- Classical model Attractors
- Stability
- Variations of the model Other topologies Other updating schemes
- Application of Boolean Networks Classification
- See also
- References
- External links
A Boolean network consists of a discrete set of boolean variables each of which has a Boolean function (possibly different for each variable) assigned to it which takes inputs from a subset of those variables and output that determines the state of the variable it is assigned to. This set of functions in effect determines a topology (connectivity) on the set of variables, which then become nodes in a network. Usually, the dynamics of the system is taken as a discrete time series where the state of the entire network at time t+1 is determined by evaluating each variable's function on the state of the network at time t. This may be done synchronously or asynchronously.[1]
Boolean networks have been used in biology to model regulatory networks. Although Boolean networks are a crude simplification of genetic reality where genes are not simple binary switches, there are several cases where they correctly capture the correct pattern of expressed and suppressed genes.[2][3]
The seemingly mathematical easy (synchronous) model was only fully understood in the mid 2000s.[4]
Classical model
A Boolean network is a particular kind of sequential dynamical system, where time and states are discrete, i.e. both the set of variables and the set of states in the time series each have a bijection onto an integer series. Such systems are like cellular automata on networks, except for the fact that when they are set up each node has a rule that is randomly chosen from all 2{{sup|2s}} possible ones with s inputs. With s=2 class 2 behavior tends to dominate. But for s>2, the behavior one sees quickly approaches what is typical for a random mapping in which the network representing the evolution of the 2{{sup|m}} states of the m underlying nodes is itself connected essentially randomly.[5]
A random Boolean network (RBN) is one that is randomly selected from the set of all possible boolean networks of a particular size, N. One then can study statistically, how the expected properties of such networks depend on various statistical properties of the ensemble of all possible networks. For example, one may study how the RBN behavior changes as the average connectivity is changed.
The first Boolean networks were proposed by Stuart A. Kauffman in 1969, as random models of genetic regulatory networks[6] but their mathematical understanding only started in the 2000s.[7][8]
Attractors
Since a Boolean network has only 2N possible states, a trajectory will sooner or later reach a previously visited state, and thus, since the dynamics are deterministic, the trajectory will fall into a steady state or cycle called an attractor (though in the broader field of dynamical systems a cycle is only an attractor if perturbations from it lead back to it). If the attractor has only a single state it is called a point attractor, and if the attractor consists of more than one state it is called a cycle attractor. The set of states that lead to an attractor is called the basin of the attractor. States which occur only at the beginning of trajectories (no trajectories lead to them), are called garden-of-Eden states[9] and the dynamics of the network flow from these states towards attractors. The time it takes to reach an attractor is called transient time.[4]
With growing computer power and increasing understanding of the seemingly simple model, different authors gave different estimates for the mean number and length of the attractors, here a brief summary of key publications.[10]
| Author | Year | Mean attractor length | Mean attractor number | comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kauffmann [6] | 1969 |  |  | |
| Bastolla/ Parisi[11] | 1998 | faster than a power law,  | faster than a power law,  | first numerical evidences |
| Bilke/ Sjunnesson[12] | 2002 | linear with system size,  | ||
| Socolar/Kauffman[13] | 2003 | faster than linear,  with with  | ||
| Samuelsson/Troein[14] | 2003 | superpolynomial growth,  | mathematical proof | |
| Mihaljev/Drossel[15] | 2005 | faster than a power law,  | faster than a power law,  |
Stability
In dynamical systems theory, the structure and length of the attractors of a network corresponds to the dynamic phase of the network. The stability of Boolean networks depends on the connections of their nodes. A Boolean network can exhibit stable, critical or chaotic behavior. This phenomenon is governed by a critical value of the average number of connections of nodes (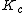 ), and can be characterized by the Hamming distance as distance measure. In the unstable regime, the distance between two initially close states on average grows exponentially in time, while in the stable regime it decreases exponentially. In this, with "initially close states" one means that the Hamming distance is small compared with the number of nodes (
), and can be characterized by the Hamming distance as distance measure. In the unstable regime, the distance between two initially close states on average grows exponentially in time, while in the stable regime it decreases exponentially. In this, with "initially close states" one means that the Hamming distance is small compared with the number of nodes ( ) in the network.
) in the network.
For N-K-model[16] the network is stable if  , critical if
, critical if  , and unstable if
, and unstable if  .
