- Terminology
- Compliance factors Health literacy Literacy Treatment cost Age Ethnicity Prescription fill rates Medication Possession Ratio Course completion
- World Health Organization Barriers to Adherence
- Improving compliance rates Role of health care providers Technology
- Health and disease management Cancer Diabetes Hypertension Mental illness
- See also
- References
- External links
In medicine, compliance (also adherence, capacitance) describes the degree to which a patient correctly follows medical advice. Most commonly, it refers to medication or drug compliance, but it can also apply to other situations such as medical device use, self care, self-directed exercises, or therapy sessions. Both patient and health-care provider affect compliance, and a positive physician-patient relationship is the most important factor in improving compliance,[1] The cost of prescription medication also plays a major role.[2]
Compliance can be confused with concordance, which is the process by which a patient and clinician make decisions together about treatment.[2]
Worldwide, non-compliance is a major obstacle to the effective delivery of health care. 2003 estimates from the World Health Organization indicated that only about 50% of patients with chronic diseases living in developed countries follow treatment recommendations with particularly low rates of adherence to therapies for asthma, diabetes, and hypertension.[1] Major barriers to compliance are thought to include the complexity of modern medication regimens, poor "health literacy" and not understanding treatment benefits, occurrence of undiscussed side effects, poor treatment satisfaction, cost of prescription medicine, and poor communication or lack of trust between a patient and his or her health-care provider.[5][6][3][4] Efforts to improve compliance have been aimed at simplifying medication packaging, providing effective medication reminders, improving patient education, and limiting the number of medications prescribed simultaneously. Studies show a great variation in terms of characteristics and effects of interventions to improve medicine adherence.[5] It is still unclear how adherence can consistently be improved in order to promote clinically important effects.[5]
Terminology
In medicine, compliance (synonymous with adherence, capacitance) describes the degree to which a patient correctly follows medical advice. Most commonly, it refers to medication or drug compliance, but it can also apply to medical device use, self care, self-directed exercises, or therapy sessions. Both patient and health-care provider affect compliance, and a positive physician-patient relationship is the most important factor in improving compliance,[6]
As of 2003, US health care professionals more commonly used the term "adherence" to a regimen rather than "compliance", because it has been thought to reflect better the diverse reasons for patients not following treatment directions in part or in full.[7][8] Additionally, the term adherence includes the ability of the patient to take medications as prescribed by their physician with regards to the correct drug, dose, route, timing, and frequency.[9] It has been noted that compliance may only refer to passively following orders.[10]
The term concordance has been used in the United Kingdom to involve a patient in the treatment process to improve compliance, and refers to a 2003 NHS initiative. In this context, the patient is informed about their condition and treatment options,involved in the decision as to which course of action to take, and partially responsible for monitoring and reporting back to the team.[11]
As of 2005, the preferred terminology remained a matter of debate.[12] As of 2007, concordance has been used to refer specifically to patient adherence to a treatment regimen which the physician sets up collaboratively with the patient, to differentiate it from adherence to a physician-only prescribed treatment regimen.[13][14][15] Despite the ongoing debate, adherence has been the preferred term for the World Health Organization,[1] The American Pharmacists Association,[16] and the U.S. National Institutes of Health Adherence Research Network.[17]
Compliance factors
An estimated half of those for whom treatment regimens are prescribed do not follow them as directed.[1]
Until recently,{{when|date=December 2017}} this was termed "non-compliance", which some regarded as meaning that someone did not follow the treatment directions due to irrational behavior or willful ignoring of instructions.{{citation needed|date=December 2017}}
Health literacy
Cost and poor understanding of the directions for the treatment, referred to as 'health literacy' have been known to be major barriers to treatment adherence.[18][19][20]
There is robust evidence that education and physical health are correlated. Poor educational attainment is a key factor in the cycle of health inequalities.[21][22][23]
Educational qualifications help to determine an individual's position in the labour market, their level of income and therefore their access to resources.{{citation needed|date=December 2017}}
Literacy
In 1999 one fifth of UK adults, nearly seven million people, had problems with basic skills, especially functional literacy and functional numeracy, described as: "The ability to read, write and speak in English, and to use mathematics at a level necessary to function at work and in society in general." This made it impossible for them to effectively take medication, read labels, follow drug regimes, and find out more.[24]
In 2003, 20% of adults in the UK had a long-standing illness or disability and a national study for the UK Department of Health, found more than one-third of people with poor or very poor health had literary skills of Entry Level 3 or below.[25]
Low levels of literacy and numeracy were found to be associated with socio-economic deprivation.[25] Adults in more deprived areas, such as the North East of England, performed at a lower level than those in less deprived areas such as the South East. Local authority tenants and those in poor health were particularly likely to lack basic skills.[25]
A 2000 analysis of over 100 UK local education authority areas found educational attainment at 15–16 years of age to be strongly associated with coronary heart disease and subsequent infant mortality.[26]
A study of the relationship of literacy to asthma knowledge revealed that 31% of asthma patients with a reading level of a ten-year-old knew they needed to see the doctors, even when they were not having an asthma attack, compared to 90% with a high school graduate reading level.[27]
Treatment cost
In 2013 the US National Community Pharmacists Association sampled for one month 1,020 Americans above age 40 for with an ongoing prescription to take medication for a chronic condition and gave a grade C+ on adherence.[28]{{better source|date=December 2017}} In 2009, this contributed to an estimated cost of $290 billion annually.[29] In 2012, increase in patient medication cost share was found to be associated with low adherence to medication.[30]
The United States is among the countries with the highest prices of prescription drugs mainly attributed to the government's lack of negotiating lower prices with monopolies in the pharmaceutical industry especially with brand name drugs.[31] In order to manage medication costs, many US patients on long term therapies fail to fill their prescription, skip or reduce doses. According to a Kaiser Family Foundation survey in 2015, about three quarters (73%) of the public think drug prices are unreasonable and blame pharmaceutical companies for setting prices so high.[32] In the same report, half of the public reported that they are taking prescription drugs and a "quarter (25%) of those currently taking prescription medicine report they or a family member have not filled a prescription in the past 12 months due to cost, and 18 percent report cutting pills in half or skipping doses".[32] In a 2009 comparison to Canada, only 8% of adults reported to have skipped their doses or not filling their prescriptions due to the cost of their prescribed medications.[33]
Age
Both young and elderly status have been associated with non-adherence.
