- Coordinates
- As a Configuration
- Images
- Related complex polyhedra Construction Images Rectified Hessian polyhedron Construction
- References
| Hessian polyhedron | |
|---|---|
Orthographic projection (triangular 3-edges outlined as black edges) | |
| Schläfli symbol | 3{3}3{3}3 |
| Coxeter diagram | 3node_1|3|3node|3|3node}} |
| Faces | 27 3{3}3 |
| Edges | 72 3{} |
| Vertices | 27 |
| Petrie polygon | Dodecagon |
| van Oss polygon | 12 3{4}2 |
| Shephard group | L3 = 3[3]3[3]3, order 648 |
| Dual polyhedron | Self-dual |
| Properties | Regular |
In geometry, the Hessian polyhedron is a regular complex polyhedron 3{3}3{3}3, {{CDD|3node_1|3|3node|3|3node}}, in 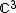 . It has 27 vertices, 72 3{} edges, and 27 3{3}3 faces. It is self-dual.
. It has 27 vertices, 72 3{} edges, and 27 3{3}3 faces. It is self-dual.
Coxeter named it after Ludwig Otto Hesse for sharing the Hessian configuration  or (94123), 9 points lying by threes on twelve lines, with four lines through each point.[1]
or (94123), 9 points lying by threes on twelve lines, with four lines through each point.[1]
Its complex reflection group is 3[3]3[3]3 or {{CDD|3node|3|3node|3|3node}}, order 648, also called a Hessian group. It has 27 copies of {{CDD|3node|3|3node}}, order 24, at each vertex. It has 24 order-3 reflections. Its Coxeter number is 12, with degrees of the fundamental invariants 3, 6, and 12, which can be seen in projective symmetry of the polytopes.
The Witting polytope, 3{3}3{3}3{3}3, {{CDD|3node_1|3|3node|3|3node|3|3node}} contains the Hessian polyhedron as cells and vertex figures.
It has a real representation as the 221 polytope, {{CDD|nodes_10r|3ab|nodes|split2|node|3|node}}, in 4-dimensional space, sharing the same 27 vertices. The 216 edges in 221 can be seen as the 72 3{} edges represented as 3 simple edges.
Coordinates
Its 27 vertices be given coordinates in 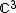 : for (λ, μ = 0,1,2).
: for (λ, μ = 0,1,2).
(0,ωλ,−ωμ)
(−ωμ,0,ωλ)
(ωλ,−ωμ,0)
where 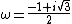 .
.
As a Configuration
Hessian polyhedron with triangular 3-edges outlined as black edges, with one face outlined as blue. | One of 12 Van oss polygons, 3{4}2, in the Hessian polyhedron |
Its symmetry by 3[3]3[3]3 or {{CDD|3node|3|3node|3|3node}}, order 648.[2]
The configuation matrix for 3{3}3{3}3 is:[3]
The number of k-face elements (f-vectors) can be read down the diagonal. The number of elements of each k-face are in rows below the diagonal. The number of elements of eac k-figure are in rows above the diagonal.
| L3 | 3node_1|3|3node|3|3node | k-face | fk | f0 | f1 | f2 | k-fig | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2 | node_x|2|3node|3|3node}} | ( ) | f0 | 27 | 8 | 8 | 3{3}3 | L3/L2 = 27*4!/4! = 27 |
| L1L1 | 3node_1|2|node_x|2|3node}} | 3{ } | f1 | 3 | 72 | 3 | 3{ } | L3/L1L1 = 27*4!/9 = 72 |
| L2 | 3node_1|3|3node|2|node_x}} | 3{3}3 | f2 | 8 | 8 | 27 | ( ) | L3/L2 = 27*4!/4! = 27 |
Images
These are 8 symmetric orthographic projections, some with overlapping vertices, shown by colors. Here the 72 triangular edges are drawn as 3-separate edges.