.
The state of a given node  is updated according to its truth table, whose outputs are randomly populated.
is updated according to its truth table, whose outputs are randomly populated.  denotes the probability of assigning an off output to a given series of input signals.
denotes the probability of assigning an off output to a given series of input signals.
If  for every node, the transition between the stable and chaotic range depends on
for every node, the transition between the stable and chaotic range depends on  . The critical value of the average number of connections is
. The critical value of the average number of connections is  .[17]
.[17]
If  is not constant, and there is no correlation between the in-degrees and out-degrees, the conditions of stability is determined by
is not constant, and there is no correlation between the in-degrees and out-degrees, the conditions of stability is determined by  [18][19][20] The network is stable if
[18][19][20] The network is stable if 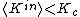 , critical if
, critical if  , and unstable if
, and unstable if  .
.
The conditions of stability are the same in the case of networks with scale-free topology where the in-and out-degree distribution is a power-law distribution:  , and
, and  , since every out-link from a node is an in-link to another.[21]
, since every out-link from a node is an in-link to another.[21]
Sensitivity shows the probability that the output of the Boolean function of a given node changes if its input changes. For random Boolean networks,
 . In the general case, stability of the network is governed by the largest eigenvalue
. In the general case, stability of the network is governed by the largest eigenvalue  of matrix
of matrix  , where
, where  , and
, and  is the adjacency matrix of the network.[22] The network is stable if
is the adjacency matrix of the network.[22] The network is stable if 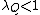 , critical if
, critical if  , unstable if
, unstable if  .
.
Variations of the model
Other topologies
One theme is to study different underlying graph topologies.
- The homogeneous case simply refers to a grid which is simply the reduction to the famous Ising model.
- Scale-free topologies may be chosen for Boolean networks.[23] One can distinguish the case where only in-degree distribution in power-law distributed,[24] or only the out-degree-distribution or both.
Other updating schemes
Classical Boolean networks (sometimes called CRBN, i.e. Classic Random Boolean Network) are synchronously updated. Motivated by the fact that genes don't usually change their state simultaneously,[25] different alternatives have been introduced. A common classification[26] is the following:
- Deterministic asynchronous updated Boolean networks (DRBNs) are not synchronously updated but a deterministic solution still exists. A node i will be updated when t ≡ Qi (mod Pi) where t is the time step.[27]
- The most general case is full stochastic updating (GARBN, general asynchronous random boolean networks). Here, one (or more) node(s) are selected at each computational step to be updated.
- The Partially-Observed Boolean Dynamical System (POBDS)[28][29][30][31] signal model differs from all previous deterministic and stochastic Boolean network models by removing the assumption of direct observability of the Boolean state vector and allowing uncertainty in the observation process, addressing the scenario encountered in practice.
Application of Boolean Networks
Classification
- The Scalable Optimal Bayesian Classification[32] developed an optimal classification of trajectories accounting for potential model uncertainty and also proposed a particle-based trajectory classification that is highly scalable for large networks with much lower complexity than the optimal solution.
See also
- NK model
References
