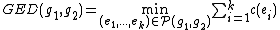- Formal definitions and properties
- Applications
- Algorithms and Complexity
- References
In mathematics and computer science, graph edit distance (GED) is a measure of similarity (or dissimilarity) between two graphs.
The concept of graph edit distance was first formalized mathematically by Alberto Sanfeliu and King-Sun Fu in 1983.[1]
A major application of graph edit distance is in inexact graph matching, such
as error-tolerant pattern recognition in machine learning.[2]
The graph edit distance between two graphs is related to the
string edit distance between strings.
With the interpretation of strings as connected, directed acyclic graphs of
maximum degree one, classical definitions
of edit distance such as Levenshtein distance,
[3][4]Hamming distance[5]and Jaro–Winkler distance may be interpreted as graph edit distances
between suitably constrained graphs. Likewise, graph edit distance is
also a generalization of tree edit distance between
rooted trees.[6][7][8][9]Formal definitions and properties
The mathematical definition of graph edit distance is dependent upon the definitions of
the graphs over which it is defined, i.e. whether and how the vertices and edges of the
graph are labeled and whether the edges are directed.
Generally, given a set of graph edit operations (also known as elementary graph operations), the graph edit distance between two graphs  and
and  , written as
, written as  can be defined as
can be defined as
where  denotes the set of edit paths transforming
denotes the set of edit paths transforming  into (a graph isomorphic to)
into (a graph isomorphic to)  and
and  is the cost of each graph edit operation
is the cost of each graph edit operation  .
.
The set of elementary graph edit operators typically includes:
vertex insertion to introduce a single new labeled vertex to a graph.
vertex deletion to remove a single (often disconnected) vertex from a graph.
vertex substitution to change the label (or color) of a given vertex.
edge insertion to introduce a new colored edge between a pair of vertices.
edge deletion to remove a single edge between a pair of vertices.
edge substitution to change the label (or color) of a given edge.
Additional, but less common operators, include operations such as edge splitting that introduces a new vertex into an edge (also creating a new edge), and edge contraction that eliminates vertices of degree two between edges (of the same color). Although such complex edit operators can be defined in terms of more elementary transformations, their use allows finer parameterization of the cost function  when the operator is cheaper than the sum of its constituents.
when the operator is cheaper than the sum of its constituents.
Applications
Graph edit distance finds applications in handwriting recognition,[10] fingerprint recognition[11] and cheminformatics.[12]
Algorithms and Complexity
Exact algorithms for computing the graph edit distance between a pair of graphs typically
transform the problem into one of finding the minimum cost edit path between the two graphs.
The computation of the optimal edit path is cast as a pathfinding search or shortest path problem, often implemented as an A* search algorithm.
In addition to exact algorithms, a number of efficient approximation algorithms are
also known.[13][14]
Despite the above algorithms sometimes working well in practice, in general the problem of computing graph edit distance is NP-complete[15] (for a proof that's available online, see Section 2 of Zeng et al.), and is even hard to approximate (formally, it is APX-hard[16]).
References
2. ^{{cite journal|first1=Xinbo|last1=Gao|first2=Bing|last2=Xiao|first3=Dacheng|last3=Tao|first4=Xuelong|last4=Li|title=A survey of graph edit distance|journal=Pattern Analysis and Applications|year=2010|volume=13|pages=113–129|doi=10.1007/s10044-008-0141-y}}
3. ^{{cite journal|author=Влади́мир И. Левенштейн|script-title=ru:Двоичные коды с исправлением выпадений, вставок и замещений символов|language=Russian|trans-title=Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions, and reversals|journal=Доклады Академий Наук СCCP|volume=163|issue=4|pages=845–848|year=1965}}
4. ^{{cite journal|last1=Levenshtein|first1=Vladimir I.|title=Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions, and reversals|journal=Soviet Physics Doklady|volume=10|number=8|pages=707–710|date=February 1966}}
