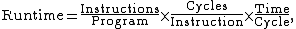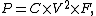- See also
- References
In computer architecture, frequency scaling (also known as frequency ramping) is the technique of increasing a processor's frequency so as to enhance the performance of the system containing the processor in question. Frequency ramping was the dominant force in commodity processor performance increases from the mid-1980s until roughly the end of 2004.
The effect of processor frequency on computer speed can be seen by looking at the equation for computer program runtime:
where instructions per program is the total instructions being executed in a given program, cycles per instruction is a program-dependent, architecture-dependent average value, and time per cycle is by definition the inverse of processor frequency.[1] An increase in frequency thus decreases runtime.
However, power consumption in a chip is given by the equation
where P is power consumption, C is the capacitance being switched per clock cycle, V is voltage, and F is the processor frequency (cycles per second).[2] Increases in frequency thus increase the amount of power used in a processor. Increasing processor power consumption led ultimately to Intel's May 2004 cancellation of its Tejas and Jayhawk processors, which is generally cited as the end of frequency scaling as the dominant computer architecture paradigm.[3]
Moore's Law was[4] still in effect when frequency scaling ended. Despite power issues, transistor densities were still doubling every 18 to 24 months. With the end of frequency scaling, new transistors (which are no longer needed to facilitate frequency scaling) are used to add extra hardware, such as additional cores, to facilitate parallel computing - a technique that is being referred to as parallel scaling.
The end of frequency scaling as the dominant cause of processor performance gains has caused an industry-wide shift to parallel computing in the form of multicore processors.
See also
- Dynamic frequency scaling
- Overclocking
- Underclocking
- Voltage scaling
References
2. ^J. M. Rabaey. Digital Integrated Circuits. Prentice Hall, 1996.
3. ^Laurie J. Flynn. [https://www.nytimes.com/2004/05/08/business/08chip.html?ex=1399348800&en=98cc44ca97b1a562&ei=5007 Intel Halts Development of 2 New Microprocessors]. New York Times, May 8, 2004.
4. ^https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2016/02/moores-law-really-is-dead-this-time/
- Bedford Stem Cell Research Foundation
- Bedford St Johns
- Bedford st johns railway station
- Bedford St Johns station
- Bedford Stuy
- Bedford-Stuy
- Bedford Stuyvesant, Brooklyn
- Bedford-Stuyvesant, Brooklyn
- Bedford sty
- Bedford stye
- Bedford TK
- Bedford to hitchin line
- Bedford to northampton line
- Bedford Town
- Bedford Town F. C.
- Bedford Town F C
- Bedford Town FC
- Bedford (town), Quebec
- Bedford town reserves.
- Bedford Town Reserves F.C.
- Bedford Township, Bedford County, PA
- Bedford Township, Coshocton County, OH
- Bedford Township, Meigs County, OH
- Bedford Township, Michigan (disambiguation)
- Bedford Township, Monroe County, Mi