- Galois connected
- Abstraction refinement loop
- References
Abstraction Model checking is for systems where an actual representation is too complex in developing the model alone. So, the design undergoes a kind of translation to scaled down "abstract" version.
The set of variables are partitioned into visible and invisible depending on their change of values. The real state space is summarized into a smaller set of the visible ones.
Galois connected
The real and the abstract state spaces are Galois connected. This means that if we take an element from the abstract space, concretize it and abstract the concretized version, the result will be equal to the original. On the other hand, if you pick an element from the real space, abstract it and concretize the abstract version, the final result will be a super set of the original.
That is,
 (
( (abstract)) = abstract
(abstract)) = abstract  (
( (real))
(real)) 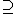 real
real
Abstraction refinement loop
A problem with abstraction model checking is that although the abstraction simulates the real, when the abstraction does not satisfy a property, it does not mean that this property actually fails in the real model. Counter examples are checked against the real state space because we obtain "spurious" counter examples. So a part of the abstraction refinement loop is:
- Obtain the abstract model
- Model check and see if everything is ok.
- If there is a counter example, then go back to the real state space and find out if it actually a counter model.
- If not, return and continue model checking.
Spurious examples are mostly generated because dead end states and bad states are abstracted to the same kind. To solve this we need to create a segregation between the 2 kinds. The next step is to find the subset of invisible variables that actually make a difference between the dead end and bad states and add this subset to the set of visible or monitored variables. If the separation proves expensive, refinement could be based on learning from samples.
References
- {{cite journal | author=Edmund M. Clarke and Orna Grumberg and David E. Long | title=Model checking and abstraction | journal=ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems| year=1994| volume=16 | issue=5 | pages=1512–1542 | doi=10.1145/186025.186051| citeseerx=10.1.1.79.3022 }}
- Hemimastigophora
- Hemimetabolism
- Hemimorphite
- Hemingfield
- Hemingford Grey
- Hemingford, NE
- Hemingford, Nebraska
- Hemingray Glass Company
- Hemingstone
- Hemingway (disambiguation)
- Hemingway Foundation/PEN Award
- Hemingway, SC
- Hemingway, South Carolina
- Hemiola
- Hemionids
- Hemiparesis
- Hemipelvectomy
- Hemipenes
- Hemipenis
- Hemiphaga
- Hemiphaga novaeseelandiae
- Hemiphyllodactylus
- Hemiplegia
- Hemiplegic
- Hemipode