2. ^{{cite journal|last1=Albert|first1=Réka|last2=Othmer|first2=Hans G|title=The topology of the regulatory interactions predicts the expression pattern of the segment polarity genes in Drosophila melanogaster|journal=Journal of Theoretical Biology|date=July 2003|volume=223|issue=1|pages=1–18|doi=10.1016/S0022-5193(03)00035-3|pmid=12782112|citeseerx=10.1.1.13.3370}}
3. ^{{cite journal|last1=Li|first1=J.|last2=Bench|first2=A. J.|last3=Vassiliou|first3=G. S.|last4=Fourouclas|first4=N.|last5=Ferguson-Smith|first5=A. C.|last6=Green|first6=A. R.|title=Imprinting of the human L3MBTL gene, a polycomb family member located in a region of chromosome 20 deleted in human myeloid malignancies |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|date=30 April 2004 |volume=101|issue=19 |pages=7341–7346 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0308195101|pmid=15123827 |pmc=409920|bibcode = 2004PNAS..101.7341L }}
4. ^1 {{cite book|last1=Drossel|first1=Barbara|editor1-last=Schuster|editor1-first=Heinz Georg|title=Chapter 3. Random Boolean Networks|date=December 2009|doi=10.1002/9783527626359.ch3|arxiv=0706.3351|series=Reviews of Nonlinear Dynamics and Complexity|publisher=Wiley|pages=69–110|isbn=9783527626359|chapter=Random Boolean Networks}}
5. ^{{cite book|last1=Wolfram|first1=Stephen|title=A New Kind of Science|date=2002|publisher=Wolfram Media, Inc.|location=Champaign, Illinois|isbn=978-1579550080|page=936|url=http://www.wolframscience.com/nks/|accessdate=15 March 2018}}
6. ^1 {{cite journal|last1=Kauffman|first1=Stuart|title=Homeostasis and Differentiation in Random Genetic Control Networks|journal=Nature|date=11 October 1969|volume=224|issue=5215|pages=177–178|doi=10.1038/224177a0|bibcode = 1969Natur.224..177K }}
7. ^{{cite book|last1=Aldana|first1=Maximo|last2=Coppersmith|first2=Susan|author2-link= Susan Coppersmith |last3=Kadanoff|first3=Leo P.|title=Boolean Dynamics with Random Couplings|journal=Perspectives and Problems in Nonlinear Sciences|date=2003|pages=23–89|doi=10.1007/978-0-387-21789-5_2|arxiv=nlin/0204062|isbn=978-1-4684-9566-9}}
8. ^{{Cite journal|arxiv=nlin.AO/0408006|last1=Gershenson|first1=Carlos|title=Introduction to Random Boolean Networks|journal=In Bedau, M., P. Husbands, T. Hutton, S. Kumar, and H. Suzuki (eds.) Workshop and Tutorial Proceedings, Ninth International Conference on the Simulation and Synthesis of Living Systems (ALife IX). Pp|volume=2004|pages=160–173|year=2004}}
9. ^{{cite book|last1=Wuensche|first1=Andrew|title=Exploring discrete dynamics : [the DDLab manual : tools for researching cellular automata, random Boolean and multivalue neworks [sic] and beyond]|date=2011|publisher=Luniver Press|location=Frome, England|isbn=9781905986316|page=16|url=https://books.google.de/books?id=qsktzY_Vg8QC&pg=PA16|accessdate=12 January 2016}}
10. ^{{cite journal|last1=Greil|first1=Florian|title=Boolean Networks as Modeling Framework|journal=Frontiers in Plant Science|date=2012|volume=3|pages=178|doi=10.3389/fpls.2012.00178|pmid=22912642|pmc=3419389}}
11. ^{{cite journal|last1=Bastolla|first1=U.|last2=Parisi|first2=G.|title=The modular structure of Kauffman networks|journal=Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena|date=May 1998|volume=115|issue=3–4|pages=219–233|doi=10.1016/S0167-2789(97)00242-X|arxiv = cond-mat/9708214 |bibcode = 1998PhyD..115..219B }}
12. ^{{cite journal|last1=Bilke|first1=Sven|last2=Sjunnesson|first2=Fredrik|title=Stability of the Kauffman model|journal=Physical Review E|date=December 2001|volume=65|issue=1|pages=016129|doi=10.1103/PhysRevE.65.016129|pmid=11800758|arxiv = cond-mat/0107035 |bibcode = 2002PhRvE..65a6129B }}
13. ^{{cite journal|last1=Socolar|first1=J.|last2=Kauffman|first2=S.|title=Scaling in Ordered and Critical Random Boolean Networks|journal=Physical Review Letters|date=February 2003|volume=90|issue=6|pages=068702|doi=10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.068702|pmid=12633339|bibcode=2003PhRvL..90f8702S|arxiv = cond-mat/0212306 }}