The elderly often have multiple health conditions, and around half of all NHS medicines are prescribed for people over retirement age, despite representing only about 20% of the UK population.[34][35] The recent National Service Framework on the care of older people highlighted the importance of taking and effectively managing medicines in this population. However, elderly individuals may face challenges, including multiple medications with frequent dosing, and potentially decreased dexterity or cognitive functioning. Patient knowledge is a concern that has been observed.
In 1999 Cline et al. identified several gaps in knowledge about medication in elderly patients discharged from hospital.[36] Despite receiving written and verbal information, 27% of older people discharged after heart failure were classed as non-adherent within 30 days. Half the patients surveyed could not recall the dose of their medication and nearly two-thirds did not know what time of day to take them. A 2001 study by Barat et al. evaluated the medical knowledge and factors of adherence in a population of 75-year-olds living at home. They found that 40% of elderly patients do not know the purpose of their regimen and only 20% knew the consequences of non-adherence.[37] Comprehension, polypharmacy, living arrangement, multiple doctors, and use of compliance aids was correlated with adherence. According to a conservative estimate 10% of all hospital admissions{{where|date=December 2017}} are through patients not managing their medication.{{citation needed|date=March 2013}}
In children with asthma self-management compliance is critical and co-morbidites have been noted to affect outcomes; in 2013 it has been suggested that electronic monitoring may help adherence.[38]
Social factors of treatment adherence have been studied in children and adolescent psychiatric disorders:
- Young people who felt supported by their family and doctor, and had good motivation, were more likely to comply.[39]
- Young adults may stop taking their medication in order to fit in with their friends, or because they lack insight of their illness.[39]
- Those who did not feel their condition to be a threat to their social well-being were eight times more likely to comply than those who perceived it as such a threat.[40][41]
- Non-adherence is often encountered among children and young adults; young males are relatively poor at adherence.[42][43]
Ethnicity
People of different ethnic backgrounds have unique adherence issues through literacy, physiology, culture or poverty.{{citation needed|date=March 2013}} There are few published studies on adherence in medicine taking in ethnic minority communities. Ethnicity and culture influence some health-determining behaviour, such as participation in screening programmes and attendance at follow-up appointments.[44][45]
Prieto et al emphasised the influence of ethnic and cultural factors on adherence. They pointed out that groups differ in their attitudes, values and beliefs about health and illness. This view could affect adherence, particularly with preventive treatments and medication for asymptomatic conditions. Additionally, some cultures fatalistically attribute their good or poor health to their god(s), and attach less importance to self-care than others.[46] also
Measures of adherence may need to be modified for different ethnic or cultural groups. In some cases, it may be advisable to assess patients from a cultural perspective before making decisions about their individual treatment.{{citation needed|date=December 2017}}
Prescription fill rates
Not all patients will fill the prescription at a pharmacy. In a 2010 U.S. study, 20–30% of prescriptions were never filled at the pharmacy.[47][48] Reasons people do not fill prescriptions include the cost of the medication,[49][16] A US nationwide survey of 1,010 adults in 2001 found that 22% chose not to fill prescriptions because of the price, which is similar to the 20–30% overall rate of unfilled prescriptions.[49] Other factors are doubting the need for medication, or preference for self-care measures other than medication.[50][51] Convenience, side effects and lack of demonstrated benefit are also factors.{{citation needed|date=December 2017}}
Medication Possession Ratio
Prescription medical claims records can be used to estimate medication adherence based on fill rate. Patients can be routinely defined as being 'Adherent Patients' if the amount of medication furnished is at least 80% based on days' supply of medication divided by the number of days patient should be consuming the medication. This percentage is called the medication possession ratio (MPR). 2013 work has suggested that a medication possession ratio of 90% or above may be a better threshold for deeming consumption as 'Adherent'.[52]
Two forms of MPR can be calculated, fixed and variable.[53] Calculating either is relatively straightforward, for Variable MPR (VMPR) it is calculated as the number of days' supply divided by the number of elapsed days including the last prescription.
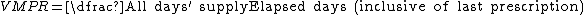
For the Fixed MPR (FMPR) the calculation is similar but the denominator is the number of days in a year whilst the numerator is constrained to be the number of days' supply within the year that the patient has been prescribed.
