| 释义 |
- Notation
- Character tables Nonaxial symmetries Cyclic symmetries Cyclic groups (Cn) Reflection groups (Cnh) Pyramidal groups (Cnv) Improper rotation groups (Sn) Dihedral symmetries Dihedral groups (Dn) Prismatic groups (Dnh) Antiprismatic groups (Dnd) Polyhedral symmetries Cubic groups Icosahedral groups Linear (cylindrical) groups
- See also
- Notes
- External links
- Further reading
This lists the character tables for the more common molecular point groups used in the study of molecular symmetry. These tables are based on the group-theoretical treatment of the symmetry operations present in common molecules, and are useful in molecular spectroscopy and quantum chemistry. Information regarding the use of the tables, as well as more extensive lists of them, can be found in the references.[1][2][3][4][5] Notation For each non-linear group, the tables give the most standard notation of the finite group isomorphic to the point group, followed by the order of the group (number of invariant symmetry operations). The finite group notation used is: Zn: cyclic group of order n, Dn: dihedral group isomorphic to the symmetry group of an n–sided regular polygon, Sn: symmetric group on n letters, and An: alternating group on n letters. The character tables then follow for all groups. The rows of the character tables correspond to the irreducible representations of the group, with their conventional names in the left margin. The naming conventions are as follows: - A and B are singly degenerate representations, with the former transforming symmetrically around the principal axis of the group, and the latter asymmetrically. E, T, G, H, ... are doubly, triply, quadruply, quintuply, ... degenerate representations.
- g and u subscripts denote symmetry and antisymmetry, respectively, with respect to a center of inversion. Subscripts "1" and "2" denote symmetry and antisymmetry, respectively, with respect to a nonprincipal rotation axis. Higher numbers denote additional representations with such asymmetry.
- Single prime ( ' ) and double prime ( '' ) superscripts denote symmetry and antisymmetry, respectively, with respect to a horizontal mirror plane σh, one perpendicular to the principal rotation axis.
All but the two rightmost columns correspond to the symmetry operations which are invariant in the group. In the case of sets of similar operations with the same characters for all representations, they are presented as one column, with the number of such similar operations noted in the heading. The body of the tables contain the characters in the respective irreducible representations for each respective symmetry operation, or set of symmetry operations. The two rightmost columns indicate which irreducible representations describe the symmetry transformations of the three Cartesian coordinates (x, y and z), rotations about those three coordinates (Rx, Ry and Rz), and functions of the quadratic terms of the coordinates(x2, y2, z2, xy, xz, and yz). The symbol i used in the body of the table denotes the imaginary unit: i 2 = −1. Used in a column heading, it denotes the operation of inversion. A superscripted uppercase "C" denotes complex conjugation. Character tables Nonaxial symmetries These groups are characterized by a lack of a proper rotation axis, noting that a  rotation is considered the identity operation. These groups have involutional symmetry: the only nonidentity operation, if any, is its own inverse. rotation is considered the identity operation. These groups have involutional symmetry: the only nonidentity operation, if any, is its own inverse. In the group  , all functions of the Cartesian coordinates and rotations about them transform as the , all functions of the Cartesian coordinates and rotations about them transform as the  irreducible representation. irreducible representation. | Point Group | Canonical Group | Order | Character Table |  | 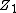 |  | | 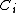 | 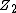 | 2 | |  | 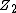 |  | | |
Cyclic symmetries The families of groups with these symmetries have only one rotation axis. Cyclic groups (Cn) The cyclic groups are denoted by Cn. These groups are characterized by an n-fold proper rotation axis Cn. The C1 group is covered in the nonaxial groups section. | C2 | Z2 | 2 | | | E | C2 | | | A | 1 | 1 | Rz, z | x2, y2, z2, xy | | B | 1 | −1 | Rx, Ry, x, y | xz, yz |
| | C3 | Z3 | 3 | | | E | C3 | C32 | θ = e2πi /3 | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz, z | x2 + y2 | | E | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | (Rx, Ry),
(x, y) | (x2 - y2, xy),
(xz, yz) | |
| | C4 | Z4 | 4 | | | E | C4 | C2 | C43 | | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz, z | x2 + y2, z2 | | B | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | x2 − y2, xy | | E | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | (Rx, Ry),
(x, y) | (xz, yz) | |
| | C5 | Z5 | 5 | | | E | C5 | C52 | C53 | C54 | θ = e2πi /5 | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz, z | x2 + y2, z2 | | E1 | 1
1 | θ
θC | θ2
(θ2)C | (θ2)C
θ2 | θC
θ | (Rx, Ry),
(x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 1
1 | θ2
(θ2)C | θC
θ | θ
θC | (θ2)C
θ2 | | (x2 - y2, xy) | |
| | C6 | Z6 | 6 | | | E | C6 | C3 | C2 | C32 | C65 | θ = e2πi /6 | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz, z | x2 + y2, z2 | | B | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | E1 | 1
1 | θ
θC | −θC
−θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | θC
−θ | (Rx, Ry),
(x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | | (x2 − y2, xy) | |
| | C8 | Z8 | 8 | | | E | C8 | C4 | C83 | C2 | C85 | C43 | C87 | θ = e2πi /8 | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz, z | x2 + y2, z2 | | B | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | E1 | 1
1 | θ
θC | i
−i | −θC
−θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | −i
i | θC
θ | (Rx, Ry),
(x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | E3 | 1
1 | −θ
−θC | i
−i | θC
θ | −1
−1 | θ
θC | −i
i | −θC
−θ | | | |
| |
Reflection groups (Cnh) The reflection groups are denoted by Cnh. These groups are characterized by i) an n-fold proper rotation axis Cn; ii) a mirror plane σh normal to Cn. The C1h group is the same as the Cs group in the nonaxial groups section. | C2h | Z2 × Z2 | 4 | | | E | C2 | i | σh | | | Ag | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz | x2, y2, z2, xy | | Bg | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | Rx, Ry | xz, yz | | Au | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | z | | | Bu | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | x, y | | |
| | C3h | Z6 | 6 | | | E | C3 | C32 | σh | S3 | S35 | θ = e2πi /3 | | A' | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz | x2 + y2, z2 | | E' | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | (x, y) | (x2 − y2, xy) | | A'' | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | z | | | E'' | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | −θC
−θ | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | |
| | C4h | Z2 × Z4 | 8 | | | E | C4 | C2 | C43 | i | S43 | σh | S4 | | | Ag | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz | x2 + y2, z2 | | Bg | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | x2 − y2, xy | | Eg | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | Au | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | z | | | Bu | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | | | | Eu | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | −1
−1 | −i
i | 1
1 | i
−i | (x, y) | | |
| | C5h | Z10 | 10 | | | E | C5 | C52 | C53 | C54 | σh | S5 | S57 | S53 | S59 | θ = e2πi /5 | | A' | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz | x2 + y2, z2 | | E1' | 1
1 | θ
θC | θ2
(θ2)C | (θ2)C
θ2 | θC
θ | 1
1 | θ
θC | θ2
(θ2)C | (θ2)C
θ2 | θC
θ | (x, y) | | | E2' | 1
1 | θ2
(θ2)C | θC
θ | θ
θC | (θ2)C
θ2 | 1
1 | θ2
(θ2)C | θC
θ | θ
θC | (θ2)C
θ2 | | (x2 - y2, xy) | | A'' | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | z | | | E1'' | 1
1 | θ
θC | θ2
(θ2)C | (θ2)C
θ2 | θC
θ | −1
−1 | −θ
-θC | −θ2
−(θ2)C | −(θ2)C
−θ2 | −θC
−θ | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | E2'' | 1
1 | θ2
(θ2)C | θC
θ | θ
θC | (θ2)C
θ2 | −1
−1 | −θ2
−(θ2)C | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | −(θ2)C
−θ2 | | | |
| | C6h | Z2 × Z6 | 12 | | | E | C6 | C3 | C2 | C32 | C65 | i | S35 | S65 | σh | S6 | S3 | θ = e2πi /6 | | Ag | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz | x2 + y2, z2 | | Bg | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | E1g | 1
1 | θ
θC | −θC
−θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | θC
θ | 1
1 | θ
θC | −θC
−θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | θC
θ | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | E2g | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | Au | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | z | | | Bu | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | | | | E1u | 1
