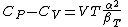- References
Julius von Mayer derived a relation between specific heat at constant pressure and the specific heat at constant volume for an ideal gas. The relation is:
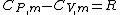 ,
,
where CP,m is the molar specific heat at constant pressure, CV,m is the specific heat at constant volume and R is the gas constant.
For more general homogeneous substances, not just ideal gases, the difference takes the form,
(see relations between heat capacities), where 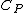 is the heat capacity of a body at constant pressure,
is the heat capacity of a body at constant pressure, 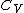 is the heat capacity at constant volume,
is the heat capacity at constant volume,  is the volume,
is the volume, 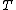 is the temperature,
is the temperature,  is the thermal expansion coefficient and
is the thermal expansion coefficient and 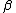 is the isothermal compressibility.
is the isothermal compressibility.
From this relation, several inferences can be made:[1]
- Since isothermal compressibility
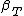 is positive for all phases and the square of thermal expansion coefficient
is positive for all phases and the square of thermal expansion coefficient  is a positive quantity or zero, the specific heat at constant-pressure is always greater than or equal to specific heat at constant-volume.
is a positive quantity or zero, the specific heat at constant-pressure is always greater than or equal to specific heat at constant-volume.
≥
- As the absolute temperature of the system approaches zero, the difference between CP,m and CV,m also approaches zero.
- For incompressible substances, CP,m and CV,m are identical. Also for substances that are nearly incompressible, such as solids and liquids, the difference between the two specific heats is negligible.
References
- ГОСТ 27463-87
- ГОСТ IEC 60062
- ГОСТ IEC 60062-2014
- ГУЛАГ
- Газета.Ru
- Галицько-Волинське князівство
- Гана Найденова
- Гарпастум
- Гена́дзь Васі́левіч Наві́цкі
- Гена́дзь Наві́цкі
- Геннадий Алексеевич Леонов
- Геннадий Леонов
- Генрих Григорьевич Ягода
- Гео́ргий Ка́рлович Кре́йер
- Гео́ргий Кре́йер
- Георг Стірнгельм
- Георг Шернъельм
- Георгий Иванович Бобриков
- Георгий Робертович Васмунд
- Герой нашего времени
- Гилане
- Гимн Советского Союза
- Гимн Южной Осетии
- Глеб Михайлович Ванновский
- Глюк'oza