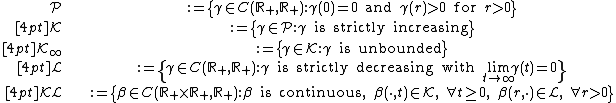- References
In applied mathematics, comparison functions are several classes of continuous functions, which are used in stability theory to characterize the stability properties of control systems as Lyapunov stability, uniform asymptotic stability etc.
Let  be a space of continuous functions acting from
be a space of continuous functions acting from 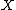 to
to  . The most important classes of comparison functions are:
. The most important classes of comparison functions are:
Functions of class  are also called positive-definite functions.
are also called positive-definite functions.
One of the most important properties of comparison functions is given by Sontag’s 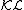 -Lemma[1], named after Eduardo Sontag. It says that for each
-Lemma[1], named after Eduardo Sontag. It says that for each  and any
and any 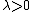 there exist
there exist  :
:

|{{EquationRef|1}}}}
Many further useful properties of comparison functions can be found in [2][3].
Comparison functions are primarily used to obtain quantitative restatements of stability properties as Lyapunov stability, uniform asymptotic stability, etc. These restatements are often more useful than the qualitative definitions of stability properties given in  language.
language.
As an example, consider an ordinary differential equation
{{NumBlk|:|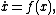
|{{EquationRef|2}}}}
where  is locally Lipschitz. Then:
is locally Lipschitz. Then:
- ({{EquationNote|2}}) is globally stable if and only if there is a
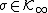 so that for any initial condition
so that for any initial condition  and for any
and for any  it holds that
it holds that
|{{EquationRef|3}}}}
- ({{EquationNote|2}}) is globally asymptotically stable if and only if there is a
 so that for any initial condition
so that for any initial condition  and for any
and for any  it holds that
it holds that
|{{EquationRef|4}}}}
Comparison functions formalism is widely used in the input-to-state stability theory.
References
2. ^W. Hahn. Stability of motion. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1967.
3. ^C. M. Kellett. A compendium of comparison function results. Mathematics of Control, Signals, and Systems, 26(3):339–374, 2014.
- Attar Singh
- Attarsuiya
- Attasecond
- Attatash
- Atta Toy
- Atta Toy (Robot Chicken episode)
- Attaullah Khan Esakhelvi
- Attaullah Shah Bukhari
- Atta ur rahman
- Atta-ur-Rahman
- Atta-ur-Rahman (chemist)
- Attavar
- Attavyros (municipality)
- Attawapiskat
- Attawapiskat 91A
- Attawapiskat Airport
- At-Tawba 29
- Attayampatti
- At-Tayyib Abu'l-Qasim
- AT&T Before SBC
- AT & T Bell Laboratories Technical Journal
- AT&T Bell Laboratories Technical Journal
- AT&T Broadband
- At&t building
- AT&T Building