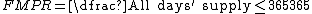
For medication in tablet form it is relatively straightforward to calculate the number of days' supply based on a prescription. Some medications are less straightforward though because a prescription of a given number of doses may have a variable number of days' supply because the number of doses to be taken per day varies, for example with preventative corticosteroid inhalers prescribed for asthma where the number of inhalations to be taken daily may vary between individuals based on the severity of the disease.{{citation needed|date=December 2017}}
Course completion
Once started, patients seldom follow treatment regimens as directed, and seldom complete the course of treatment.[16][7] In respect of hypertension, 50% of patients completely drop out of care within a year of diagnosis.[54] Persistence with first-line single antihypertensive drugs is extremely low during the first year of treatment.[55] As far as lipid-lowering treatment is concerned, only one third of patients are compliant with at least 90% of their treatment.[56] Intensification of patient care interventions (e.g. electronic reminders, pharmacist-led interventions, healthcare professional education of patients) improves patient adherence rates to lipid-lowering medicines, as well as total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol levels.[57]
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated in 2003 that only 50% of people complete long-term therapy for chronic illnesses as they were prescribed, which puts patient health at risk.[58] For example, in 2002 statin compliance dropped to between 25–40% after two years of treatment, with patients taking statins for what they perceive to be preventative reasons being unusually poor compliers.[59]
A wide variety of packaging approaches have been proposed to help patients complete prescribed treatments. These approaches include formats that increase the ease of remembering the dosage regimen as well as different labels for increasing patient understanding of directions.[60][61] For example, medications are sometimes packed with reminder systems for the day and/or time of the week to take the medicine.[61] Some evidence shows that reminder packaging may improve clinical outcomes such as blood pressure.[61]
A not-for-profit organisation called the Healthcare Compliance Packaging Council of Europe] (HCPC-Europe) was set up{{when|date=December 2017}} between the pharmaceutical industry, the packaging industry with representatives of European patients organisations. The mission of HCPC-Europe is to assist and to educate the healthcare sector in the improvement of patient compliance through the use of packaging solutions. A variety of packaging solutions have been developed by this collaboration.[62]
World Health Organization Barriers to Adherence
The World Health Organization (WHO) groups barriers to medication adherence into five categories; health care team and system-related factors, social and economic factors, condition-related factors, therapy-related factors, and patient-related factors. Common barriers include:[63]
| Barrier | Category |
|---|---|
| Poor Patient-provider Relationship | Health Care Team and System |
| Inadequate Access to Health Services | Health Care Team and System |
| High Medication Cost | Social and Economic |
| Cultural Beliefs | Social and Economic |
| Level of Symptom Severity | Condition |
| Availability of Effective Treatments | Condition |
| Immediacy of Beneficial Effects | Therapy |
| Side Effects | Therapy |
| Stigma Surrounding Disease | Patient |
| Inadequate Knowledge of Treatment | Patient |
Improving compliance rates
Role of health care providers
Health care providers play a great role in improving adherence issues. Providers can improve patient interactions through motivational interviewing and active listening.[64] Health care providers should work with patients to devise a plan that is meaningful for the patient's needs. A relationship that offers trust, cooperation, and mutual responsibility can greatly improve the connection between provider and patient for a positive impact.[10]
Technology
In 2012 it was predicted that as telemedicine technology improves, physicians will have better capabilities to remotely monitor patients in real-time and to communicate recommendations and medication adjustments using personal mobile devices, such as smartphones, rather than waiting until the next office visit.[65]
Medication Event Monitoring Systems, as in the form of smart medicine bottle tops, smart pharmacy vials or smart blister packages as used in clinical trials and other applications where exact compliance data are required, work without any patient input, and record the time and date the bottle or vial was accessed, or the medication removed from a blister package. The data can be read via proprietary readers, or NFC enabled devices, such as smartphones or tablets. A 2009 study stated that such devices can help improve adherence.[66]
Health and disease management
A WHO study estimates that only 50% of patients suffering from chronic diseases in developed countries follow treatment recommendations.[1] The
Asthma non-compliance (28–70% worldwide) increases the risk of severe asthma attacks requiring preventable ER visits and hospitalisations; compliance issues with asthma can be caused by a variety of reasons including: difficult inhaler use, side effects of medications, and cost of the treatment.[67]
Cancer
200,000 new cases of cancer are diagnosed each year in the UK. One in three adults in the UK will develop cancer that can be life-threatening, and 120,000 people will be killed by their cancer each year. This accounts for 25% of all deaths in the UK. However while 90% of cancer pain can be effectively treated, only 40% of patients adhere to their medicines due to poor understanding.{{citation needed|date=December 2012}}
The reasons for non-adherence have been given by patients as follows:
- The poor quality of information available to them about their treatment{{citation needed|date=December 2012}}
- A lack of knowledge as to how to raise concerns whilst on medication{{citation needed|date=December 2012}}
- Concerns about unwanted effects{{citation needed|date=December 2012}}
- Issues about remembering to take medication{{citation needed|date=December 2012}}
Partridge et al (2002) identified evidence to show that adherence rates in cancer treatment are variable, and sometimes surprisingly poor. The following table is a summary of their findings:[68]
| Type of Cancer | Measure of non-Adherence | Definition of non-Adherence | Rate of Non-Adherence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Haematological malignancies | Serum levels of drug metabolites | Serum levels below expected threshold | 83% |
| Breast cancer | Self-report | Taking less than 90% of prescribed medicine | 47% |
| Leukemia or non Hodgkin's lymphoma | Level of drug metabolite in urine | Level lower than expected | 33% |
| Leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, non Hodgkin's | Self-report and parent report | More than one missed dose per month | 35% |
| Lymphoma, other malignancies | Serum bioassay | Not described | |
| Hodgkin's disease, acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) | Biological markers | Level lower than expected | 50% |
| ALL | Level of drug metabolite in urine | Level lower than expected | 42% |
| ALL | Level of drug metabolites in blood | Level lower than expected | 10% |
| ALL | Level of drug metabolites in blood | Level lower than expected | 2% |
- Medication event monitoring system - a medication dispenser containing a microchip that records when the container is opened and from Partridge et al (2002)
In 1998, trials evaluating Tamoxifen as a preventative agent have shown dropout rates of around one-third:
- 36% in the Royal Marsden Tamoxifen Chemoprevention Study of 1998[69]
- 29% in the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project of 1998[70]
In March 1999, the "Adherence in the International Breast Cancer Intervention Study" evaluating the effect of a daily dose of Tamoxifen for five years in at-risk women aged 35–70 years was[71]
- 90% after one year
- 83% after two years
- 74% after four years
Diabetes
Patients with diabetes are at high risk of developing coronary heart disease and usually have related conditions that make their treatment regimens even more complex, such as hypertension, obesity and depression[72] which are also characterised by poor rates of adherence.[73]
- Diabetes non-compliance is 98% in US{{citation needed|date=December 2017}} and the principal cause of complications related to diabetes including nerve damage and kidney failure.{{citation needed|date=December 2017}}
- Among patients with Type 2 Diabetes, adherence was found in less than one third of those prescribed sulphonylureas and/or metformin. Patients taking both drugs achieve only 13% adherence.[74]
Hypertension
- Hypertension non-compliance (93% in US, 70% in UK){{citation needed|date=December 2017}} is the main cause of uncontrolled hypertension-associated heart attack and stroke.
