- Definition
- Properties
- References
In probability theory, an intensity measure is a measure that is derived from a random measure. The intensity measure is a non-random measure and is defined as the expectation value of the random measure of a set, hence it corresponds to the average volume the random measure assigns to a set. The intensity measure contains important information about the properties of the random measure. A Poisson point process, interpreted as a random measure, is for example uniquely determined by its intensity measure. [1]
Definition
Let  be a random measure on the measurable space
be a random measure on the measurable space  and denote the expected value of a random element
and denote the expected value of a random element  with
with  .
.
The intensity measure
of  is defined as
is defined as
for all  .[2] [3]
.[2] [3]
Note the difference in notation between the expectation value of a random element  , denoted by
, denoted by  and the intensity measure of the random measure
and the intensity measure of the random measure  , denoted by
, denoted by 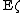 .
.
Properties
The intensity measure 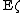 is always s-finite and satisfies
is always s-finite and satisfies
for every positive measurable function  on
on  .[3]
.[3]
References
- List of video games developed in Ireland
- List of video games developed in Portugal
- List of video games developed in Slovakia
- List of video games developed in the Republic of Ireland
- List of video games in the WWE 2K Games series
- List of video games known for negative reception
- List of video games notable for positive reception
- List of video games published by Aksys Games
- List of video games published by Microsoft Studios
- List of video games published by Sony Computer Entertainment
- List of video games published by Sony Interactive Entertainment
- List of video games published by Sunsoft
- List of video games published by THQ Nordic
- List of video games set during World War I
- List of video games that support cross-platform play
- List of video games using Miis
- List of video games with generally negative reception
- List of video game terms
- List of video game webcomics
- List of Videopac games
- List of videos games written in Python
- List of Video Star episodes
- List of Videoton FC managers
- List of Videoton FC records and statistics
- List of Videoton FC seasons


