae has been translated from Gauss's Ciceronian Latin into English and German. The German edition includes all of his papers on number theory: all the proofs of quadratic reciprocity, the determination of the sign of the Gauss sum, the investigations into biquadratic reciprocity, and unpublished notes.
- {{Citation
| last1 = Gauss
| first1 = Carl Friedrich
| last2 = Clarke
| first2 = Arthur A.
| title = Disquisitiones Arithemeticae
| edition = 2nd corrected
| publisher = Springer
| location = New York
| year = 1986
| isbn = 0-387-96254-9
| postscript = (translated into English)
}}.
- {{Citation
| last1 = Gauss
| first1 = Carl Friedrich
| last2 = Maser
| first2 = H.
| title = Untersuchungen über hohere Arithmetik (Disquisitiones Arithemeticae & other papers on number theory)
| edition = 2nd
| publisher = Chelsea
| location = New York
| year = 1965
| isbn = 0-8284-0191-8
| postscript = (translated into German)
}}.
- {{Citation
| last = Landau
| first = Edmund
| title = Elementary Number Theory
| publisher = Chelsea
| location = New York
| year = 1966
}}.
- {{Cite book
| last = Ore
| first = Oystein
| author-link = Oystein Ore
| title = Number Theory and its History
| publisher = Dover
| year = 1988
| pages = 259–271
| isbn = 0-486-65620-9
}}{{refend}}
External links
- {{springer|title=Wilson theorem|id=p/w098010}}
- {{Mathworld|urlname=WilsonsTheorem|title=Wilson's Theorem}}
- Mizar system proof: http://mizar.org/version/current/html/nat_5.html#T22
- St. Petersburg Institute of Fine Mechanics and Optics
- St. Petersburg Institute of International Trade, Economics and Law
- St. Petersburg International Airport
- St. Petersburg International Economic Forum
- St. Petersburg Kickers
- St. Petersburg Luna Park
- St. Petersburg McCormick Kickers
- St. Petersburg Metro
- St Petersburg Metro
- St. Petersburg Museum of History
- St. Petersburg Naval Institute
- St Petersburg, New Zealand
- St. Petersburg Oblast
- St Petersburg Open
- St. Petersburg Orange Blossom Open
- St. Petersburg Orange Classic
- St. Petersburg Philharmonia
- St. Petersburg Philharmonic
- St. Petersburg Police Department
- St. Petersburg Police Department (Florida)
- St. Petersburg Public Library
- St. Petersburg race riot, 1996
- St. Petersburg race riot. 1996
- St. Petersburg River Yacht Club
- St. Petersburg, Russia