- See also
- References
- External links
A BK-tree is a metric tree suggested by Walter Austin Burkhard and Robert M. Keller{{ref|BK73}} specifically adapted to discrete metric spaces.
For simplicity, let us consider integer discrete metric  . Then, BK-tree is defined in the following way. An arbitrary element a is selected as root node. The root node may have zero or more subtrees. The k-th subtree is recursively built of all elements b such that
. Then, BK-tree is defined in the following way. An arbitrary element a is selected as root node. The root node may have zero or more subtrees. The k-th subtree is recursively built of all elements b such that 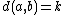 . BK-trees can be used for approximate string matching in a dictionary {{ref|BN98}}.{{example needed|date=March 2019}}
. BK-trees can be used for approximate string matching in a dictionary {{ref|BN98}}.{{example needed|date=March 2019}}
See also
- Levenshtein distance – the distance metric commonly used when building a BK-tree
- Damerau–Levenshtein distance – a modified form of Levenshtein distance that allows transpositions
References
- {{note|BK73}} W. Burkhard and R. Keller. Some approaches to best-match file searching, CACM, 1973
- {{note|BCMW04}} R. Baeza-Yates, W. Cunto, U. Manber, and S. Wu. Proximity matching using fixed queries trees. In M. Crochemore and D. Gusfield, editors, 5th Combinatorial Pattern Matching, LNCS 807, pages 198–212, Asilomar, CA, June 1994.
- {{note|BN98}} Ricardo Baeza-Yates and Gonzalo Navarro. Fast Approximate String Matching in a Dictionary. Proc. SPIRE'98
External links
- A BK-tree implementation in [https://github.com/vy/bk-tree Common Lisp] with test results and performance graphs.
- An explanation of BK-Trees and their relationship to metric spaces
- An explanation of BK-Trees with an implementation in C#
- A BK-tree implementation in Lua [https://profan.github.io/lua-bk-tree/]
1 : Trees (data structures)
- Prince Abdullah bin Al-Ali
- Prince Abo
- Prince Adedayo Clement Adeyeye
- Prince Adewale Aladesanmi
- Prince Affie
- Prince Agyemang
- Prince Ahmed Ali Ahmedzai
- Prince Air
- Prince A. Jackson, Jr.
- Prince Albert (disambiguation)
- Prince Albert No. 461
- Prince Albert of Saxony (1875-1900)
- Prince Albert Raiders roster
- Prince Albert's Light Infantry (Somersetshire Regiment)
- Prince Albert's Model Cottage
- Prince Albert's yew
- Prince Albert Taylor, Jr.
- Prince Albrecht of Croÿ
- Prince Albrecht of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg
- Prince Aleksandar of Yugoslavia (1924-2016)
- Prince Aleksandar of Yugoslavia (1924–2016)
- Prince Aleksandar of Yugoslavia (born 1924)
- Prince Aleksandar of Yugoslavia (born 1982)
- Prince Aleksandar of Yugoslavia the Elder
- Prince Aleksandar of Yugoslavia the elder