1 | θ
θC | −θC
−θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | θC
θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | θC
θ | 1
1 | θ
θC | −θC
−θ | (x, y) | | | E2u | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −θ
−θC | −1
−1 | θC
θ | θ
θC | −1
−1 | θC
θ | θ
θC | | |
| |
Pyramidal groups (Cnv) The pyramidal groups are denoted by Cnv. These groups are characterized by i) an n-fold proper rotation axis Cn; ii) n mirror planes σv which contain Cn. The C1v group is the same as the Cs group in the nonaxial groups section. | C2v | Z2 × Z2
(=D2) | 4 | | | E | C2 | σv | σv' | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z | x2 , y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | xy | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | Ry, x | xz | | B2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | Rx, y | yz | |
| | C3v | D3 | 6 | | | E | 2 C3 | 3 σv | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz | | | E | 2 | −1 | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (x2 − y2, xy), (xz, yz) | |
| | C4v | D4 | 8 | | | E | 2 C4 | C2 | 2 σv | 2 σd | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | x2 − y2 | | B2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | | xy | | E | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (xz, yz) | |
| | C5v | D5 | 10 | | | E | 2 C5 | 2 C52 | 5 σv | θ = 2π/5 | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz | | | E1 | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | |
| | C6v | D6 | 12 | | | E | 2 C6 | 2 C3 | C2 | 3 σv | 3 σd | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | B2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | | | | E1 | 2 | 1 | −1 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 2 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) |
| |
Improper rotation groups (Sn) The improper rotation groups are denoted by Sn. These groups are characterized by an n-fold improper rotation axis Sn, where n is necessarily even. The S2 group is the same as the Ci group in the nonaxial groups section. Sn groups with an odd value of n are identical to Cnh groups of same n and are therefore not considered here (in particular, S1 is identical to Cs). The S8 table reflects the 2007 discovery of errors in older references.[4] Specifically, (Rx, Ry) transform not as E1 but rather as E3. | S4 | Z4 | 4 | | | E | S4 | C2 | S43 | | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz, | x2 + y2, z2 | | B | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | z | x2 − y2, xy | | E | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | (Rx, Ry),
(x, y) | (xz, yz) | |
| | S6 | Z6 | 6 | | | E | S6 | C3 | i | C32 | S65 | θ = e2πi /6 | | Ag | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz | x2 + y2, z2 | | Eg | 1
1 | θC
θ | θ
θC | 1
1 | θC
θ | θ
θC | (Rx, Ry) | (x2 − y2, xy),
(xz, yz) | | Au | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | z | | | Eu | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | θ
θC | −1
−1 | θC
θ | −θ
−θC | (x, y) | | |
| | S8 | Z8 | 8 | | | E | S8 | C4 | S83 | i | S85 | C42 | S87 | θ = e2πi /8 | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Rz | x2 + y2, z2 | | B | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | z | | | E1 | 1
1 | θ
θC | i
−i | −θC
−θ | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | −i
i | θC
θ | (x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | 1
1 | i
−i | −1
−1 | −i
i | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | E3 | 1
1 | −θC
−θ | −i
i | θ
θC | −1
−1 | θC
θ | i
−i | −θ
−θC | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | |
| |
Dihedral symmetries The families of groups with these symmetries are characterized by 2-fold proper rotation axes normal to a principal rotation axis. Dihedral groups (Dn) The dihedral groups are denoted by Dn. These groups are characterized by i) an n-fold proper rotation axis Cn; ii) n 2-fold proper rotation axes C2 normal to Cn. The D1 group is the same as the C2 group in the cyclic groups section. | D2 | Z2 × Z2
(=D2) | 4 | | | E | C2 (z) | C2 (x) | C2 (y) | | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2, y2, z2 | | B1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz, z | xy | | B2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | Ry, y | xz | | B3 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | Rx, x | yz | |
| | D3 | D3 | 6 | | | E | 2 C3 | 3 C2 | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz, z | | | E | 2 | −1 | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (x2 − y2, xy), (xz, yz) | |