14. ^{{cite journal|last1=Samuelsson|first1=Björn|last2=Troein|first2=Carl|title=Superpolynomial Growth in the Number of Attractors in Kauffman Networks|journal=Physical Review Letters|date=March 2003|volume=90|issue=9|doi=10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.098701|bibcode=2003PhRvL..90i8701S|pmid=12689263|page=098701}}
15. ^{{cite journal|last1=Mihaljev|first1=Tamara|last2=Drossel|first2=Barbara|title=Scaling in a general class of critical random Boolean networks|journal=Physical Review E|date=October 2006|volume=74|issue=4|pages=046101|doi=10.1103/PhysRevE.74.046101|pmid=17155127|arxiv = cond-mat/0606612 |bibcode = 2006PhRvE..74d6101M }}
16. ^{{cite journal |last=Kauffman |first=S. A. |date=1969 |title=Metabolic stability and epigenesis in randomly constructed genetic nets |journal=Journal of Theoretical Biology |volume=22 |issue=3 |pages=437–467 |doi=10.1016/0022-5193(69)90015-0|pmid=5803332 }}
17. ^{{Cite journal|title = Random Networks of Automata: A Simple Annealed Approximation|url = http://stacks.iop.org/0295-5075/1/i=2/a=001?key=crossref.8cf81041d96c6144f3a397d9cf72cf09|journal = Europhysics Letters (EPL)|date = 1986-01-15|pages = 45–49|volume = 1|issue = 2|doi = 10.1209/0295-5075/1/2/001|first = B|last = Derrida|first2 = Y|last2 = Pomeau|bibcode = 1986EL......1...45D}}
18. ^{{Cite journal|title = Phase transitions and antichaos in generalized Kauffman networks|url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/037596019400876Q|journal = Physics Letters A|date = 1995-01-02|pages = 331–334|volume = 196|issue = 5–6|doi = 10.1016/0375-9601(94)00876-Q|first = Ricard V.|last = Solé|first2 = Bartolo|last2 = Luque|bibcode = 1995PhLA..196..331S}}
19. ^{{Cite journal|title = Phase transitions in random networks: Simple analytic determination of critical points|journal = Physical Review E|date = 1997-01-01|pages = 257–260|volume = 55|issue = 1|doi = 10.1103/PhysRevE.55.257|first = Bartolo|last = Luque|first2 = Ricard V.|last2 = Solé|bibcode = 1997PhRvE..55..257L}}
20. ^{{Cite journal|title = From topology to dynamics in biochemical networks |journal = Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science|date = 2001-12-01|issn = 1054-1500|pages = 809–815|volume = 11|issue = 4|doi = 10.1063/1.1414882|pmid = 12779520 |first = Jeffrey J.|last = Fox|first2 = Colin C.|last2 = Hill|bibcode = 2001Chaos..11..809F}}
21. ^{{Cite journal|title = A natural class of robust networks|journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|date = 2003-07-22|issn = 0027-8424|pmc = 166377|pmid = 12853565|pages = 8710–8714|volume = 100|issue = 15|doi = 10.1073/pnas.1536783100|first = Maximino|last = Aldana|first2 = Philippe|last2 = Cluzel|bibcode = 2003PNAS..100.8710A}}
22. ^{{Cite journal|title = The effect of network topology on the stability of discrete state models of genetic control|journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|date = 2009-05-19|issn = 0027-8424|pmc = 2688895|pmid = 19416903|pages = 8209–8214|volume = 106|issue = 20|doi = 10.1073/pnas.0900142106|first = Andrew|last = Pomerance|first2 = Edward|last2 = Ott|first3 = Michelle|last3 = Girvan|first4 = Wolfgang|last4 = Losert|arxiv = 0901.4362|bibcode = 2009PNAS..106.8209P}}
23. ^{{cite journal|last1=Aldana|first1=Maximino|title=Boolean dynamics of networks with scale-free topology|journal=Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena|date=October 2003|volume=185|issue=1|pages=45–66|doi=10.1016/s0167-2789(03)00174-x|arxiv=cond-mat/0209571|bibcode=2003PhyD..185...45A}}
24. ^{{cite journal|last1=Drossel|first1=Barbara|last2=Greil|first2=Florian|title=Critical Boolean networks with scale-free in-degree distribution|journal=Physical Review E|date=4 August 2009|volume=80|issue=2|pages=026102|doi=10.1103/PhysRevE.80.026102|pmid=19792195|arxiv=0901.0387|bibcode=2009PhRvE..80b6102D}}
25. ^{{cite book|last1=Harvey|first1=Imman|last2=Bossomaier|first2=Terry|editor1-last=Husbands|editor1-first=Phil|editor2-last=Harvey|editor2-first=Imman|title=Time out of joint: Attractors in asynchronous random Boolean networks|journal=Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Artificial Life (ECAL97)|date=1997|pages=67–75|url=https://books.google.de/books?id=ccp8fzlyorAC&pg=PA67|publisher=MIT Press|isbn=9780262581578}}
