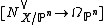- Examples Schemes Example 1 Deligne–Mumford stacks
- Symmetric obstruction theory
- Notes
- References
- See also
In algebraic geometry, given a Deligne–Mumford stack X, a perfect obstruction theory for X consists of:
- a perfect two-term complex
 in the derived category
in the derived category  of quasi-coherent étale sheaves on X, and
of quasi-coherent étale sheaves on X, and - a morphism
 , where
, where  is the cotangent complex of X, that induces an isomorphism on
is the cotangent complex of X, that induces an isomorphism on  and an epimorphism on
and an epimorphism on  .
.
The notion was introduced by {{harv|Behrend–Fantechi|1997}} for an application to the intersection theory on moduli stacks; in particular, to define a virtual fundamental class.
Examples
Schemes
Consider a regular embedding  fitting into a cartesian square
fitting into a cartesian square
where  are smooth. Then, the complex
are smooth. Then, the complex
(in degrees
)
forms a perfect obstruction theory for X.[1] The map comes from the composition
This is a perfect obstruction theory because the complex comes equipped with a map to  coming from the maps
coming from the maps 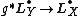 and
and  . Note that the associated virtual fundamental class is
. Note that the associated virtual fundamental class is 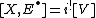
Example 1
Consider a smooth projective variety 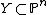 . If we set
. If we set 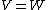 , then the perfect obstruction theory in
, then the perfect obstruction theory in 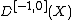 is
is
and the associated virtual fundamental class is
In particular, if  is a smooth local complete intersection then the perfect obstruction theory is the cotangent complex (which is the same as the truncated cotangent complex).
is a smooth local complete intersection then the perfect obstruction theory is the cotangent complex (which is the same as the truncated cotangent complex).
Deligne–Mumford stacks
The previous construction works too with Deligne–Mumford stacks.
Symmetric obstruction theory
By definition, a symmetric obstruction theory is a perfect obstruction theory together with nondegenerate symmetric bilinear form.
Example: Let f be a regular function on a smooth variety (or stack). Then the set of critical points of f carries a symmetric obstruction theory in a canonical way.
Example: Let M be a complex symplectic manifold. Then the (scheme-theoretic) intersection of Lagrangian submanifolds of M carries a canonical symmetric obstruction theory.
Notes
References
- {{Cite arXiv|last=Behrend|first=K.|eprint=math/0507523v2|title=Donaldson–Thomas invariants via microlocal geometry|year=2005}}
- {{Cite journal|last=Behrend|first=K.|last2=Fantechi|first2=B.|date=1997-03-01|title=The intrinsic normal cone|journal=Inventiones Mathematicae|language=en|volume=128|issue=1|pages=45–88|doi=10.1007/s002220050136|issn=0020-9910|bibcode=1997InMat.128...45B|arxiv=alg-geom/9601010}}
- {{Cite web|url=https://mathoverflow.net/questions/206804/understanding-the-obstruction-cone-of-a-symmetric-obstruction-theory/211932#211932|title=Understanding the obstruction cone of a symmetric obstruction theory|last=Oesinghaus|first=Jakob |website=MathOverflow|date=2015-07-20|access-date=2017-07-19}}
See also
- Behrend function
- Gromov–Witten invariant
- Emiliano Tellechea
- Emiliano Tortolano
- Emiliano Té
- Emiliano Veliaj
- Emiliano Vladimir Ramos Hernandez
- Emilianow
- Emilianow, Gostynin County
- Emilianow, Greater Poland Voivodeship
- Emilianowka
- Emilianow, Lowicz County
- Emilianow, Lublin Voivodeship
- Emilianowo
- Emilianowo (disambiguation)
- Emilianowo, Gmina Ilawa
- Emilianowo, Gmina Iława
- Emilianowo, Gmina Susz
- Emilianowo, Greater Poland Voivodeship
- Emilianowo, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship
- Emilianowo, West Pomeranian Voivodeship
- Emilianow-Posrednik
- Emilianow, Sieradz County
- Emilianow, Sochaczew County
- Emilianow, Sokolow County
- Emilianow, Tomaszow Mazowiecki County
- Emilianow, Wolomin County