| | D4 | D4 | 8 | | | E | 2 C4 | C2 | 2 C2' | 2 C2'' | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz, z | | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | x2 − y2 | | B2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | | xy | | E | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (xz, yz) | |
| | D5 | D5 | 10 | | | E | 2 C5 | 2 C52 | 5 C2 | θ=2π/5 | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz, z | | | E1 | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | |
| | D6 | D6 | 12 | | | E | 2 C6 | 2 C3 | C2 | 3 C2' | 3 C2'' | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz, z | | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | B2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | | | | E1 | 2 | 1 | −1 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (xz, yz) | | E2 | 2 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) |
| |
Prismatic groups (Dnh) The prismatic groups are denoted by Dnh. These groups are characterized by i) an n-fold proper rotation axis Cn; ii) n 2-fold proper rotation axes C2 normal to Cn; iii) a mirror plane σh normal to Cn and containing the C2s. The D1h group is the same as the C2v group in the pyramidal groups section. The D8h table reflects the 2007 discovery of errors in older references.[4] Specifically, symmetry operation column headers 2S8 and 2S83 were reversed in the older references. | D2h | Z2×Z2×Z2
(=Z2×D2) | 8 | | | E | C2 | C2 (x) | C2 (y) | i | σ(xy) | σ(xz) | σ(yz) | | | Ag | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2, y2, z2 | | B1g | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | xy | | B2g | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | Ry | xz | | B3g | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | Rx | yz | | Au | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | B1u | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | z | | | B2u | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | y | | | B3u | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | x | | |
| | D3h | D6 | 12 | | | E | 2 C3 | 3 C2 | σh | 2 S3 | 3 σv | | | A1' | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2' | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz | | | E' | 2 | −1 | 0 | 2 | −1 | 0 | (x, y) | (x2 − y2, xy) | | A1'' | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2'' | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | z | | | E'' | 2 | −1 | 0 | −2 | 1 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | |
| | D4h | Z2×D4 | 16 | | | E | 2 C4 | C2 | 2 C2' | 2 C2'' | i | 2 S4 | σh | 2 σv | 2 σd | | | A1g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2g | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1g | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | x2 − y2 | | B2g | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | | xy | | Eg | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | A1u | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2u | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | z | | | B1u | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | | | | B2u | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | Eu | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | (x, y) | | |
| | D5h | D10 | 20 | | | E | 2 C5 | 2 C52 | 5 C2 | σh | 2 S5 | 2 S53 | 5 σv | θ=2π/5 | | A1' | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2' | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz | | | E1' | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | (x, y) | | | E2' | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | A1'' | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2'' | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | z | | | E1'' | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | −2 | −2 cos(θ) | −2 cos(2θ) | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | E2'' | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | −2 | −2 cos(2θ) | −2 cos(θ) | 0 | | | |
| | D6h | Z2×D6 | 24 | | | E | 2 C6 | 2 C3 | C2 | 3 C2' | 3 C2'' | i | 2 S3 | 2 S6 | σh | 3 σd | 3 σv | | | A1g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1g | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | B2g | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | | | | E1g | 2 | 1 | −1 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | −1 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | E2g | 2 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | A1u | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2u | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | z | | | B1u | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | | | | B2u | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | | | E1u | 2 | 1 | −1 | −2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | −1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | (x, y) | | | E2u | 2 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 1 | 1 | −2 | 0 | 0 | | |
