- General model form Solids Example: standard linear solid model Liquids Example: three parameter fluid
- References
The Generalized Maxwell model also known as the Maxwell–Wiechert model (after James Clerk Maxwell and E Wiechert[1][2]) is the most general form of the linear model for viscoelasticity. In this model several Maxwell elements are assembled in parallel. It takes into account that the relaxation does not occur at a single time, but in a set of times. Due to the presence of molecular segments of different lengths, with shorter ones contributing less than longer ones, there is a varying time distribution. The Wiechert model shows this by having as many spring–dashpot Maxwell elements as are necessary to accurately represent the distribution. The figure on the right shows the generalised Wiechert model.[3][4]
General model form
Solids
Given  elements with moduli
elements with moduli  , viscosities
, viscosities  , and relaxation times
, and relaxation times 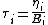
The general form for the model for solids is given by {{citation needed|date=November 2014}}:
{{Equation box 1 |title = General Maxwell Solid Model ({{EquationRef|1}}) |equation =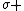


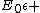
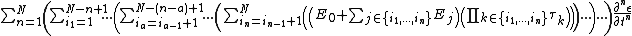
|cellpadding = 6 |border = 1 |border colour = black |background colour = white}}{{divhide|This may be more easily understood by showing the model in a slightly more expanded form:}}{{Equation box 1 |title = General Maxwell Solid Model ({{EquationRef|2}}) |equation =
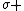







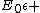



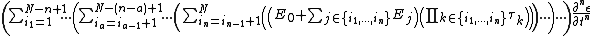

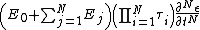
|cellpadding = 6 |border = 1 |border colour = black |background colour = white}}{{divhide|end}}
Example: standard linear solid model
Following the above model with  elements yields the standard linear solid model:
elements yields the standard linear solid model:
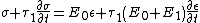
|cellpadding = 6 |border = 1 |border colour = black |background colour = white}}
Liquids
Given  elements with moduli
elements with moduli  , viscosities
, viscosities  , and relaxation times
, and relaxation times 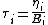
The general form for the model for liquids is given by:
{{Equation box 1 |title = General Maxwell Fluid Model ({{EquationRef|4}}) |equation =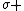



|cellpadding = 6 |border = 1 |border colour = black |background colour = white}}{{divhide|This may be more easily understood by showing the model in a slightly more expanded form:}}{{Equation box 1 |title = General Maxwell Fluid Model ({{EquationRef|5}}) |equation =
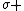








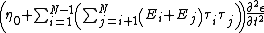

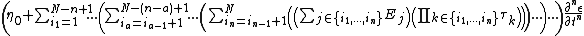

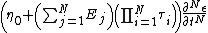
|cellpadding = 6 |border = 1 |border colour = black |background colour = white}}{{divhide|end}}
Example: three parameter fluid
The analogous model to the standard linear solid model is the three parameter fluid, also known as the Jeffrey model:[5]
{{Equation box 1 |title = Three Parameter Maxwell Fluid Model ({{EquationRef|6}}) |equation =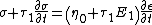
|cellpadding = 6 |border = 1 |border colour = black |background colour = white}}
References
2. ^Wiechert, E (1893); "Gesetze der elastischen Nachwirkung für constante Temperatur", Annalen der Physik, 286, 335–348, 546–570
3. ^Roylance, David (2001); "Engineering Viscoelasticity", 14-15
4. ^Tschoegl, Nicholas W. (1989); "The Phenomenological Theory of Linear Viscoelastic Behavior", 119-126
5. ^{{cite book| last = Gutierrez-Lemini| first = Danton| authorlink =| title = Engineering Viscoelasticity| publisher = Springer| series =| volume =| edition =| year = 2013| location =| pages = 88| language =| url = https://books.google.com/books?id=MbjBAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA88&lpg=PA88&dq=three+parameter+fluid+viscoelasticity| doi =| id =| isbn = 9781461481393| mr =| zbl =| jfm =}}
- Terrorism in Pakistan
- Terrorism in Philippines
- Terrorism in Russia
- Terrorism in Singapore
- Terrorism in Somalia
- Terrorism in South Africa
- Terrorism in Sweden
- Terrorism in Syria
- Terrorism in Tajikistan
- Terrorism in Thailand
- Terrorism in the Grip of Justice
- Terrorism in the Iraq War
- Terrorism in the Philippines
- Terrorism in the UK
- Terrorism in the united states
- Terrorism in Uganda
- Terrorism in Uzbekistan
- Terrorism Knowledge Base
- Terrorism legislation
- Terrorism of Kazakhstan
- Terrorism: Opposing Viewpoints (2000)
- Terrorism: Opposing Viewpoints (2004)
- Terrorism threat level
- Terrorist (album)
- Terrorist and Disruptive Activities Act