- In 1975, only about 50% took at least 80% of their prescribed anti-hypertensive medications.[75]
As a result of poor compliance,{{citation needed|date=February 2017}} 75% of patients with a diagnosis of hypertension do not achieve optimum blood-pressure control.{{citation needed|date=February 2017}}
Mental illness
A 2003 review found that 41–59% of mentally ill patients took their medication infrequently or not at all.[76]
A 2006 review investigated the effects of compliance therapy for schizophrenia: and found no clear evidence to suggest that compliance therapy was beneficial for people with schizophrenia and related syndromes.[77]
See also
- Drug withdrawal
References
2. ^{{cite web |publisher=National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence |date=3 March 2008 |title=Medicines concordance (involving patients in decisions about prescribed medicines) |url=http://guidance.nice.org.uk/page.aspx?o=267072 |access-date=2011-12-31 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070427195630/http://guidance.nice.org.uk/page.aspx?o=267072 |archive-date=2007-04-27 |dead-url=yes |df= }}
3. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Elliott RA, Marriott JL |title=Standardised assessment of patients' capacity to manage medications: a systematic review of published instruments |journal=BMC Geriatr |volume=9|pages=27 |year=2009 |pmid=19594913 |pmc=2719637 |doi=10.1186/1471-2318-9-27}}
4. ^{{cite journal | vauthors = Berhe DF, Taxis K, Haaijer-Ruskamp FM, Mulugeta A, Mengistu YT, Burgerhof JG, Mol PG | year = 2017 | title = Impact of adverse drug events and treatment satisfaction on patient adherence with antihypertensive medication – a study in ambulatory patients | url = | journal = Br J Clin Pharmacol | volume = 83| issue = 9| pages = 2107–2117 | doi = 10.1111/bcp.13312 | pmid = 28429533 | pmc = 5555859 }}
5. ^1 {{Cite journal|last=Nieuwlaat|first=Robby|last2=Wilczynski|first2=Nancy|last3=Navarro|first3=Tamara|last4=Hobson|first4=Nicholas|last5=Jeffery|first5=Rebecca|last6=Keepanasseril|first6=Arun|last7=Agoritsas|first7=Thomas|last8=Mistry|first8=Niraj|last9=Iorio|first9=Alfonso|date=2014-11-20|title=Interventions for enhancing medication adherence|journal=The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews|issue=11|pages=CD000011|doi=10.1002/14651858.CD000011.pub4|issn=1469-493X|pmid=25412402}}
6. ^{{cite book |author=World Health Organization |title=Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action |publisher=World Health Organisation |location=Geneva |year=2003 |isbn=978-92-4-154599-0 |url=http://www.who.int/chp/knowledge/publications/adherence_full_report.pdf}}
7. ^1 2 {{cite journal |author=Ngoh LN |title=Health literacy: a barrier to pharmacist-patient communication and medication adherence |journal=J Am Pharm Assoc (2003) |volume=49 |issue=5 |pages=e132–46; quiz e147–9 |year=2009 |pmid=19748861 |doi=10.1331/JAPhA.2009.07075}}
8. ^{{cite journal |author=Tilson HH |title=Adherence or compliance? Changes in terminology |journal=Annals of Pharmacotherapy |year=2004 |volume=38 |issue=1 |pages=161–2 |pmid=14742813 |doi=10.1345/aph.1D207}}
9. ^Viswanathan M, Golin CE, Jones CD, Ashok M, Blalock S, Wines RCM, Coker-Schwimmer EJL, Grodensky CA, Rosen DL, Yuen A, Sista P, Lohr KN. Medication Adherence Interventions: Comparative Effectiveness. Closing the Quality Gap: Revisiting the State of the Science. Evidence Report No. 208. Prepared by RTI International–University of North Carolina Evidence-based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-2007-10056-I. AHRQ Publication No. 12-E010-EF. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. September 2012.