| | D8h | Z2×D8 | 32 | | | E | 2 C8 | 2 C83 | 2 C4 | C2 | 4 C2' | 4 C2'' | i | 2 S83 | 2 S8 | 2 S4 | σh | 4 σd | 4 σv | θ=21/2 | | A1g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1g | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | | | B2g | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | | | | E1g | 2 | θ | −θ | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | θ | −θ | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | E2g | 2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | E3g | 2 | −θ | θ | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | −θ | θ | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | | | | A1u | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2u | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | z | | | B1u | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | | | | B2u | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | | | | E1u | 2 | θ | −θ | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | −θ | θ | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | (x, y) | | | E2u | 2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | −2 | 0 | 0 | | | | E3u | 2 | −θ | θ | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | −2 | θ | −θ | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | |
| |
Antiprismatic groups (Dnd) The antiprismatic groups are denoted by Dnd. These groups are characterized by i) an n-fold proper rotation axis Cn; ii) n 2-fold proper rotation axes C2 normal to Cn; iii) n mirror planes σd which contain Cn. The D1d group is the same as the C2h group in the reflection groups section. | D2d | D4 | 8 | | | E | 2 S4 | C2 | 2 C2' | 2 σd | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2, y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | x2 − y2 | | B2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | z | xy | | E | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry), (x, y) | (xz, yz) | |
| | D3d | D6 | 12 | | | E | 2 C3 | 3 C2 | i | 2 S6 | 3 σd | | | A1g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2g | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz | | | Eg | 2 | −1 | 0 | 2 | −1 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (x2 − y2, xy), (xz, yz) | | A1u | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2u | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | z | | | Eu | 2 | −1 | 0 | −2 | 1 | 0 | (x, y) | | |
| | D4d | D8 | 16 | | | E | 2 S8 | 2 C4 | 2 S83 | C2 | 4 C2' | 4 σd | θ=21/2 | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | | | B2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | z | | | E1 | 2 | θ | 0 | −θ | −2 | 0 | 0 | (x, y) | | | E2 | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | E3 | 2 | −θ | 0 | θ | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | |
| | D5d | D10 | 20 | | | E | 2 C5 | 2 C52 | 5 C2 | i | 2 S10 | 2 S103 | 5 σd | θ=2π/5 | | A1g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2g | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz | | | E1g | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | E2g | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | A1u | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2u | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | z | | | E1u | 2 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(2θ) | 0 | −2 | −2 cos(2θ) | −2 cos(θ) | 0 | (x, y) | | | E2u | 2 | 2 cos(2θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | −2 | −2 cos(θ) | −2 cos(2θ) | 0 | | | |
| | D6d | D12 | 24 | | | E | 2 S12 | 2 C6 | 2 S4 | 2 C3 | 2 S125 | C2 | 6 C2' | 6 σd | θ=31/2 | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | Rz | | | B1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | | | B2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | z | | | E1 | 2 | θ | 1 | 0 | −1 | −θ | −2 | 0 | 0 | (x, y) | | | E2 | 2 | 1 | −1 | −2 | −1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | E3 | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | | | | E4 | 2 | −1 | −1 | 2 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | | | E5 | 2 | −θ | 1 | 0 | −1 | θ | −2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | |
