- Applications
- References
In mathematical logic, an implication graph is a skew-symmetric directed graph G = (V, E) composed of vertex set V and directed edge set E. Each vertex in V represents the truth status of a Boolean literal, and each directed edge from vertex u to vertex v represents the material implication "If the literal u is true then the literal v is also true". Implication graphs were originally used for analyzing complex Boolean expressions.
Applications
A 2-satisfiability instance in conjunctive normal form can be transformed into an implication graph by replacing each of its disjunctions by a pair of implications. For example, the statement  can be rewritten as the pair
can be rewritten as the pair 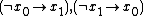 . An instance is satisfiable if and only if no literal and its negation belong to the same strongly connected component of its implication graph; this characterization can be used to solve 2-satisfiability instances in linear time.[1]
. An instance is satisfiable if and only if no literal and its negation belong to the same strongly connected component of its implication graph; this characterization can be used to solve 2-satisfiability instances in linear time.[1]
In CDCL SAT-solvers, unit propagation can be naturally associated with an implication graph that captures all possible ways of deriving all implied literals from decision literals,[2] which is then used for clause learning.
References
2. ^{{cite conference|author1=Paul Beame |author2=Henry Kautz |author3=Ashish Sabharwal |title = Understanding the Power of Clause Learning| conference = IJCAI | pages = 1194–1201|year = 2003|url=https://www.cs.rochester.edu/u/kautz/papers/learnIjcai.pdf}}
- Ernest Arlett
- Ernest Arnfield
- Ernest Arthur Davies
- Ernest Arthur Edghill
- Ernest Arthur Hart
- Ernest Arthur Muret
- Ernest Arthur Payne
- Ernest Arushanov
- Ernest Asante
- Ernest A. Smith
- Ernestas Setkus
- Ernestas Šetkus
- Ernest Atkins
- Ernest A. Tolin
- Ernest Attah
- Ernest August, 3rd Duke of Cumberland
- Ernest Augustus Anderson
- Ernest Augustus, Duke of Brunswick-Lueneburg
- Ernest Augustus, Duke of Brunswick-Luneburg
- Ernest Augustus, Duke of York
- Ernest Augustus Edgcumbe, 3rd Earl of Mount Edgcumbe
- Ernest Augustus, Elector of Brunswick-Lueneburg
- Ernest Augustus, Elector of Hanover
- Ernest Augustus I, Duke of Saxe-Eisenach
- Ernest Augustus I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar