- Rationale Ultra-deep sequencing Transcriptome sequencing
- Calculation
- Physical coverage
- References
Rationale
Even though the sequencing accuracy for each individual nucleotide is very high, the very large number of nucleotides in the genome means that if an individual genome is only sequenced once, there will be a significant number of sequencing errors. Furthermore, many positions in a genome contain rare single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Hence to distinguish between sequencing errors and true SNPs, it is necessary to increase the sequencing accuracy even further by sequencing individual genomes a large number of times.
Ultra-deep sequencing
The term "ultra-deep" can sometimes also refer to higher coverage (>100-fold), which allows for detection of sequence variants in mixed populations.[4][5][6] In the extreme, error-corrected sequencing approaches such as Maximum-Depth Sequencing can make it so that coverage of a given region approaches the throughput of a sequencing machine, allowing coverages of >10^8.[7]
Transcriptome sequencing
Deep sequencing of transcriptomes, also known as RNA-Seq, provides both the sequence and frequency of RNA molecules that are present at any particular time in a specific cell type, tissue or organ.[8] Counting the number of mRNAs that are encoded by individual genes provides an indicator of protein-coding potential, a major contributor to phenotype.[9] Improving methods for RNA sequencing is an active area of research both in terms of experimental and computational methods.[10]
Calculation
The average coverage for a whole genome can be calculated from the length of the original genome (G), the number of reads (N), and the average read length (L) as 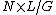 . For example, a hypothetical genome with 2,000 base pairs reconstructed from 8 reads with an average length of 500 nucleotides will have 2× redundancy. This parameter also enables one to estimate other quantities, such as the percentage of the genome covered by reads (sometimes also called coverage). A high coverage in shotgun sequencing is desired because it can overcome errors in base calling and assembly. The subject of DNA sequencing theory addresses the relationships of such quantities.[2]
. For example, a hypothetical genome with 2,000 base pairs reconstructed from 8 reads with an average length of 500 nucleotides will have 2× redundancy. This parameter also enables one to estimate other quantities, such as the percentage of the genome covered by reads (sometimes also called coverage). A high coverage in shotgun sequencing is desired because it can overcome errors in base calling and assembly. The subject of DNA sequencing theory addresses the relationships of such quantities.[2]
Physical coverage
Sometimes a distinction is made between sequence coverage and physical coverage. Where sequence coverage is the average number of times a base is read, physical coverage is the average number of times a base is read or spanned by mate paired reads.[2][11][12]
References
2. ^1 2 {{Cite journal|last=Sims|first=David|last2=Sudbery|first2=Ian|last3=Ilott|first3=Nicholas E.|last4=Heger|first4=Andreas|last5=Ponting|first5=Chris P.|title=Sequencing depth and coverage: key considerations in genomic analyses|journal=Nature Reviews Genetics|volume=15|issue=2|pages=121–132|doi=10.1038/nrg3642|pmid=24434847|year=2014}}
3. ^{{Cite journal|last=Mardis|first=Elaine R.|date=2008-09-01|title=Next-Generation DNA Sequencing Methods|journal=Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics|volume=9|issue=1|pages=387–402|doi=10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164359|issn=1527-8204|pmid=18576944}}