| E6 [12] | Aut(E6) [18/2] | D5 [8] | D4 / A2 [6] |
|---|---|---|---|
(1=red,3=orange) | (1) | (1,3) | (3,9) |
| B6 [12/2] | A5 [6] | A4 [5] | A3 / D3 [4] |
(1,3) | (1,3) | (1,2) | (1,4,7) |
Related complex polyhedra
| Double Hessian polyhedron | |
|---|---|
| Schläfli symbol | 2{4}3{3}3 |
| Coxeter diagram | node_1|4|3node|3|3node}} |
| Faces | 72 2{4}3 |
| Edges | 216 {} |
| Vertices | 54 |
| Petrie polygon | Octadecagon |
| van Oss polygon | {6} |
| Shephard group | M3 = 3[3]3[4]2, order 1296 |
| Dual polyhedron | Rectified Hessian polyhedron, 3{3}3{4}2 |
| Properties | Regular |
The Hessian polyhedron can be seen as an alternation of {{CDD|node_1|4|3node|3|3node}}, {{CDD|node_h|4|3node|3|3node}} = {{CDD|label-33|nodes_10ru|split2|node|label3}}. This double Hessian polyhedron has 54 vertices, 216 simple edges, and 72 {{CDD|node_1|4|3node}} faces. Its vertices represent the union of the vertices {{CDD|3node_1|3|3node|3|3node}} and its dual {{CDD|3node|3|3node|3|3node_1}}.
Its complex reflection group is 3[3]3[4]2, or {{CDD|3node|3|3node|4|node}}, order 1296. It has 54 copies of {{CDD|3node|3|3node}}, order 24, at each vertex. It has 24 order-3 reflections and 9 order-2 reflections. Its coxeter number is 18, with degrees of the fundamental invariants 6, 12, and 18 which can be seen in projective symmetry of the polytopes.
Coxeter noted that the three complex polytopes {{CDD|3node_1|3|3node|3||3node}}, {{CDD|node_1|4|3node|3||3node}}, {{CDD|3node_1|3|3node|4|node}} resemble the real tetrahedron ({{CDD|node_1|3|node|3|node}}), cube ({{CDD|node_1|4|node|3|node}}), and octahedron ({{CDD|node_1|3|node|4|node}}). The Hessian is analogous to the tetrahedron, like the cube is a double tetrahedron, and the octahedron as a rectified tetrahedron. In both sets the vertices of the first belong to two dual pairs of the second, and the vertices of the third are at the center of the edges of the second.[4]
Its real representation 54 vertices are contained by two 221 polytopes in symmetric configurations: {{CDD|nodes_10r|3ab|nodes|split2|node|3|node}} and {{CDD|nodes_01r|3ab|nodes|split2|node|3|node}}. Its vertices can also be seen in the dual polytope of 122.
Construction
The elements can be seen in a configuration matrix:
| M3 | node_1|4|3node|3|3node | k-face | fk | f0 | f1 | f2 | k-fig | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2 | node_x|2|3node|3|3node}} | ( ) | f0 | 54 | 8 | 8 | 3{3}3 | M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54 |
| L1A1 | node_1|2|node_x|2|3node}} | { } | f1 | 2 | 216 | 3 | 3{ } | M3/L1A1 = 1296/6 = 216 |
| M2 | node_1|4|3node|2|node_x}} | 2{4}3 | f2 | 6 | 9 | 72 | ( ) | M3/M2 = 1296/18 = 72 |
Images
| {{CDD>node_1|4|3node|3|3node}} polyhedron | {{CDD>node_1|4|3node|3|3node}} polyhedron with one face, 2{4}3 highlighted blue | {{CDD>node_1|4|3node|3|3node}} polyhedron with 54 vertices, in two 2 alternate color | {{CDD>label-33|nodes_10ru|split2|node|label3}} and {{CDD|label-33|nodes_01rd|split2|node|label3}}, shown here with red and blue vertices form a regular compound {{CDD|node_h3|4|3node|3|3node}} |
Rectified Hessian polyhedron
| Rectified Hessian polyhedron | |
|---|---|
| Schläfli symbol | 3{3}3{4}2 |
| Coxeter diagrams | 3node_1|3|3node|4|node}} {{CDD|3node|3|3node_1|3|3node}} or {{CDD|label3|node_1|split1|nodes|label-33}}. |
| Faces | 54 3{3}3 |
| Edges | 216 3{} |
| Vertices | 72 |
| Petrie polygon | Octadecagon |
| van Oss polygon | 9 3{4}3 |
| Shephard group | M3 = 3[3]3[4]2, order 1296 3[3]3[3]3, order 648 |
| Dual polyhedron | Double Hessian polyhedron 2{4}3{3}3 |
| Properties | Regular |
The rectification, {{CDD|3node|3|3node_1|3|3node}} doubles in symmetry as a regular complex polyhedron {{CDD|3node_1|3|3node|4|node}} with 72 vertices, 216 3{} edges, 54 3{3}3 faces. Its vertex figure is 3{4}2, and van oss polygon 3{4}3. It is dual to the double Hessian polyhedron.[5]
It has a real representation as the 122 polytope, {{CDD|nodes|3ab|nodes|split2|node|3|node_1}}, sharing the 72 vertices. Its 216 3-edges can be drawn as 648 simple edges, which is 72 less than 122's 720 edges.
