- Key establishment protocol
- Software
- See also
- References
Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) is an anonymous key agreement protocol that allows two parties, each having an elliptic-curve public–private key pair, to establish a shared secret over an insecure channel.[1][2][3] This shared secret may be directly used as a key, or to derive another key. The key, or the derived key, can then be used to encrypt subsequent communications using a symmetric-key cipher. It is a variant of the Diffie–Hellman protocol using elliptic-curve cryptography.
Key establishment protocol
The following example will illustrate how a key establishment is made. Suppose Alice wants to establish a shared key with Bob, but the only channel available for them may be eavesdropped by a third party. Initially, the domain parameters (that is,  in the prime case or
in the prime case or 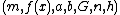 in the binary case) must be agreed upon. Also, each party must have a key pair suitable for elliptic curve cryptography, consisting of a private key
in the binary case) must be agreed upon. Also, each party must have a key pair suitable for elliptic curve cryptography, consisting of a private key  (a randomly selected integer in the interval
(a randomly selected integer in the interval  ) and a public key represented by a point
) and a public key represented by a point  (where
(where  , that is, the result of adding
, that is, the result of adding 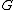 to itself
to itself  times). Let Alice's key pair be
times). Let Alice's key pair be 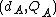 and Bob's key pair be
and Bob's key pair be  . Each party must know the other party's public key prior to execution of the protocol.
. Each party must know the other party's public key prior to execution of the protocol.
Alice computes point 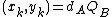 . Bob computes point
. Bob computes point  . The shared secret is
. The shared secret is  (the x coordinate of the point). Most standardized protocols based on ECDH derive a symmetric key from
(the x coordinate of the point). Most standardized protocols based on ECDH derive a symmetric key from  using some hash-based key derivation function.
using some hash-based key derivation function.
The shared secret calculated by both parties is equal, because  .
.
The only information about her private key that Alice initially exposes is her public key. So, no party other than Alice can determine Alice's private key, unless that party can solve the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem. Bob's private key is similarly secure. No party other than Alice or Bob can compute the shared secret, unless that party can solve the elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman problem.
The public keys are either static (and trusted, say via a certificate) or ephemeral (also known as ECDHE, where final 'E' stands for "ephemeral"). Ephemeral keys are temporary and not necessarily authenticated, so if authentication is desired, authenticity assurances must be obtained by other means. Authentication is necessary to avoid man-in-the-middle attacks. If one of either Alice's or Bob's public keys is static, then man-in-the-middle attacks are thwarted. Static public keys provide neither forward secrecy nor key-compromise impersonation resilience, among other advanced security properties. Holders of static private keys should validate the other public key, and should apply a secure key derivation function to the raw Diffie–Hellman shared secret to avoid leaking information about the static private key. For schemes with other security properties, see MQV.
While the shared secret may be used directly as a key, it is often desirable to hash the secret to remove weak bits due to the Diffie–Hellman exchange.[4]
Software
- Curve25519 is the set of elliptic curve parameters and the reference implementation by Daniel J. Bernstein in C. Bindings and alternative implementations are also available.
- LINE messenger app has used the ECDH protocol for its "Letter Sealing" end-to-end encryption of all messages send through said app since October 2015.[5]
See also
- Diffie–Hellman key exchange
References
2. ^Certicom Research, Standards for efficient cryptography, SEC 1: Elliptic Curve Cryptography, Version 2.0, May 21, 2009.
3. ^NSA Suite B Cryptography, Suite B Implementers' Guide to NIST SP 800-56A, July 28, 2009.
4. ^{{cite journal | last1 = Law | first1 = Laurie | author1-link = Laurie Law | last2 = Menezes | first2 = Alfred | author2-link = Alfred Menezes | last3 = Qu | first3 = Minghua | author3-link = Minghua Qu | last4 = Solinas | first4 = Jerry | author4-link = Jerry Solinas | last5 = Vanstone | first5 = Scott | author5-link = Scott Vanstone | title = An Efficient Protocol for Authenticated Key Agreement | publisher = Certicom | date = August 28, 1998 | url = http://www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/techreports/1998/corr98-05.pdf | accessdate = December 16, 2014 }}
5. ^{{cite web|author1=JI|title=New generation of safe messaging: "Letter Sealing"|url=https://engineering.linecorp.com/en/blog/detail/65/|website=LINE Engineers' Blog|publisher=LINE Corporation|accessdate=5 February 2018|date=13 October 2015}}
- Jamshoro district
- Jamshēd
- Jamshīd
- Jamsid Chemirani
- Jam Side Down
- Jam Sikandar
- Jamsil Bridge
- Jamsil (disambiguation)
- Jamsil-dong
- Jamsil Indoor Swimming Pool
- Jamsilnaru Station
- Jam Skating
- Jamskating
- Jamskie
- J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom.
- J. Am. Soc. Nephrol.
- JAM software
- Jamsola
- Jamsrangiin Sambuu
- JAMS Scheduler
- J. Am. Statist. Assoc.
- Jamstykk
- Jamsu Bridge
- Jam sugar
- Jam Taghlak