“内府官物”朱漆盘
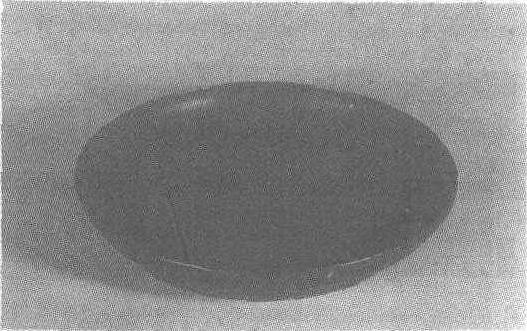
元泰定元年(公元1324年)。口径36.3厘米,足径28.5厘米,高5.9厘米。北京市延庆县清泉铺乡出土。北京市文物研究所藏。圆形,敞口,圈足,盘内外表面髹朱漆,圈足内髹黑漆,上书朱漆款识,虽被刮划,依然可辨出是“泰定元年三月漆匠作头徐祥天”,“内府官物”和“武昌路提调官同知外家奴朝散”,纵向排列,右中左分布。此盘因其款识明确标明制作时间及所有者,在元代漆器中占有重要地位。
| 词条 | “内府官物”朱漆盘 |
| 类别 | 中文百科知识 |
| 释义 | “内府官物”朱漆盘元泰定元年(公元1324年)。口径36.3厘米,足径28.5厘米,高5.9厘米。北京市延庆县清泉铺乡出土。北京市文物研究所藏。圆形,敞口,圈足,盘内外表面髹朱漆,圈足内髹黑漆,上书朱漆款识,虽被刮划,依然可辨出是“泰定元年三月漆匠作头徐祥天”,“内府官物”和“武昌路提调官同知外家奴朝散”,纵向排列,右中左分布。此盘因其款识明确标明制作时间及所有者,在元代漆器中占有重要地位。
|
| 随便看 |
开放百科全书收录579518条英语、德语、日语等多语种百科知识,基本涵盖了大多数领域的百科知识,是一部内容自由、开放的电子版国际百科全书。