地球的圈层结构Diqiu de quanceng jiegou
地球的组成物质在重力作用下按其密度大小,从地心向外,大致呈现同心状的圈层结构。这是地球结构的最大特征。组成地球的物质多种多样,既有有机物也有无机物;既有固态的、液态的,也有气态的。在地球形成、演化的数十亿年过程中,它们从里向外逐渐地排列起来形成现在的地球。在地球的表面包围着一层大气,称为大气圈,构成地球的最外层。在距地表2 000—3 000公里的高度,地球大气的密度接近星际气体的密度,通常把这个高度作为地球大气的上界。大气的90%聚集在距地表15公里高度以下的大气层内,在48公里以下集中大气的99.9%。大气圈同岩石圈、水圈、生物圈通过物质和能量交换紧密连结在一起,形成一个综合系统。大气渗透到地壳岩石裂隙、孔洞、疏松土层以及各种水体和生物体中,成为地表岩石风化、物质运移的重要营力,是地表形态的塑造者,是全球水分循环的重要环节,是生物体生长发育的必须条件。在大气层之下,地球固体岩石的表面上是一个不连续的水圈。自然界中的水以液态、气态和固态形式存在于地表、地下和空中,并以海洋、河流、湖泊、沼泽、冰川、地下水等形式组成一个既不规则又不连续的水圈。这些水在不停地运动着和互相转化着(液↔气↔固)维持着全球的水分循环和水量平衡。在水的运动和转化过程中,对地球表层物质进行着机械的、物理的和化学的作用,改变着地表形态。在地球表面具备大气、水和营养物质的条件下,就给有机物的出现奠定了基础,有机物又是生命体形成的前提。发展到现在,世界已有一百多万种动物、三十多万种植物和十几万种微生物,它们共同构成了生物圈。生物在地球表面并不单独成圈,它们寄居在大气圈、水圈和地壳表面的接触地带,从其所占空间范围看,厚度仅2—3公里,其总量仅占地球质量的一亿分之三,可见是微不足道的。但是生物圈却是构成地球表面自然环境中最活跃、最复杂的成员,是地球表面生机盎然,区别于其他天体的决定因素。通常把大气圈、水圈和生物圈合称为地球的外部圈层。
自地表以下直到地心,又可分为地壳、地幔、地核等层次,它们构成了地球的内部圈层。因为地球深处的内部构造不能直接观察,目前主要是利用地震波在地球内部传播的情况间接地推测。大约在陆地地壳平均33公里深处,纵波速度为7.6公里/秒,横波为4.2公里/秒。再向下纵波急增为8.1公里/秒,横波为4.6公里/秒。这个波速不连续面是1909年奥地利地震学家莫霍洛维奇发现的,故名莫霍洛维奇界面,简称莫霍面。在距地表2 900公里深处,纵波速度由13.64公里/秒突然降为8.1公里/秒,而横波至此完全消失。这个不连续界面是美籍德人地震学家古登堡于1914年发现的,故称为古登堡面。根据这两个不连续面将地球内部划分为三个圈层:地壳、地幔和地核。