10. ^1 {{cite journal |author1=Rifaat Nizar |author2=Abdel-Hady Elham |author3=Hasan Ali A | year = 2013| title = The golden factor in adherence to inhaled corticosteroid in asthma patients | url = | journal = Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis | volume = 62 | issue = 3| pages = 371–376 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejcdt.2013.07.010}}
11. ^{{cite journal |title=Not to be taken as directed - Putting concordance for taking medicines into practice |journal=BMJ |volume=326 |issue=7385 |pages=348–9 |date=15 February 2003 |author=Marinker and Shaw |doi=10.1136/bmj.326.7385.348}}
12. ^{{cite journal |doi=10.1056/NEJMra050100 |vauthors=Osterberg L, Blaschke T |title=Adherence to Medication |journal=N Engl J Med |year=2005 |volume=353 |issue=5 |pages=487–97 |pmid=16079372}}
13. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Bell JS, Airaksinen MS, Lyles A, Chen TF, Aslani P |title=Concordance is not synonymous with compliance or adherence |journal=Br J Clin Pharmacol |year=2007 |volume=64 |issue=5 |pages=710–1 |pmid=17875196 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02971_1.x |pmc=2203263}}
14. ^{{cite journal |author=Aronson JK |title=Compliance, concordance, adherence |journal=Br J Clin Pharmacol |year=2007 |volume=63 |issue=4 |pages=383–4 |pmid=17378797 |pmc=2203247 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02893.x}}
15. ^{{cite web |author=US NIH Office of Behavior and Social Sciences Research |url=http://obssr.od.nih.gov/pdf/Workshop_final_report.pdf |title=Framework for adherence research and translation: a blueprint for the next ten years |year=2008 |access-date=2010-05-12 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100528015152/http://obssr.od.nih.gov/pdf/Workshop_final_report.pdf |archive-date=2010-05-28 |dead-url=yes |df= }}
16. ^1 2 3 {{cite web |work=APA Highlights Newsletter |title=Enhancing Patient Adherence: Proceedings of the Pinnacle Roundtable Discussion |date=October 2004 |volume=7 |issue=4 |url=http://www.pharmacist.com/AM/Template.cfm?Section=Home2&TEMPLATE=/CM/ContentDisplay.cfm&CONTENTID=11174 |access-date=2018-10-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110615092834/http://www.pharmacist.com/AM/Template.cfm?Section=Home2&TEMPLATE=%2FCM%2FContentDisplay.cfm&CONTENTID=11174 |archive-date=2011-06-15 |dead-url=yes |df= }}
17. ^{{cite web |author=Office of Behavior and Social Sciences Research |publisher=U.S. National Institutes of Health |title=Adherence Research Network |url=http://obssr.od.nih.gov/scientific_areas/health_behaviour/adherence/adherenceresearchnetwork.aspx |accessdate=12 May 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100502064804/http://obssr.od.nih.gov/scientific_areas/health_behaviour/adherence/adherenceresearchnetwork.aspx |archive-date=2010-05-02 |dead-url=yes |df= }}
18. ^{{cite web|title=Enhancing Patient Adherence: Proceedings of the Pinnacle Roundtable Discussion|work=APA Highlights Newsletter|date=October 2004|url=http://www.pharmacist.com/AM/Template.cfm?Section=Home2&TEMPLATE=/CM/ContentDisplay.cfm&CONTENTID=11174|access-date=2018-10-02|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110615092834/http://www.pharmacist.com/AM/Template.cfm?Section=Home2&TEMPLATE=%2FCM%2FContentDisplay.cfm&CONTENTID=11174|archive-date=2011-06-15|dead-url=yes|df=}}
19. ^{{cite journal |author=Ngoh LN |year=2003 |title=Health literacy: a barrier to pharmacist-patient communication and medication adherence |journal=J Am Pharm Assoc |volume=49 |issue=5 |pages=e132–46; quiz e147–9 |doi=10.1331/JAPhA.2009.07075 |pmid=19748861}}
20. ^{{cite journal|vauthors=Elliott RA, Marriott JL |year=2009 |title=Standardised assessment of patients' capacity to manage medications: a systematic review of published instruments |journal=BMC Geriatr |volume=9 |page=27 |doi=10.1186/1471-2318-9-27 |pmc=2719637 |pmid=19594913}}
21. ^{{cite report |author=Donald Acheson |year=1998 |title=Independent inquiry into inequalities in health}}
22. ^{{cite report |publisher=HM Government |year=2002 |title=Tackling health inequalities}}
23. ^{{cite journal|vauthors=Park DC, Hertzog C, Leventhal H, Morrell RW, Leventhal E, Birchmore D, Martin M, Bennett J |year=1999 |title=Medication adherence in rheumatoid arthritis patients: older is wiser |journal=Journal of the American Geriatrics Society |volume=47 |issue=2 |pages=172–183|doi=10.1111/j.1532-5415.1999.tb04575.x }}
24. ^Moser Report Summary educationengland.org, 14 pages (1999)retrieved 28. 12. 2017
25. ^1 2 {{cite web|vauthors=Williams J, Clemens S, Oleinikova K, Tarvin K |year=2003 |title=The skills for life survey. A national needs and impact survey of literacy, numeracy and ICT skills |location=London |publisher=Department for Education and Skills |url=https://www.education.gov.uk/publications/RSG/BasicSkills/Page3/RB490}}
26. ^{{Cite journal |publisher=Department of Health and Treasury |year=2000 |title=Cross-cutting government review, Tackling health inequalities |postscript={{inconsistent citations}}}}
27. ^{{Cite journal|date=1998-10-01|title=Inadequate Literacy Is a Barrier to Asthma Knowledge and Self-Care|journal=Chest|language=en|volume=114|issue=4|pages=1008–1015|doi=10.1378/chest.114.4.1008|issn=0012-3692|last1=Williams|first1=Mark V.|last2=Baker|first2=David W.|last3=Honig|first3=Eric G.|last4=Lee|first4=Theodore M.|last5=Nowlan|first5=Adam}}
28. ^New Report Card on Medication Use Gives Americans a C+ Pharmacy Times. JUNE 25, 2013
