水尺
测量江河、湖泊、水库等水面高程的一种装置。将尺寸刻画的搪瓷板或油漆木板,装钉在水体稳定的岸边桩架上或建筑物上。预先测出水尺零点高程,水面切在水尺上的位置是水位读数。将水位读数加上水尺零点高程,即为水体水面的高程。
水尺hydrometric gauge
用于测量江河、湖库和渠道水位的设备。最常见的为直立式水尺,还有倾斜式、矮桩式、混合式和悬垂式等类型。可根据河床的土质及稳定程度、断面形状及水流情况,从中选用一种或几种。
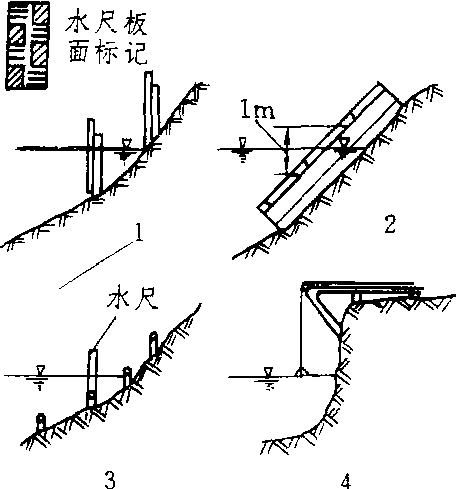
水尺
1.直立式 2. 倾斜式3. 矮桩式 4. 悬锤式
| 词条 | 水尺 |
| 类别 | 中文百科知识 |
| 释义 | 水尺测量江河、湖泊、水库等水面高程的一种装置。将尺寸刻画的搪瓷板或油漆木板,装钉在水体稳定的岸边桩架上或建筑物上。预先测出水尺零点高程,水面切在水尺上的位置是水位读数。将水位读数加上水尺零点高程,即为水体水面的高程。 水尺hydrometric gauge用于测量江河、湖库和渠道水位的设备。最常见的为直立式水尺,还有倾斜式、矮桩式、混合式和悬垂式等类型。可根据河床的土质及稳定程度、断面形状及水流情况,从中选用一种或几种。
水尺 1.直立式 2. 倾斜式3. 矮桩式 4. 悬锤式 |
| 随便看 |
开放百科全书收录579518条英语、德语、日语等多语种百科知识,基本涵盖了大多数领域的百科知识,是一部内容自由、开放的电子版国际百科全书。