4. ^{{cite journal|date=September 2011|title=Accurate and comprehensive sequencing of personal genomes|journal=Genome Res.|volume=21|issue=9|pages=1498–505|doi=10.1101/gr.123638.111|pmc=3166834|pmid=21771779|vauthors=Ajay SS, Parker SC, Abaan HO, Fajardo KV, Margulies EH}}
5. ^{{Cite journal|last=Mirebrahim|first=Hamid|last2=Close|first2=Timothy J.|last3=Lonardi|first3=Stefano|date=2015-06-15|title=De novo meta-assembly of ultra-deep sequencing data|url=http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/31/12/i9|journal=Bioinformatics|volume=31|issue=12|pages=i9–i16|doi=10.1093/bioinformatics/btv226|issn=1367-4803|pmid=26072514|pmc=4765875}}
6. ^{{Cite journal|last=Beerenwinkel|first=Niko|last2=Zagordi|first2=Osvaldo|date=2011-11-01|title=Ultra-deep sequencing for the analysis of viral populations|url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1879625711000629|journal=Current Opinion in Virology|volume=1|issue=5|pages=413–418|doi=10.1016/j.coviro.2011.07.008|pmid=22440844}}
7. ^{{cite journal|journal=Nature|volume=534|issue=7609|doi=10.1038/nature18313|pmid=27338792|title=Rates and mechanisms of bacterial mutagenesis from maximum-depth sequencing|pages=693–696|pmc=4940094|year=2016|last1=Jee|first1=J.|last2=Rasouly|first2=A.|last3=Shamovsky|first3=I.|last4=Akivis|first4=Y.|last5=Steinman|first5=S.|last6=Mishra|first6=B.|last7=Nudler|first7=E.}}
8. ^{{Cite journal|last=Malone|first=John H.|last2=Oliver|first2=Brian|date=2011-01-01|title=Microarrays, deep sequencing and the true measure of the transcriptome|journal=BMC Biology|volume=9|pages=34|doi=10.1186/1741-7007-9-34|pmid=21627854|pmc=3104486|issn=1741-7007}}
9. ^{{cite journal|year=2011|title=Deep sequencing the transcriptome reveals seasonal adaptive mechanisms in a hibernating mammal|journal=PLOS ONE|volume=6|issue=10|pages=e27021|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0027021|pmc=3203946|pmid=22046435|vauthors=Hampton M, Melvin RG, Kendall AH, Kirkpatrick BR, Peterson N, Andrews MT}}
10. ^{{cite journal|year=2015|title=An optimized kit-free method for making strand-specific deep sequencing libraries from RNA fragments.|journal=Nucleic Acids Res.|volume=43|issue=1|pages=e2|doi=10.1093/nar/gku1235|pmid=25505164|vauthors=Heyer EE, Ozadam H, Ricci EP, Cenik C, Moore MJ|pmc=4288154}}
11. ^{{Cite journal | last1 = Meyerson | first1 = M. | last2 = Gabriel | first2 = S. | last3 = Getz | first3 = G. | doi = 10.1038/nrg2841 | title = Advances in understanding cancer genomes through second-generation sequencing | journal = Nature Reviews Genetics | volume = 11 | issue = 10 | pages = 685–696 | year = 2010 | pmid = 20847746| pmc = }}
12. ^{{cite journal |last1=Ekblom |first1=Robert |last2=Wolf |first2=Jochen B. W. |title=A field guide to whole‐genome sequencing, assembly and annotation |journal=Evolutionary Applications |date=2014 |volume=7 |issue=9 |pages=1026–42 |doi=10.1111/eva.12178 |pmid=25553065 |pmc=4231593 }}
- Lebanon in the Eurovision Song Contest 2005
- Lebanon-Israel relations
- Lebanon Law School
- Lebanon, Michigan
- Lebanon Micropolitan Area
- Lebanon micropolitan statistical area
- Lebanon Micropolitan Statistical Area
- Lebanon, MO mSA
- Lebanon Mountain Trail
- Lebanon, MO µSA
- Lebanon Municipal Airport
- Lebanon national football team results (2010–19)
- Lebanon national futsal team
- Lebanon national handball team
- Lebanon national rugby league team match results
- Lebanon national rugby union team
- Lebanon national under-20 football team
- Lebanon national under-23 football team
- Lebanon Navy
- Lebanon, New Hampshire micropolitan area
- Lebanon, New Hampshire Micropolitan Area
- Lebanon, New Hampshire Micropolitan Statistical Area
- Lebanon, New Hampshire micropolitan statistical area
- Lebanon, New Hampshire-Vermont Micropolitan Area
- Lebanon, New Hampshire-Vermont micropolitan area