29. ^Thinking Outside the Pillbox: A System-wide Approach to Improving Patient Adherence for Chronic Disease." NEHI. 2009
30. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Eaddy MT, Cook CL, O'Day K, Burch SP, Cantrell CR | year = 2012 | title = How Patient Cost-Sharing Trends Affect Adherence and Outcomes: A Literature Review | url = | journal = Pharmacy and Therapeutics | volume = 37 | issue = 1| pages = 45–55}}
31. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Kesselheim AS, Avorn J, Sarpatwari A | year = 2016 | title = The High Cost of Prescription Drugs in the United States Origins and Prospects for Reform | url = | journal = JAMA | volume = 316 | issue = 8| pages = 858–871 | doi = 10.1001/jama.2016.11237| pmid = 27552619 }}
32. ^1 Kaiser Family Foundation: Poll Finds Nearly Three Quarters of Americans Say Prescription Drug Costs Are Unreasonable, and Most Blame Drug Makers Rather Than Insurers for the Problem
33. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Kennedy J, Morgan S | year = 2009| title = Cost-related prescription nonadherence in the united states and Canada: A system-level comparison using the 2007 international health policy survey in seven countries | url = | journal = Clinical Therapeutics | volume = 31 | issue = 1| pages = 213–219 | doi = 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.01.006}}
34. ^UK Department of Health (2001): National Service Framework for Older People, London.
35. ^UK Office of Health Economics (2000): Compendium of Health Statistics, 12th Edition, London.
36. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Cline CM, Bjorck-Linne AK, Israelsson BY, Willenheimer RB, Erhardt LR |year=1999 |title=Non-adherence and knowledge of prescribed medication in elderly patients with heart failure |journal=European Journal of Heart Failure |volume=1 |pages=145–149 |doi=10.1016/S1388-9842(99)00014-8 |pmid=10937924 |issue=2}}
37. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Barat I, Andreasen F, Damsgaard EM |year=2001 |title=Drug therapy in the elderly: what doctors believe and patients actually do |journal=British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology |volume=51 |issue=6 |pages=615–622 |doi=10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01401.x |pmid=11422022 |pmc=2014493}}
38. ^{{Cite journal|title = Exploring the impact of elevated depressive symptoms on the ability of a tailored asthma intervention to improve medication adherence among urban adolescents with asthma.|date = Nov 2013|journal = Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology |doi = 10.1186/1710-1492-9-45|pmid = 24479403 |volume=9 |issue = 1|pages=45 |pmc=3832221 |vauthors=Guglani L, Havstad SL, Ownby DR, Saltzgaber J, Johnson DA, Johnson CC, Joseph CL}}
39. ^1 {{Cite journal|title = An Approach to Maximizing Treatment Adherence of Children and Adolescents with Psychotic Disorders and Major Mood Disorders|date = Nov 2005|journal = Canadian Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Review |doi = | pmc=2553227 |pmid=19030524 |volume=14 |issue = 4|pages=106–13 |vauthors=Gearing RE, Mian IA}}
40. ^{{cite journal|vauthors=Mitchell WG, Scheier LM, Baker SA |year=2000 |title=Adherence to treatment in children with epilepsy: who follows 'doctor's orders'? |journal=Epilepsia |volume=41 |issue=12 |pages=1616–25|doi=10.1111/j.1499-1654.2000.001616.x|pmid=11114221}}
41. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Otero S, Hodes M |year=2000 |title=Maternal expressed emotion and treatment compliance of children with epilepsy |journal=Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology |volume=42 |issue=9 |pages=604–8 |doi=10.1111/j.1469-8749.2000.tb00365.x |pmid=11034453}}
42. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Dolder CR, Lacro JP, Dunn LB, Jeste DV |year=2002 |title=Antipsychotic medication adherence: Is there a difference between typical and atypical agents? |journal=American Journal of Psychiatry |volume=159 |pages=103–108 |doi=10.1176/appi.ajp.159.1.103 |pmid=11772697 |issue=1}}
43. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Nosé M, Barbui C, Gray R, Tansella M |year=2003 |title=Clinical interventions for treatment non-adherence in psychosis: meta-analysis |journal=British Journal of Psychiatry |volume=183 |pages=197–206 |doi=10.1192/bjp.183.3.197 |pmid=12948991 |issue=3}}
44. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Courtenay WH, McCreary DR, Merighi JR |year=2002 |title=Gender and ethnic differences in health beliefs and behaviours |journal=Journal of Health Psychology |volume=7 |issue=3 |pages=219–231 |doi=10.1177/1359105302007003216 |pmid=22114246}}
45. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Meyerowitz BE, Richardson J, Hudson S, Leedham B |year=1998 |title=Ethnicity and cancer outcomes: behavioural and psychosocial considerations |journal=Psychological Bulletin |volume=123 |issue=1 |pages=47–70 |doi=10.1037/0033-2909.123.1.47 |pmid=9461853}}
46. ^{{cite journal |year=1997 |title=Multicultural issues in organ transplantation: the influence of patients' cultural perspectives on adherence with treatment |journal=Clinical Transplantation |volume=11 |issue=6 |pages=529–535 |vauthors=Prieto LR, Miller DS, Gayowski T, Marino IR |pmid=9408680}}
47. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Fischer MA, Stedman MR, Lii J |title=Primary medication non-adherence: analysis of 195,930 electronic prescriptions |journal=J Gen Intern Med |volume=25 |issue=4 |pages=284–90 |date=April 2010 |pmid=20131023 |doi=10.1007/s11606-010-1253-9 |pmc=2842539 |display-authors=etal}}