| |
Polyhedral symmetries These symmetries are characterized by having more than one proper rotation axis of order greater than 2. Cubic groups These polyhedral groups are characterized by not having a C5 proper rotation axis. | T | A4 | 12 | | | E | 4 C3 | 4 C32 | 3 C2 | θ=e2π i/3 | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2 + z2 | | E | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | 1
1 | | (2 z2 − x2 − y2,
x2 − y2) | | T | 3 | 0 | 0 | −1 | (Rx, Ry, Rz),
(x, y, z) | (xy, xz, yz) | |
| | Td | S4 | 24 | | | E | 8 C3 | 3 C2 | 6 S4 | 6 σd | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2 + z2 | | A2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | | | | E | 2 | −1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | (2 z2 − x2 − y2,
x2 − y2) | | T1 | 3 | 0 | −1 | 1 | −1 | (Rx, Ry, Rz) | | | T2 | 3 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 1 | (x, y, z) | (xy, xz, yz) | |
| | Th | Z2×A4 | 24 | | | E | 4 C3 | 4 C32 | 3 C2 | i | 4 S6 | 4 S65 | 3 σh | θ=e2π i/3 | | Ag | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2 + z2 | | Au | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | Eg | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | 1
1 | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | 1
1 | | (2 z2 − x2 − y2,
x2 − y2) | | Eu | 1
1 | θ
θC | θC
θ | 1
1 | −1
−1 | −θ
−θC | −θC
−θ | −1
−1 | | | | Tg | 3 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | −1 | (Rx, Ry, Rz) | (xy, xz, yz) | | Tu | 3 | 0 | 0 | −1 | −3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | (x, y, z) | | |
| | O | S4 | 24 | | | E | 6 C4 | 3 C2 (C42) | 8 C3 | 6 C2 | | | A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2 + z2 | | A2 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | | | E | 2 | 0 | 2 | −1 | 0 | | (2 z2 − x2 − y2,
x2 − y2) | | T1 | 3 | 1 | −1 | 0 | −1 | (Rx, Ry, Rz),
(x, y, z) | | | T2 | 3 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 1 | | (xy, xz, yz) | |
| | Oh | Z2×S4 | 48 | | | E | 8 C3 | 6 C2 | 6 C4 | 3 C2 (C42) | i | 6 S4 | 8 S6 | 3 σh | 6 σd | | | A1g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2 + z2 | | A2g | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | | | | Eg | 2 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | −1 | 2 | 0 | | (2 z2 − x2 − y2,
x2 − y2) | | T1g | 3 | 0 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | −1 | −1 | (Rx, Ry, Rz) | | | T2g | 3 | 0 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 3 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 1 | | (xy, xz, yz) | | A1u | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | A2u | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | | | | Eu | 2 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | −2 | 0 | 1 | −2 | 0 | | | | T1u | 3 | 0 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −3 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | (x, y, z) | | | T2u | 3 | 0 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −1 | | |
| |
Icosahedral groups {{see also|Icosahedral symmetry}}These polyhedral groups are characterized by having a C5 proper rotation axis. | I | A5 | 60 | | | E | 12 C5 | 12 C52 | 20 C3 | 15 C2 | θ=π/5 | | A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2 + z2 | | T1 | 3 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(3θ) | 0 | −1 | (Rx, Ry, Rz),
(x, y, z) | | | T2 | 3 | 2 cos(3θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | −1 | | | | G | 4 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0 | | | | H | 5 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | | (2 z2 − x2 − y2,
x2 − y2,
xy, xz, yz) | |
| | Ih | Z2×A5 | 120 | | | E | 12 C5 | 12 C52 | 20 C3 | 15 C2 | i | 12 S10 | 12 S103 | 20 S6 | 15 σ | θ=π/5 | | Ag | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | x2 + y2 + z2 | | T1g | 3 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(3θ) | 0 | −1 | 3 | 2 cos(3θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | −1 | (Rx, Ry, Rz) | | | T2g | 3 | 2 cos(3θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | −1 | 3 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(3θ) | 0 | −1 | | | | Gg | 4 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0 | | | | Hg | 5 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | | (2 z2 − x2 − y2,
x2 − y2,