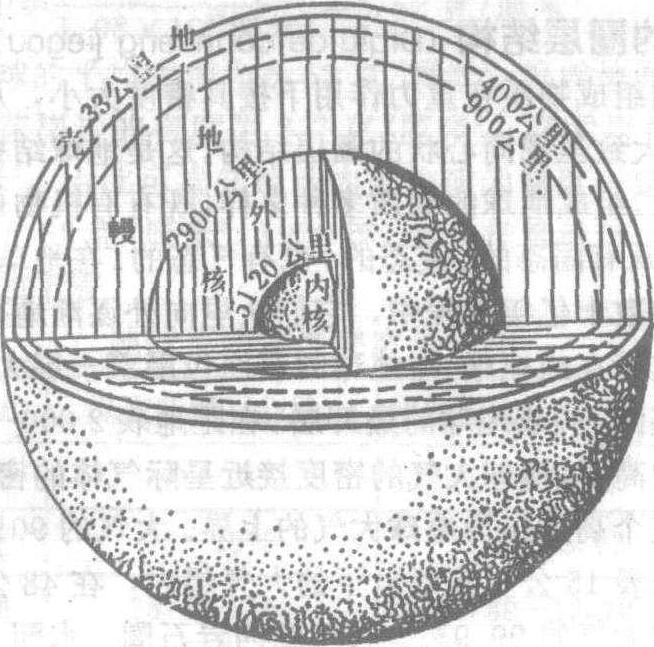
地球内部圈层构造示意图
地壳:位于莫霍面以上部分称为地壳。地壳表层岩石平均密度2.65克/厘米3,处在常温、常压下。地壳底部密度增加到2.9克/厘米3,温度高达1 000℃左右,压力可达1万个大气压。地壳的总体积只占整个地球体积的1%;其质量仅占地球总质量的0.8%。地壳又可分为大陆型和海洋型,大陆型地壳厚度大,平均厚约33公里,高山地区厚度更大,我国西藏及天山地区可达70公里厚。大洋型地壳厚度小,平均只有7.3公里。按组成岩石类型地壳又可分为上下两层,上层主要由花岗岩和沉积岩组成,称为花岗岩层。此层在山区厚度可达40公里,在平原区平均厚为10公里左右,在大洋底则很薄,甚至缺失。下层主要由玄武岩组成,称玄武岩层,在陆上较厚,可达30公里,在深海底仅为5—8公里厚。因为这两层的化学成分都是以硅铝为主,又称为硅铝层。地壳之下为橄榄岩层,密度较大,属上地幔,因其铁镁含量较高,又称硅镁层。
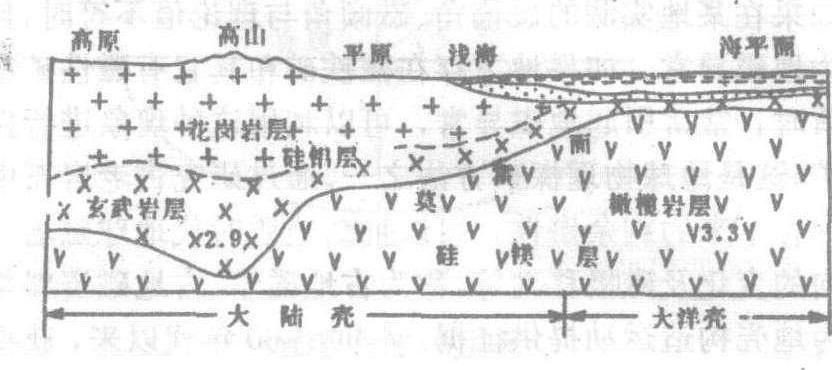
地壳构造示意图
地幔:莫霍面以下古登堡面以上的圈层,底界深为2 900公里,其体积占地球总体积的82%,质量占67.8%,物质密度从上部的3.32克/厘米3向下递增到5.66克/厘米3,底界面上压力可达140万个大气压,温度从上部的1 200℃到下部增到2 000℃。按地震波变化,以984公里深为界把地幔分为上下两部分。上地幔以橄榄岩为主,称为橄榄岩层。在距地表50—250公里范围内存在一个地震波低速层,称为软流层。它可能是岩浆的发源地,地壳运动、岩浆活动、火山喷发和地震活动等都可能与此层有关,它可能是其上部岩石圈板块运动的趋动力,中源和深源地震的震源都发生在上地幔中。下地幔主要由金属硫化物和氧化物组成,因其铁、镍、铬、镁等金属化合物增加,又称为金属矿带层。
地核:古登堡面以下到地心称为地核。根据地震波传播情况,又可分为外核与内核。从2 900—5 100公里范围称为外核。在外核部分地震波的横波完全消失,只有纵波能通过,而且波速减慢,所以外核的物质可能是液态的。5 100公里以下到地心,为内核。在这里地震波的横波重新出现,纵波波速也有突然增大的现象。由此推测内核物质可能是固态的。据推测地核物质非常致密,密度可达9.7—17.9克/厘米3。按体积地核只占整个地球的17%,但其质量却占31.5%。地核内压力可达300—360万个大气压,温度为2 000—3 000℃,最高不超过5 000℃。推测,地核为铁镍物质所组成。