5. ^{{cite journal |last=Hamming |first=Richard W. |author-link=Richard W. Hamming |mr=0035935 |issue=2 |journal=Bell System Technical Journal |pages=147–160 |title=Error detecting and error correcting codes |url=http://www.caip.rutgers.edu/~bushnell/dsdwebsite/hamming.pdf |volume=29 |year=1950 |doi=10.1002/j.1538-7305.1950.tb00463.x |deadurl=bot: unknown |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20060525060427/http://www.caip.rutgers.edu/~bushnell/dsdwebsite/hamming.pdf |archivedate=2006-05-25 |df= |hdl=10945/46756 }}
6. ^{{cite journal|last1=Shasha|first1=D|last2=Zhang|first2=K|title=Simple fast algorithms for the editing distance between trees and related problems|journal=SIAM J. Comput.|volume=18|number=6|pages=1245–1262|year=1989|doi=10.1137/0218082|citeseerx=10.1.1.460.5601}}
7. ^{{cite journal|last1=Zhang|first1=K|title=A constrained edit distance between unordered labeled trees|journal=Algorithmica|volume=15|number=3|pages=205–222|year=1996|doi=10.1007/BF01975866}}
8. ^{{cite journal|last1=Bille|first1=P|title=A survey on tree edit distance and related problems|journal=Theor. Comput. Sci.|volume=337|issue=1–3|pages=22–34|year=2005|doi=10.1016/j.tcs.2004.12.030}}
9. ^{{cite journal|last1=Demaine|first1=Erik D.|author1-link=Erik Demaine|last2=Mozes|first2=Shay|last3=Rossman|first3=Benjamin|last4=Weimann|first4=Oren|issue = 1|journal = ACM Transactions on Algorithms|mr = 2654906|page = A2|title = An optimal decomposition algorithm for tree edit distance|volume = 6|year = 2010|doi = 10.1145/1644015.1644017|citeseerx=10.1.1.163.6937}}
10. ^{{citation|last1=Fischer|first1=Andreas|last2=Suen|first2=Ching Y.|last3=Frinken|first3=Volkmar|last4=Riesen|first4=Kaspar|last5=Bunke|first5=Horst|contribution=A Fast Matching Algorithm for Graph-Based Handwriting Recognition|title=Graph-Based Representations in Pattern Recognition|series=Lecture Notes in Computer Science|volume=7877|pages=194–203|year=2013|doi=10.1007/978-3-642-38221-5_21|isbn=978-3-642-38220-8}}
11. ^{{citation|last1=Neuhaus|first1=Michel|last2=Bunke|first2=Horst|contribution=A Graph Matching Based Approach to Fingerprint Classification using Directional Variance|title=Audio- and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication|series=Lecture Notes in Computer Science|volume=3546|pages=191–200|year=2005|doi=10.1007/11527923_20|isbn=978-3-540-27887-0}}
12. ^{{cite journal|last1=Birchall|first1=Kristian|last2=Gillet|first2=Valerie J.|last3=Harper|first3=Gavin|last4=Pickett|first4=Stephen D.|title=Training Similarity Measures for Specific Activities: Application to Reduced Graphs|journal=Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling|volume=46|number=2|pages=557–586|date=Jan 2006|doi=10.1021/ci050465e|pmid=16562986}}
13. ^{{cite book|last1=Neuhaus|first1=Michel|last2=Bunke|first2=Horst|title=Bridging the Gap between Graph Edit Distance and Kernel Machines|series=Machine Perception and Artificial Intelligence|volume=68|publisher=World Scientific|isbn=978-9812708175|date=Nov 2007}}
14. ^{{cite book|last=Riesen|first=Kaspar|title=Structural Pattern Recognition with Graph Edit Distance: Approximation Algorithms and Applications|series=Advances in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition|publisher=Springer|isbn=978-3319272511|date=Feb 2016 }}
15. ^{{Cite book|title=Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness|last=Garey and Johnson|publisher=W. H. Freeman and Company|year=1979|isbn=978-0-7167-1045-5|location=|pages=}}
16. ^{{Cite book|last=Lin|first=Chih-Long|date=1994-08-25|publisher=Springer Berlin Heidelberg|isbn=9783540583257|editor-last=Du|editor-first=Ding-Zhu|series=Lecture Notes in Computer Science|pages=74–82|language=en|doi=10.1007/3-540-58325-4_168|editor-last2=Zhang|editor-first2=Xiang-Sun|title = Algorithms and Computation|volume = 834|chapter=Hardness of approximating graph transformation problem}}
- Julio Iemma
- Julio Iglesias, Jr.
- Julio Iglesias, Sr.
- Julio Illescas
- Julio Jemison
- Julio Jobet
- Julio Jose Gonzalez
- Julio José González
- Julio José Iglesias, Jr.
- Julio J. Rotemberg
- Julio Jung
- Julio Just Gimeno
- Julio Lacerda
- Julio Leon (disambiguation)
- Julio Ligorría
- Julio Lopez Chavez
- Julio Lopez (rower)
- Julio López
- Julio López Chávez
- Julio Macat
- Julio Mario Santo Domingo, Jr.
- Julio Mayora
- Julio Mboumba
- Julio Medaglia
- Julio Medina