48. ^{{cite news |author=Norton M |publisher=Reuters Health |title=Many patients may not fill their prescriptions |year=2010 |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE61G3QX20100217 |accessdate=May 12, 2010}}
49. ^1 2 {{cite news |publisher=Harris Interactive |title=Out-of-pocket costs may be a substantial barrier to prescription drug compliance |url=http://www.harrisinteractive.com/news/newsletters/healthnews/HI_HealthCareNews2001Vol1_iss32.pdf |accessdate=May 12, 2010}}
50. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Shah NR, Hirsch AG, Zacker C, Taylor S, Wood GC, Stewart WF |title=Factors associated with first-fill adherence rates for diabetic medications: a cohort study |journal=J Gen Intern Med |volume=24 |issue=2 |pages=233–7 |date=February 2009 |pmid=19093157 |pmc=2629003 |doi=10.1007/s11606-008-0870-z}}
51. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Shah NR, Hirsch AG, Zacker C |title=Predictors of first-fill adherence for patients with hypertension |journal=Am. J. Hypertens. |volume=22 |issue=4 |pages=392–6 |date=April 2009 |pmid=19180061 |pmc=2693322 |doi=10.1038/ajh.2008.367 |display-authors=etal}}
52. ^{{cite journal | vauthors = Watanabe JH, Bounthavong M, Chen T | date = Mar 2013 | title = Revisiting the medication possession ratio threshold for adherence in lipid management | url = | journal = Curr Med Res Opin | volume = 29 | issue = 3| pages = 175–80 | doi = 10.1185/03007995.2013.766164 | pmid = 23320610 }}
53. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Kozma CM, Dickson M, Phillips AL, Meletiche D | year = 2013 | title = Medication possession ratio: implications of using fixed and variable observation periods in assessing adherence with disease-modifying drugs in patients with multiple sclerosis | url = | journal = Patient Prefer Adherence | volume = 7 | issue = | pages = 509–516 | doi = 10.2147/PPA.S40736| pmid = 23807840 | pmc = 3685450 }}
54. ^{{cite journal |author=Mapes RE |year=1977 |title=Physicians' drug innovation and relinquishment |journal=Social Science & Medicine |volume=11 |pages=619–24 |doi=10.1016/0037-7856(77)90044-0 |issue=11–13}}
55. ^{{cite journal |vauthors = Mazzaglia G, Mantovani LG, Sturkenboom M, Filippi A, Trifiro G, Cricelli C, Brignoli O, Caputi AP |title=Patterns of persistence with antihypertensive medications in newly diagnosed hypertensive patients in Italy: a retrospective cohort study in primary care|journal=Hypertens|volume=23 |issue=11 |pages=2093–100|date= November 2005 |pmid= |doi=10.1097/01.hjh.0000186832.41125.8a}}
56. ^{{cite journal |author=Sung JC |date=Oct 1998 |title=Factors affecting patient compliance with antihyperlipidemic medications in an HMO population |journal=Am J Manag Care |volume=4 |issue=10 |pages=1421–30 |pmid=10338735|display-authors=etal}}
57. ^{{Cite journal|last=van Driel|first=Mieke L.|last2=Morledge|first2=Michael D.|last3=Ulep|first3=Robin|last4=Shaffer|first4=Johnathon P.|last5=Davies|first5=Philippa|last6=Deichmann|first6=Richard|date=2016-12-21|title=Interventions to improve adherence to lipid-lowering medication|journal=The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews|volume=12|pages=CD004371|doi=10.1002/14651858.CD004371.pub4|issn=1469-493X|pmid=28000212|pmc=4163627}}
58. ^{{cite book |author=World Health Organization |year=2003 |title=Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action |location=Geneva |publisher=World Health Organisation |isbn=978-92-4-154599-0 |url=http://www.who.int/chp/knowledge/publications/adherence_full_report.pdf}}
59. ^{{cite journal |author=Jackevicius CA |year=2002 |title=Adherence with statin therapy in elderly patients with and without acute coronary syndromes |journal=JAMA |volume=288 |issue=4 |pages=462–467 |doi=10.1001/jama.288.4.462 |pmid=12132976 |display-authors=etal}}
60. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Shrank W, Avorn J, Rolon C, Shekelle P |title=Effect of content and format of prescription drug labels on readability, understanding, and medication use: a systematic review |journal=Annals of Pharmacotherapy |volume=41 |issue=5 |pages=783–801 |date=May 2007 |pmid=17426075 |doi=10.1345/aph.1H582}}
61. ^1 2 {{Cite journal|last=Mahtani|first=Kamal R.|last2=Heneghan|first2=Carl J.|last3=Glasziou|first3=Paul P.|last4=Perera| first4=Rafael|date=2011-09-07|title=Reminder packaging for improving adherence to self-administered long-term medications| journal=The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews| issue=9| pages=CD005025| doi=10.1002/14651858.CD005025.pub3| issn=1469-493X|pmid=21901694}}
62. ^[https://web.archive.org/web/20081019100628/http://www.hcpc-europe.org/cms/front_content.php?idcat=94 Healthcare Compliance Packaging Council of Europe] www.hcpc-europe.org
63. ^{{Cite web|url=http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4883e/7.2.html|title=Adherence to Long-Term Therapies - Evidence for Action: Section II - Improving adherence rates: guidance for countries: Chapter V - Towards the solution: 1. Five interacting dimensions affect adherence|website=apps.who.int|access-date=2018-03-23}}
64. ^Stefanacci, Richard G., DO, MGH, MBA, AGSF, CMD, and Scott Guerin, PhD. "Why Medication Adherence Matters To Patients, Payers, Providers." Managed Care Jan. 2013. Accessed Nov 2, 2014
65. ^Marisa Torrieri, "Patient compliance: technology tools for physicians" Physicians Practice, September 2012.
