- Equation
- See also
The General Selection Model (GSM) is a model of population genetics that describes how a population's allele frequencies will change when acted upon by natural selection.
Equation
The General Selection Model applied to a single gene with two alleles (let's call them A1 and A2) is encapsulated by the equation:
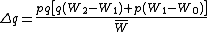
where:
is the frequency of allele A1
is the frequency of allele A2
is the rate of evolutionary change of the frequency of allele A2
are the relative fitnesses of homozygous A1, heterozygous (A1A2), and homozygous A2 genotypes respectively.
is the mean population relative fitness.
In words:
The product of the relative frequencies,  , is a measure of the genetic variance. The quantity pq is maximized when there is an equal frequency of each gene, when
, is a measure of the genetic variance. The quantity pq is maximized when there is an equal frequency of each gene, when 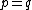 . In the GSM, the rate of change
. In the GSM, the rate of change  is proportional to the genetic variation.
is proportional to the genetic variation.
The mean population fitness 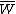 is a measure of the overall fitness of the population. In the GSM, the rate of change
is a measure of the overall fitness of the population. In the GSM, the rate of change  is inversely proportional to the mean fitness
is inversely proportional to the mean fitness 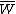 —i.e. when the population is maximally fit, no further change can occur.
—i.e. when the population is maximally fit, no further change can occur.
The remainder of the equation, 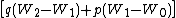 , refers to the mean effect of an allele substitution. In essence, this term quantifies what effect genetic changes will have on fitness.
, refers to the mean effect of an allele substitution. In essence, this term quantifies what effect genetic changes will have on fitness.
See also
- Darwinian Fitness
- Hardy-Weinberg principle
- Population genetics
- Otto Modersohn
- Otto Montag
- Otto Moritz Ludwig von Engelhardt
- Otto M. Peterson
- Otto Mueller (politician)
- Otto Muller (novelist)
- Otto Muller (painter)
- Otto Muller (priest)
- Ottomány
- Otto Männel
- Otto Mønsted
- Otto Müller (novelist)
- Otto Müller (painter)
- Otto Müller (priest)
- Otto Nagel
- Otto Nagel (wrestler)
- Otto, NC
- Ottone Calderari
- Otto Necas
- Ottone del Carretto
- Ottone Frangipane
- Ottonel
- Ottonel Frontignan
- Ottonel Muscotally
- Ottonel muskotaly