xy, xz, yz) | | Au | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | | | | T1u | 3 | 2 cos(θ) | 2 cos(3θ) | 0 | −1 | −3 | −2 cos(3θ) | −2 cos(θ) | 0 | 1 | (x, y, z) | | | T2u | 3 | 2 cos(3θ) | 2 cos(θ) | 0 | −1 | −3 | −2 cos(θ) | −2 cos(3θ) | 0 | 1 | | | | Gu | 4 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 0 | −4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 0 | | | | Hu | 5 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | −5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −1 | | | |
| |
Linear (cylindrical) groups These groups are characterized by having a proper rotation axis C∞ around which the symmetry is invariant to any rotation. | C∞v | | | E | 2 C∞Φ | ... | ∞ σv | | | A1=Σ+ | 1 | 1 | ... | 1 | z | x2 + y2, z2 | | A2=Σ− | 1 | 1 | ... | −1 | Rz | | | E1=Π | 2 | 2 cos(Φ) | ... | 0 | (x, y), (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | E2=Δ | 2 | 2 cos(2Φ) | ... | 0 | | (x2 - y2, xy) | | E3=Φ | 2 | 2 cos(3Φ) | ... | 0 | | | | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | | | |
| | D∞h | | | E | 2 C∞Φ | ... | ∞ σv | i | 2 S∞Φ | ... | ∞ C2 | | | Σg+ | 1 | 1 | ... | 1 | 1 | 1 | ... | 1 | | x2 + y2, z2 | | Σg− | 1 | 1 | ... | −1 | 1 | 1 | ... | −1 | Rz | | | Πg | 2 | 2 cos(Φ) | ... | 0 | 2 | −2 cos(Φ) | .. | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | | Δg | 2 | 2 cos(2Φ) | ... | 0 | 2 | 2 cos(2Φ) | .. | 0 | | (x2 − y2, xy) | | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | | | | Σu+ | 1 | 1 | ... | 1 | −1 | −1 | ... | −1 | z | | | Σu− | 1 | 1 | ... | −1 | −1 | −1 | ... | 1 | | | | Πu | 2 | 2 cos(Φ) | ... | 0 | −2 | 2 cos(Φ) | .. | 0 | (x, y) | | | Δu | 2 | 2 cos(2Φ) | ... | 0 | −2 | −2 cos(2Φ) | .. | 0 | | | | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | | |
| |
See also - Linear combination of atomic orbitals (molecular orbital method)
- Raman spectroscopy
- Vibrational spectroscopy (molecular vibration)
- List of small groups
- Cubic harmonics
Notes 1. ^{{cite book | last = Drago | first = Russell S. | title = Physical Methods in Chemistry | publisher = W.B. Saunders Company | year = 1977 | isbn = 0-7216-3184-3}}
2. ^{{cite book | last=Cotton | first = F. Albert | title = Chemical Applications of Group Theory | publisher = John Wiley & Sons: New York | year = 1990 | isbn = 0-471-51094-7}}
3. ^{{cite web | last = Gelessus | first = Achim | title = Character tables for chemically important point groups | publisher = Jacobs University, Bremin; Computational Laboratory for Analysis, Modeling, and Visualization | date=2007-07-12 | url=http://symmetry.jacobs-university.de/ | accessdate=2007-07-12 }}
4. ^1 2 {{cite journal | last=Shirts | first=Randall B. | title=Correcting Two Long-Standing Errors in Point Group Symmetry Character Tables | journal=Journal of Chemical Education | volume=84 | issue=1882 | publisher=American Chemical Society | year=2007 | url=http://jchemed.chem.wisc.edu/Journal/Issues/2007/Nov/abs1882.html | accessdate= 2007-10-16 | doi=10.1021/ed084p1882 | pages=1882|bibcode = 2007JChEd..84.1882S }}
5. ^{{cite web | url=http://www.webqc.org/symmetry.php | title=POINT GROUP SYMMETRY CHARACTER TABLES | last= Vanovschi | first=Vitalii | accessdate=2008-10-29 | publisher=WebQC.Org}}
External links- Character tables for many more point groups (includes symmetry transformations of Cartesian products up to sixth order)
Further reading - {{cite book | last = Bunker | first = Philip |author2=Jensen, Per | title = Molecular Symmetry and Spectroscopy, Second edition | publisher = NRC Research Press | year = 2006 | location = Ottawa | isbn = 0-660-19628-X}}
4 : Theoretical chemistry|Physical chemistry|Group theory|Finite groups |
 rotation is considered the identity operation. These groups have involutional symmetry: the only nonidentity operation, if any, is its own inverse.
rotation is considered the identity operation. These groups have involutional symmetry: the only nonidentity operation, if any, is its own inverse. , all functions of the Cartesian coordinates and rotations about them transform as the
, all functions of the Cartesian coordinates and rotations about them transform as the  irreducible representation.
irreducible representation.
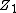

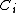
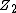

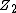


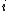
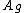
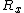 ,
,  ,
, 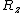
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 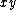 ,
, 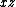 ,
, 
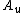

 ,
,  ,
,