26. ^{{cite book|last1=Gershenson|first1=Carlos|editor1-last=Standish|editor1-first=Russell K|editor2-last=Bedau|editor2-first=Mark A|title=Classification of Random Boolean Networks|journal=Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Artificial Life|date=2002|volume=8|pages=1–8|url=https://books.google.de/books?id=si_KlRbL1XoC&pg=PA1|accessdate=12 January 2016|arxiv=cs/0208001|series=Artificial Life|location=Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA|isbn=9780262692816|bibcode=2002cs........8001G}}
27. ^{{cite book|last1=Gershenson|first1=Carlos|last2=Broekaert|first2=Jan|last3=Aerts|first3=Diederik|title=Contextual Random Boolean Networks|journal=Advances in Artificial Life|date=14 September 2003|volume=2801|pages=615–624|doi=10.1007/978-3-540-39432-7_66|arxiv=nlin/0303021|series=Lecture Notes in Computer Science|trans-title=7th European Conference, ECAL 2003|location=Dortmund, Germany|isbn=978-3-540-39432-7}}
28. ^{{Cite journal|last=Imani|first=M.|last2=Braga-Neto|first2=U. M.|date=2017-01-01|title=Maximum-Likelihood Adaptive Filter for Partially Observed Boolean Dynamical Systems|url=http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7581014/|journal=IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing|volume=65|issue=2|pages=359–371|doi=10.1109/TSP.2016.2614798|issn=1053-587X|arxiv=1702.07269|bibcode=2017ITSP...65..359I}}
29. ^{{Cite book|chapter-url=http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7418342/|title=Optimal state estimation for boolean dynamical systems using a boolean Kalman smoother - IEEE Xplore Document|pages=972–976|last=Imani|first=M.|last2=Braga-Neto|first2=U. M.|language=en-US|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170213090725/http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7418342/|doi=10.1109/GlobalSIP.2015.7418342|chapter=Optimal state estimation for boolean dynamical systems using a boolean Kalman smoother|year=2015|isbn=978-1-4799-7591-4}}
30. ^{{Cite book|last=Imani|first=M.|last2=Braga-Neto|first2=U. M.|language=en-US|doi=10.1109/ACC.2016.7524920|title=2016 American Control Conference (ACC)|pages=227–232|year=2016|isbn=978-1-4673-8682-1}}
31. ^{{Cite book|last=Imani|first=M.|last2=Braga-Neto|first2=U.|date=2016-12-01|title=Point-based value iteration for partially-observed Boolean dynamical systems with finite observation space|journal=2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC)|pages=4208–4213|doi=10.1109/CDC.2016.7798908|isbn=978-1-5090-1837-6}}
32. ^Hajiramezanali, E. & Imani, M. & Braga-Neto, U. & Qian, X. & Dougherty, E.. Scalable Optimal Bayesian Classification of Single-Cell Trajectories under Regulatory Model Uncertainty. ACMBCB'18. https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3233689
- Dubrova, E., Teslenko, M., Martinelli, A., (2005). Kauffman Networks: Analysis and Applications, in "Proceedings of International Conference on Computer-Aided Design", pages 479-484.
External links
- DDLab
- Analysis of Dynamic Algebraic Models (ADAM) v1.1
- [https://sourceforge.net/projects/rbn/ RBNLab]
- NetBuilder Boolean Networks Simulator
- [https://web.archive.org/web/20090214202740/http://www.rustyspigot.com/software/BooleanNetwork/?url=%2Fsoftware%2FBooleanNetwork Open Source Boolean Network Simulator]
- JavaScript Kauffman Network
- Probabilistic Boolean Networks (PBN)
- A SAT-based tool for computing attractors in Boolean Networks
- CoLoMoTo (Consortium for Logical Models and Tools)
- Boniperti
- Boni Petcoff
- Boni pueri
- Boni Pueri
- Boni Pueri, the Czech Boys Choir
- Bonisa
- Bonisa nakaza
- Bonislaw
- Bonislaw, Mlawa County
- Bonislaw, Sierpc County
- Bonis Peninsula
- Bonistan
- Bonisław
- Bonisław, Mława County
- Bonisław, Sierpc County
- Bonit
- Bonita Beach
- Bonita BPM
- Bonita Canyon Drive
- Bonita Canyon Elementary School
- Bonita Canyon Highway
- Bonita de Mas
- Bonita de Más
- Bonita (disambiguation)
- Bonita Falls