- History
- Notation
- Polynomials Dynamical plane = z-plane Uniformization Formal definition of dynamic ray Properties Parameter plane = c-plane Uniformization Formal definition of parameter ray Definition of
 External angle Computation of external argument
External angle Computation of external argument - Transcendental maps
- Images Dynamic rays Parameter rays
- Programs that can draw external rays
- See also
- References
- External links
An external ray is a curve that runs from infinity toward a Julia or Mandelbrot set.[1]
Although this curve is only rarely a half-line (ray) it is called a ray because it is an image of a ray.
External rays are used in complex analysis, particularly in complex dynamics and geometric function theory.
History
External rays were introduced in Douady and Hubbard's study of the Mandelbrot set
Notation
External rays of (connected) Julia sets on dynamical plane are often called dynamic rays.
External rays of the Mandelbrot set (and similar one-dimensional connectedness loci) on parameter plane are called parameter rays.
Polynomials
Dynamical plane = z-plane
External rays are associated to a compact, full, connected subset  of the complex plane as :
of the complex plane as :
- the images of radial rays under the Riemann map of the complement of

- the gradient lines of the Green's function of

- field lines of Douady-Hubbard potential[2]
- an integral curve of the gradient vector field of the Green's function on neighborhood of infinity[3]
External rays together with equipotential lines of Douady-Hubbard potential ( level sets) form a new polar coordinate system for exterior ( complement ) of  .
.
In other words the external rays define vertical foliation which is orthogonal to horizontal foliation defined by the level sets of potential.[4]
Uniformization
Let 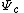 be the conformal isomorphism from the complement (exterior) of the closed unit disk
be the conformal isomorphism from the complement (exterior) of the closed unit disk  to the complement of the filled Julia set
to the complement of the filled Julia set 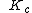 .
.
where  denotes the extended complex plane.
denotes the extended complex plane.
Let  denote the Boettcher map[5].
denote the Boettcher map[5].
 is a uniformizing map of the basin of attraction of infinity, because it conjugates
is a uniformizing map of the basin of attraction of infinity, because it conjugates  on the complement of the filled Julia set
on the complement of the filled Julia set  to
to  on the complement of the unit disk:
on the complement of the unit disk:
and
A value 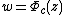 is called the Boettcher coordinate for a point
is called the Boettcher coordinate for a point  .
.


