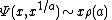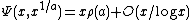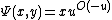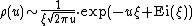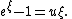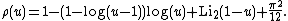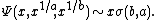- Definition
- Applications
- Estimation
- Computation
- Extension
- See also
- References
- Further reading
In analytic number theory, the Dickman function or Dickman–de Bruijn function ρ is a special function used to estimate the proportion of smooth numbers up to a given bound.
It was first studied by actuary Karl Dickman, who defined it in his only mathematical publication,[1] and later studied by the Dutch mathematician Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn.[2][3]
Definition
The Dickman–de Bruijn function  is a continuous function that satisfies the delay differential equation
is a continuous function that satisfies the delay differential equation
with initial conditions 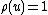 for 0 ≤ u ≤ 1. Dickman proved that, when
for 0 ≤ u ≤ 1. Dickman proved that, when  is fixed, we have
is fixed, we have
where 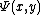 is the number of y-smooth (or y-friable) integers below x.
is the number of y-smooth (or y-friable) integers below x.
Ramaswami later gave a rigorous proof that for fixed a, 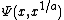 was asymptotic to
was asymptotic to  , with the error bound
, with the error bound
in big O notation.[4]
Applications
The main purpose of the Dickman–de Bruijn function is to estimate the frequency of smooth numbers at a given size. This can be used to optimize various number-theoretical algorithms, and can be useful of its own right.
It can be shown using 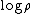 that[5]
that[5]
which is related to the estimate 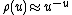 below.
below.
The Golomb–Dickman constant has an alternate definition in terms of the Dickman–de Bruijn function.
Estimation
A first approximation might be 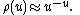 A better estimate is[6]
A better estimate is[6]
where Ei is the exponential integral and ξ is the positive root of
A simple upper bound is 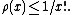
 |  |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | -1}} |
| 3 | -2}} |
| 4 | -3}} |
| 5 | -4}} |
| 6 | -5}} |
| 7 | -7}} |
| 8 | -8}} |
| 9 | -9}} |
| 10 | -11}} |
Computation
For each interval [n − 1, n] with n an integer, there is an analytic function  such that
such that 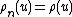 . For 0 ≤ u ≤ 1,
. For 0 ≤ u ≤ 1, 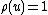 . For 1 ≤ u ≤ 2,
. For 1 ≤ u ≤ 2, 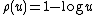 . For 2 ≤ u ≤ 3,
. For 2 ≤ u ≤ 3,
with Li2 the dilogarithm. Other  can be calculated using infinite series.[6]
can be calculated using infinite series.[6]
An alternate method is computing lower and upper bounds with the trapezoidal rule;[7] a mesh of progressively finer sizes allows for arbitrary accuracy. For high precision calculations (hundreds of digits), a recursive series expansion about the midpoints of the intervals is superior.[8]
Extension
Friedlander defines a two-dimensional analog 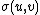 of
of  .[9] This function is used to estimate a function
.[9] This function is used to estimate a function 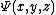 similar to de Bruijn's, but counting the number of y-smooth integers with at most one prime factor greater than z. Then
similar to de Bruijn's, but counting the number of y-smooth integers with at most one prime factor greater than z. Then
See also
- Buchstab function, a function used similarly to estimate the number of rough numbers, whose convergence to
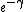 is controlled by the Dickman function
is controlled by the Dickman function - Golomb–Dickman constant
References
2. ^{{cite journal |first=N. G. |last=de Bruijn |url=http://alexandria.tue.nl/repository/freearticles/597499.pdf |title=On the number of positive integers ≤ x and free of prime factors > y |journal=Indagationes Mathematicae |volume=13 |year=1951 |pages=50–60 }}
3. ^{{cite journal |first=N. G. |last=de Bruijn |url=http://alexandria.tue.nl/repository/freearticles/597534.pdf |title=On the number of positive integers ≤ x and free of prime factors > y, II |journal=Indagationes Mathematicae |volume=28 |issue= |year=1966 |pages=239–247 }}
4. ^{{cite journal |first=V. |last=Ramaswami |url=http://www.ams.org/bull/1949-55-12/S0002-9904-1949-09337-0/S0002-9904-1949-09337-0.pdf |title=On the number of positive integers less than
 and free of prime divisors greater than xc |journal=Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society |volume=55 |issue=12 |year=1949 |pages=1122–1127 |doi= 10.1090/s0002-9904-1949-09337-0 | mr=0031958}}
and free of prime divisors greater than xc |journal=Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society |volume=55 |issue=12 |year=1949 |pages=1122–1127 |doi= 10.1090/s0002-9904-1949-09337-0 | mr=0031958}}5. ^{{cite journal |first=A. |last=Hildebrand |first2=G. |last2=Tenenbaum |url=http://archive.numdam.org/article/JTNB_1993__5_2_411_0.pdf |title=Integers without large prime factors |journal=Journal de théorie des nombres de Bordeaux |volume=5 |issue=2 |year=1993 |pages=411–484 |doi=10.5802/jtnb.101}}
6. ^{{cite journal |first=Eric |last=Bach |first2=René |last2=Peralta |url=http://cr.yp.to/bib/1996/bach-semismooth.pdf |title=Asymptotic Semismoothness Probabilities |journal=Mathematics of Computation |volume=65 |issue=216 |pages=1701–1715 |year=1996 |doi=10.1090/S0025-5718-96-00775-2 }}
7. ^1 {{cite journal |first=J. |last=van de Lune |first2=E. |last2=Wattel |title=On the Numerical Solution of a Differential-Difference Equation Arising in Analytic Number Theory |journal=Mathematics of Computation |volume=23 |issue=106 |year=1969 |pages=417–421 |doi=10.1090/S0025-5718-1969-0247789-3 }}
8. ^{{cite journal |first=George |last=Marsaglia |first2=Arif |last2=Zaman |first3=John C. W. |last3=Marsaglia |title=Numerical Solution of Some Classical Differential-Difference Equations |journal=Mathematics of Computation |volume=53 |issue=187 |year=1989 |pages=191–201 |jstor= |doi=10.1090/S0025-5718-1989-0969490-3 }}
9. ^{{cite journal |first=John B. |last=Friedlander |url=http://plms.oxfordjournals.org/content/s3-33/3/565 |title=Integers free from large and small primes |journal=Proc. London Math. Soc. |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=565–576 |year=1976 |doi=10.1112/plms/s3-33.3.565 }}
Further reading
- {{Cite arxiv
|first1=David
|last1=Broadhurst
|title=Dickman polylogarithms and their constants
|eprint=1004.0519
|year=2010
|class=math-ph
}}
- {{cite journal
|first1=Kannan
|last1=Soundararajan
|title=An asymptotic expansion related to the Dickman function
|arxiv=1005.3494
|year=2012
|journal=Ramanujan Journal
|volume=29
|issue=1–3
|doi=10.1007/s11139-011-9304-3
|mr=2994087
|pages=25–30
}}
- {{mathworld|urlname=DickmanFunction|title=Dickman function}}
- SkyService
- Skyservice Airlines
- SkyService Airlines
- Sky Shuttle
- Sky Soap
- Sky soldiers
- Sky Sports Active
- Sky Sports International Open
- Sky Sports International Open (snooker)
- Sky Sports News
- Sky Sports Racing
- Sky Sports Xtra
- Sky's the Limit (The Temptations album)
- Skystriker
- Sky-surfer
- Skysurfer
- Skysurfer Strike Force
- Skysurfing
- Sky Sword I
- Sky Sword II
- Skytale
- SkyTeam
- Skyteam
- Sky Team Alliance
- SkyTeam Alliance