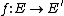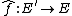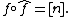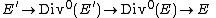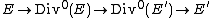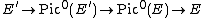- Definition
- History
- Dual isogeny (elliptic curve case)
- Construction of the dual isogeny
- Poincaré line bundle
- Notes
- References
In mathematics, a dual abelian variety can be defined from an abelian variety A, defined over a field K.
Definition
To an abelian variety A over a field k, one associates a dual abelian variety Av (over the same field), which is the solution to the following moduli problem. A family of degree 0 line bundles parametrized by a k-variety T is defined to be a line bundle L on
A×T such that
- for all
 , the restriction of L to A×{t} is a degree 0 line bundle,
, the restriction of L to A×{t} is a degree 0 line bundle, - the restriction of L to {0}×T is a trivial line bundle (here 0 is the identity of A).
Then there is a variety Av and a family of degree 0 line bundles P,{{clarify|Bundles on what?|date=July 2014}} the Poincaré bundle, parametrized by Av such that a family L on T is associated a unique morphism f: T → Av so that L is isomorphic to the pullback of P along the morphism 1A×f: A×T → A×Av. Applying this to the case when T is a point, we see that the points of Av correspond to line bundles of degree 0 on A, so there is a natural group operation on Av given by tensor product of line bundles, which makes it into an abelian variety.
In the language of representable functors one can state the above result as follows. The contravariant functor, which associates to each k-variety T the set of families of degree 0 line bundles on T and to each k-morphism f: T → T' the mapping induced by the pullback with f, is representable. The universal element representing this functor is the pair (Av, P).
This association is a duality in the sense that there is a natural isomorphism between the double dual Avv and A (defined via the Poincaré bundle) and that it is contravariant functorial, i.e. it associates to all morphisms f: A → B dual morphisms fv: Bv → Av in a compatible way. The n-torsion of an abelian variety and the n-torsion of its dual are dual to each other when n is coprime to the characteristic of the base. In general - for all n - the n-torsion group schemes of dual abelian varieties are Cartier duals of each other. This generalizes the Weil pairing for elliptic curves.
History
The theory was first put into a good form when K was the field of complex numbers. In that case there is a general form of duality between the Albanese variety of a complete variety V, and its Picard variety; this was realised, for definitions in terms of complex tori, as soon as André Weil had given a general definition of Albanese variety. For an abelian variety A, the Albanese variety is A itself, so the dual should be Pic0(A), the connected component of what in contemporary terminology is the Picard scheme.
For the case of the Jacobian variety J of a compact Riemann surface C, the choice of a principal polarization of J gives rise to an identification of J with its own Picard variety. This in a sense is just a consequence of Abel's theorem. For general abelian varieties, still over the complex numbers, A is in the same isogeny class as its dual. An explicit isogeny can be constructed by use of an invertible sheaf L on A (i.e. in this case a holomorphic line bundle), when the subgroup
K(L)
of translations on L that take L into an isomorphic copy is itself finite. In that case, the quotient
A/K(L)
is isomorphic to the dual abelian variety Â.
This construction of  extends to any field K of characteristic zero.[1] In terms of this definition, the Poincaré bundle, a universal line bundle can be defined on
A × Â.
The construction when K has characteristic p uses scheme theory. The definition of K(L) has to be in terms of a group scheme that is a scheme-theoretic stabilizer, and the quotient taken is now a quotient by a subgroup scheme.[2]
Dual isogeny (elliptic curve case)
Given an isogeny
of elliptic curves of degree  , the dual isogeny is an isogeny
, the dual isogeny is an isogeny
of the same degree such that
Here  denotes the multiplication-by-
denotes the multiplication-by- isogeny
isogeny 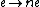 which has degree
which has degree 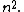
Construction of the dual isogeny
Often only the existence of a dual isogeny is needed, but it can be explicitly given as the composition
where 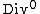 is the group of divisors of degree 0. To do this, we need maps
is the group of divisors of degree 0. To do this, we need maps 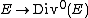 given by
given by 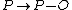 where
where  is the neutral point of
is the neutral point of  and
and 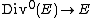 given by
given by 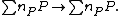
To see that 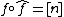 , note that the original isogeny
, note that the original isogeny  can be written as a composite
can be written as a composite
and that since  is finite of degree
is finite of degree  ,
, 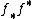 is multiplication by
is multiplication by  on
on 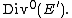
Alternatively, we can use the smaller Picard group 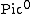 , a quotient of
, a quotient of 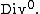 The map
The map 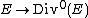 descends to an isomorphism,
descends to an isomorphism, 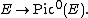 The dual isogeny is
The dual isogeny is
Note that the relation 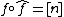 also implies the conjugate relation
also implies the conjugate relation 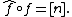 Indeed, let
Indeed, let 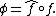 Then
Then 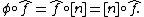 But
But  is surjective, so we must have
is surjective, so we must have 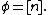
Poincaré line bundle
The product of an abelian variety and its dual has a canonical line bundle, called the Poincaré line bundle.[3] The corresponding height for varieties defined over number fields is sometimes called the Poincaré height.
Notes
2. ^Mumford, Abelian Varieties, p.123 onwards
3. ^{{cite book | title=An Introduction to Invariants and Moduli | volume=81 | series=Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics | first=Shigeru | last=Mukai | translator=W. M. Oxbury | publisher=Cambridge University Press | year=2003 | isbn=0-521-80906-1 | zbl=1033.14008 | pages=400, 412–413 }}
References
- {{cite book
| last = Mumford
| first = David
| authorlink = David Mumford
| title = Abelian Varieties
| publisher = Oxford University Press
| isbn = 978-0-19-560528-0
| edition = 2nd
| date = 1985
}}{{PlanetMath attribution|id=3226|title=Dual isogeny}}
- Atefeh Riazi
- Atef El Tayeb
- Atef Helmi
- Atef Helmy
- A te (Fiorella Mannoia album)
- Atef mohamed ebeid
- Atef Mohammed Ebeid
- Atef Najib
- Atef najib
- Atef Salem
- Atef Sedki Cabinet
- Atef Tarawneh
- Ategana
- Ate Gay
- Atege
- Ategumia actealis
- Ategumia crocealis
- Ategumia dilecticolor
- Ategumia insipidalis
- Ategumia longidentalis
- Ategumia lotanalis
- Ategumia nalotalis
- Atehuan
- Ateius Capito
- Atek