| {{CDD>3node_1|3|3node|4|node}} or {{CDD|3node|3|3node_1|3|3node}} has 72 vertices, 216 3-edges, and 54 3{4}2 faces | {{CDD>3node_1|3|3node|4|node}} with one blue face, 3{3}3 highlighted | {{CDD>3node_1|3|3node|4|node}} with one of 9 van oss polygon, 3{4}3, highlighted |
Construction
The elements can be seen in two configuration matrices, a regular and quasiregular form.
| M3 | 3node_1|3|3node|4|node | k-face | fk | f0 | f1 | f2 | k-fig | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2>{{CDD|node_x|2|3node|4|node}} | ( ) | f0 | 72 | 9 | 6 | 3{4}2 | M3/M2 = 1296/18 = 72 | |
| L1A1 | 3node_1|2|node_x|2|node}} | 3{ } | f1 | 3 | 216 | 2 | { } | M3/L1A1 = 1296/3/2 = 216 |
| L2 | 3node_1|3|3node|2|node_x}} | 3{3}3 | f2 | 8 | 8 | 54 | ( ) | M3/L2 = 1296/24 = 54 |
| L3 | 3node|3|3node_1|3|3node | k-face | fk | f0 | f1 | f2 | k-fig | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1L1 | 3node|2|node_x|2|3node}} | ( ) | f0 | 72 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 3{ }×3{ } | L3/L1L1 = 648/9 = 72 |
| L1 | node_x|2|3node_1|2|node_x}} | 3{ } | f1 | 3 | 216 | 1 | 1 | { } | L3/L1 = 648/3 = 216 |
| L2 | 3node|3|3node_1|2|node_x}} | 3{3}3 | f2 | 8 | 8 | 27 | * | ( ) | L3/L2 = 648/24 = 27 |
| {{CDD|node_x|2|3node_1|3|3node}} | 8 | 8 | * | 27 |
References
2. ^Coxeter Regular Convex Polytopes, 12.5 The Witting polytope
3. ^Coxeter, Complex Regular polytopes, p.132
4. ^Coxeter, Complex Regular Polytopes, p.127
5. ^Coxeter, H. S. M., Regular Complex Polytopes, second edition, Cambridge University Press, (1991). p.30 and p.47
- Coxeter, H. S. M. and Moser, W. O. J.; Generators and Relations for Discrete Groups (1965), esp pp 67–80.
- Coxeter, H. S. M.; Regular Complex Polytopes, Cambridge University Press, (1974).
- Coxeter, H. S. M. and Shephard, G.C.; Portraits of a family of complex polytopes, Leonardo Vol 25, No 3/4, (1992), pp 239–244,
- Zeda Sakara
- Zed Bias
- Zed Blade
- Zed Books
- Zed-car (disambiguation)
- ZED (Cirque du Soleil)
- Zed (Cirque du Soleil)
- Zeddine
- ZED (disambiguation)
- Zed (disambiguation)
- Zeddy Saileti
- Zedea
- Ze de Angola
- Zede-Dianhoun
- Zedek
- Zedekiah Anaw
- Zedekiah b. Abraham Anaw
- Zedekiah's Cave
- Zedel
- Zedelgem, Belgium
- Zeder
- Zederman
- Zedginidze
- Zed Group
- Zedi
