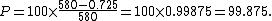- Mathematical definition
- Log reduction and percentage reduction
- See also
- References
The log reduction achieved by a decontamination process is a measure of the reduction in the concentration of a contaminant. The name reflects that the measure is expressed on a logarithmic scale, using base 10. An increase by 1 corresponds to a reduction in the concentration of the contaminant by a factor of 10. A 0-log reduction means that there is no reduction. A 1-log reduction would correspond to a reduction of 90 percent from the original concentration. A 2-log reduction corresponds to a reduction of 99 percent from the original concentration.[1]
Mathematically, the log reduction is the base-10 logarithm of the ratio between the concentrations before and after treatment. Some other measures using a logarithmic scale to express a ratio are the decibel, the astronomical magnitude and the pH scale.
Mathematical definition
Let {{mvar|c}}b and {{mvar|c}}a be the numerical values of the concentrations of a given contaminant, respectively before and after treatment, following a defined process.
It is irrelevant in what units these concentrations are given, provided that both use the same units.
Then an {{mvar|R}}-log reduction is achieved, where
{{mvar|R}} = log10 {{mvar|c}}b − log10 {{mvar|c}}a = − log10 ({{mvar|c}}a / {{mvar|c}}b).
For the purpose of presentation, the value of {{mvar|R}} is rounded down to a desired precision, usually to a whole number.
- Example
Let the concentration of some contaminant be 580 ppm before and 0.725 ppm after treatment. Then
{{mvar|R}} = − log10 (0.725/580) = − log10 0.00125 = 2.903...
Rounded down, {{mvar|R}} is 2, so a 2-log reduction is achieved.
Conversely, an {{mvar|R}}-log reduction means that a reduction by a factor of 10{{mvar|R}} has been achieved.
Log reduction and percentage reduction
Reduction is often expressed as a percentage. The closer it is to 100%, the better.
Letting {{mvar|c}}b and {{mvar|c}}a be as before, a reduction by {{mvar|P}}% is achieved, where
[2]
- Example
Let, as in the earlier example, the concentration of some contaminant be 580 ppm before and 0.725 ppm after treatment. Then
So this is (better than) a 99% reduction, but not yet quite a 99.9% reduction.
The following table summarizes the most common cases.
| Log reduction | Percentage |
|---|---|
| 1-log reduction | 90% |
| 2-log reduction | 99% |
| 3-log reduction | 99.9% |
| 4-log reduction | 99.99% |
| 5-log reduction | 99.999% |
In general, if {{mvar|R}} is a whole number, an {{mvar|R}}-log reduction corresponds to a percentage reduction with {{mvar|R}} leading digits "9" in the percentage (provided that it is at least 10%).
See also
- Decimal reduction time
References
2. ^{{cite web |title=Log and Percent Reductions in Microbiology and Antimicrobial Testing |publisher=Microchem Laboratory |url=https://microchemlab.com/information/log-and-percent-reductions-microbiology-and-antimicrobial-testing |date=December 16, 2015 |accessdate=December 7, 2018}}
- Supernova (Lisa Lopes album)
- Super Nova Racing
- Supernova (Rock Star band)
- Supernova (Rock Star band) (disambiguation)
- Supernova Search Team
- Supernova (television)
- Supernova (The Echoing Green album)
- Supernova (TV series)
- Supernove
- Super Noypi
- Super nuke
- Supernumerarii
- Supernumerary
- Supernumerary actor
- Supernumerary body part
- Supernumerary bodypart
- Supernumerary body parts
- Supernumerary bodyparts
- Supernumerary breast
- Supernumerary digit
- Supernumerary kidney
- Supernumerary Limb
- Supernumerary organ
- Supernumerary Police
- Supernumerary rainbow