66. ^{{cite journal|last=Santschi|first=V|author2=Chiolero, A |author3=Burnier, M |title=Electronic monitors of drug adherence: tools to make rational therapeutic decisions.|journal=Journal of Hypertension|date=Nov 2009|volume=27|issue=11|pages=2294–5; author reply 2295|pmid=20724871|doi=10.1097/hjh.0b013e328332a501}}
67. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Bender BG, Bender SE | year = 2005 | title = Patient-identified barriers to asthma treatment adherence: responses to interviews, focus groups, and questionnaires | url = | journal = Immunol Allergy Clin North Am | volume = 25 | issue = 1| pages = 107–130 | doi=10.1016/j.iac.2004.09.005| pmid = 15579367 }}
68. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Partridge AH, Avorn J, Wang PS, Winer EP |year=2002 |title=Adherence to therapy with oral antineoplastic agents |journal=Journal of the National Cancer Institute |volume=94 |issue=9 |pages=652–61 |doi=10.1093/jnci/94.9.652 |pmid=11983753}}
69. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Powels T, Eeles R, Ashley S |year=1998 |title=Interim analysis of the incidence of breast cancer in the Royal Marsden Hospital Tamoxifen randomized chemoprevention trial |journal=Lancet |volume=352 |pages=98–101 |pmid=9672274 |issue=9122 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(98)85012-5| display-authors=etal}}
70. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL |year=1998 |title=Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Projects P-1 Study |journal=Journal of the National Cancer Institute |volume=90 |pages=1371–88 |doi=10.1093/jnci/90.18.1371 |pmid=9747868 |issue=18 |display-authors=etal}}
71. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Cuzick J, Edwards R |year=1999 |title=Drop-outs in Tamoxifen prevention trials |journal=Lancet |volume=353 |page=930 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(05)75043-1 |pmid=10094016 |issue=9156}}
72. ^{{cite journal|vauthors=Lustman PJ, Griffiths LS, Clouse RE |year=1997 |title=Depression in adults with diabetes |journal=Seminars in Clinical Neuropsychiatry |volume=2 |pages=15–23|pmid=10320439|issue=1|doi=10.1053/SCNP00200015|doi-broken-date=2019-02-17 }}
73. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Ciechanowski PS, Katon WJ, Russo JE |year=2000 |title=Depression and diabetes: impact of depression symptoms pn adherence, function, and costs |journal=Archives of Internal Medicine |volume=27 |pages=3278–85 |doi=10.1001/archinte.160.21.3278 |issue=21}}
74. ^{{cite journal|vauthors=Donnan PT, MacDonald TM, Morris AD |year=2002 |title=Adherence to prescribed oral hypoglyacaemic medication in a population of patients with Type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study |journal=Diabetic Medicine |volume=19 |issue=4 |pages=279–84|doi=10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00689.x|pmid=11942998}}
75. ^{{cite journal |author=David l |year=1975 |title=Randomised clinical trial of strategies for improving medication compliance in primary hypertension |journal=Lancet |volume=305 |issue=7918 |pages=1205–7 |pmid=48832 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(75)92192-3 |display-authors=etal}}
76. ^{{cite journal|vauthors=Dolder CR, Lacro JP, Leckband S, Jeste DV |year=2003 |title=Interventions to improve antipsychotic medication adherence: Review of recent literature |journal=Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology |volume=23 |issue=4 |pages=389–399|doi=10.1097/01.jcp.0000085413.08426.41|pmid=12920416}}
77. ^{{cite journal|last1=McIntosh| first1=A| last2=Conlon|first2=L| first3=S| last3=Lawrie|title=Compliance therapy for schizophrenia|journal=Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews|date=2006|volume=3| issue=3|url=http://www.cochrane.org/CD003442/SCHIZ_compliance-therapy-for-schizophrenia|pages=CD003442.pub2 |doi=10.1002/14651858.CD003442.pub2| pmid=16856009}}
External links
- Adherence to long-term therapies, a report from the World Health Organization
- Technology report on NFC enabled smart medication packages
- East Hampshire District Council election, 1999
- East Hampshire District Council election, 2003
- East Hampshire District Council election, 2007
- East Hampshire District Council election, 2011
- East Hampshire District Council election, 2015
- East Hampton Center for Contemporary Art
- Easthampton, Herefordshire
- East Hampton High
- East Hampton (LIRR station)
- Easthampton, Mass.
- East Hampton station (LIRR)
- East Hampton UFSD
- Eastham Railroad Station
- Eastham, Richard
- East Hangtou Station
- East Hannibal, Illinois
- East Hants (district municipality), Nova Scotia
- East Hants Municipal District
- East Hants Municipal District, Nova Scotia
- East Hants Municipality
- East Hants Municipality, Nova Scotia
- East Hants, Nova Scotia
- East Hants, Nova Scotia (district municipality)
- East Hants, Nova Scotia (municipal district)
- East Hararghe