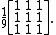- Implementation
- See also
- References
A box blur (also known as a box linear filter) is a spatial domain linear filter in which each pixel in the resulting image has a value equal to the average value of its neighboring pixels in the input image. It is a form of low-pass ("blurring") filter. A 3 by 3 box blur can be written as matrix
Due to its property of using equal weights, it can be implemented using a much simpler accumulation algorithm, which is significantly faster than using a sliding-window algorithm.[1]
Box blurs are frequently used to approximate a Gaussian blur.[2] By the central limit theorem, repeated application of a box blur will approximate a Gaussian blur.
In the frequency domain, a box blur has zeros and negative components. That is, a sine wave with a period equal to the size of the box will be blurred away entirely, and wavelengths shorter than the size of the box may be phase-reversed, as seen when two bokeh circles touch to form a bright spot where there would be a dark spot between two bright spots in the original image.
Implementation
A box blur can be implemented as an image effect that affects the whole screen.
The blurred color of the current pixel is the average of the current pixel's color and its 8 neighboring pixels.
The following pseudocode shows how to implement such an image effect.
For each iteration do:
{ For each pixel on the screen do: { uv = sample coordinates of the current pixel texel = screen texel size // X X X > upperRow // X P X > centerRow // X X X > bottomRow // Final value is average of the three rows upperRow = sample(screen, uv + (-texel.x, texel.y)) //Top left + sample(screen, uv + (0, texel.y)) //Top center + sample(screen, uv + (texel.x, texel.y)); //Top right centerRow = sample(screen, uv + (-texel.x, 0)) //Middle left + sample(screen, uv) //Current pixel + sample(screen, uv + (texel.x, 0)); //Middle right bottomRow = sample(screen, uv + (-texel.x, -texel.y)) //Bottom left + sample(screen, uv + (0, -texel.y)) //Bottom center + sample(screen, uv + (texel.x, -texel.y)); //Bottom right return (upperRow + centerRow + bottomRow) / 9; }}
See also
- Gaussian blur
- Gaussian filter
- Median filter
References
2. ^W3C SVG1.1 specification, 15.17 Filter primitive 'feGaussianBlur'.
- Cedric Calvin Bonniface Clementine
- Cedric Coutouly
- Cedric Cox (footballer)
- Cedric Dent
- Cedric De Zutter
- Cedric de Zutter
- Cedric Doumbe
- Cedric Dubler
- Cedric D'Ulivo
- Cedric Elmes
- Cedric E. Mills
- Cedric Errol Carr
- Cedric Frère
- Cedric Gasser
- Cedric Gates
- Cedric Gervais discography
- Cedric G. Gyles
- Cedric Goncalves
- Cedric Gondo
- Cedric Gyles
- Cedric Hayden (Oregon politician)
- Cedric Hayden (politician)
- Cedric Herrou
- Cedric Hubbell Whitman
- Cedric Itten