- Kodaira dimension
 Rational surfaces Quadric surfaces Rational cubic surfaces Rational quartic surfaces Other rational surfaces in space Other families of rational surfaces Non-rational ruled surfaces Class VII surfaces
Rational surfaces Quadric surfaces Rational cubic surfaces Rational quartic surfaces Other rational surfaces in space Other families of rational surfaces Non-rational ruled surfaces Class VII surfaces - Kodaira dimension
 K3 surfaces Enriques surfaces Abelian surfaces Other classes of dimension-
K3 surfaces Enriques surfaces Abelian surfaces Other classes of dimension- surfaces
surfaces - Kodaira dimension

- Kodaira dimension
 (surfaces of general type)
(surfaces of general type) - Families of surfaces with members in multiple classes
- See also
- References
- External links
This is a list of named algebraic surfaces, compact complex surfaces, and families thereof, sorted according to the Enriques–Kodaira classification.
Kodaira dimension 
Rational surfaces
- Projective plane
Quadric surfaces
- Cone (geometry)
- Cylinder
- Ellipsoid
- Hyperboloid
- Paraboloid
- Sphere
- Spheroid
Rational cubic surfaces
- Cayley nodal cubic surface, a certain cubic surface with 4 nodes
- Cayley's ruled cubic surface
- Clebsch surface or Klein icosahedral surface
- Fermat cubic
- Monkey saddle
- Parabolic conoid
- Plücker's conoid
- Whitney umbrella
Rational quartic surfaces
- Châtelet surfaces
- Dupin cyclides, inversions of a cylinder, torus, or double cone in a sphere
- Gabriel's horn
- Right circular conoid
- Roman surface or Steiner surface, a realization of the real projective plane in real affine space
- Tori, surfaces of revolution generated by a circle about a coplanar axis
Other rational surfaces in space
- Boy's surface, a sextic realization of the real projective plane in real affine space
- Enneper surface, a nonic minimal surface
- Henneberg surface, a minimal surface of degree 15
- Bour's minimal surface, a surface of degree 16
- Richmond surfaces, a family of minimal surfaces of variable degree
Other families of rational surfaces
- Coble surfaces
- Del Pezzo surfaces, surfaces with an ample anticanonical divisor
- Hirzebruch surfaces, rational ruled surfaces
- Segre surfaces, intersections of two quadrics in projective 4-space
- Unirational surfaces of characteristic 0
- Veronese surface, the Veronese embedding of the projective plane into projective 5-space
- White surfaces, the blow-up of the projective plane at
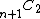 points by the linear system of degree-
points by the linear system of degree- curves through those points
curves through those points- Bordiga surfaces, the White surfaces determined by families of quartic curves
Non-rational ruled surfaces
Class VII surfaces
- Vanishing second Betti number:
- Hopf surfaces
- Inoue surfaces; several other families discovered by Inoue have also been called "Inoue surfaces"
- Positive second Betti number:
- Enoki surfaces
- Inoue–Hirzebruch surfaces
- Kato surfaces
Kodaira dimension 
K3 surfaces
- Kummer surfaces
- Tetrahedroids, special Kummer surfaces
- Wave surface, a special tetrahedroid
- Plücker surfaces, birational to Kummer surfaces
- Weddle surfaces, birational to Kummer surfaces
- Smooth quartic surfaces
- Supersingular K3 surfaces
Enriques surfaces
- Reye congruences, the locus of lines that lie on two out of three general quadric surfaces in projective space
Abelian surfaces
- Horrocks–Mumford surfaces, surfaces of degree 10 in projective 4-space that are the zero locus of sections of the rank-two Horrocks–Mumford bundle
Other classes of dimension- surfaces
surfaces
- Non-classical Enriques surfaces, a variation on the notion of Enriques surfaces that only exist in characteristic two
- Hyperelliptic surfaces or bielliptic surfaces; quasi-hyperelliptic surfaces are a variation of this notion that exist only in characteristics two and three
- Kodaira surfaces
Kodaira dimension 
- Dolgachev surfaces
Kodaira dimension  (surfaces of general type)
(surfaces of general type)
- Barlow surfaces
- Beauville surfaces
- Burniat surfaces
- Campedelli surfaces; surfaces of general type with the same Hodge numbers as Campedelli surfaces are called numerical Campidelli surfaces
- Castelnuovo surfaces
- Catanese surfaces
- Fake projective planes or Mumford surfaces, surfaces with the same Betti numbers as projective plane but not isomorphic to it
- Fano surface of lines on a non-singular 3-fold; sometimes, this term is taken to mean del Pezzo surface
- Godeaux surfaces; surfaces of general type with the same Hodge numbers as Godeaux surfaces are called numerical Godeaux surfaces
- Horikawa surfaces
- Todorov surfaces
Families of surfaces with members in multiple classes
- Surfaces that are also Shimura varieties:
- Hilbert modular surfaces
- Humbert surfaces
- Picard modular surfaces
- Shioda modular surfaces
- Elliptic surfaces, surfaces with an elliptic fibration; quasielliptic surfaces constitute a modification this idea that occurs in finite characteristic
- Raynaud surfaces and generalized Raynaud surfaces, certain quasielliptic counterexamples to the conclusions of the Kodaira vanishing theorem
- Exceptional surfaces, surfaces whose Picard number achieve the bound set by the central Hodge number h1,1
- Kähler surfaces, complex surfaces with a Kähler metric; equivalently, surfaces for which the first Betti number b1 is even
- Minimal surfaces, surfaces that can't be obtained from another by blowing up at a point; they have no connection with the minimal surfaces of differential geometry
- Nodal surfaces, surfaces whose only singularities are nodes
- Cayley's nodal cubic, which has 4 nodes
- Kummer surfaces, quartic surfaces with 16 nodes
- Togliatti surface, a certain quintic with 31 nodes
- Barth surfaces, referring to a certain sextic with 65 nodes and decic with 345 nodes
- Labs surface, a certain septic with 99 nodes
- Endrass surface, a certain surface of degree 8 with 168 nodes
- Sarti surface, a certain surface of degree 12 with 600 nodes
- Quotient surfaces, surfaces that are constructed as the orbit space of some other surface by the action of a finite group; examples include Kummer, Godeaux, Hopf, and Inoue surfaces
- Zariski surfaces, surfaces in finite characteristic that admit a purely inseparable dominant rational map from the projective plane
See also
- Enriques–Kodaira classification
- List of surfaces
References
- Compact Complex Surfaces by Wolf P. Barth, Klaus Hulek, Chris A.M. Peters, Antonius Van de Ven {{isbn|3-540-00832-2}}
- Complex algebraic surfaces by Arnaud Beauville, {{isbn|0-521-28815-0}}
External links
- Mathworld has a long list of algebraic surfaces with pictures.
- Some more pictures of algebraic surfaces, especially ones with many nodes.
- Pictures of algebraic surfaces by Herwig Hauser.
- Free program SURFER to visualize algebraic surfaces in real-time, including a user gallery.
3 : Complex surfaces|Algebraic surfaces|Mathematics-related lists
- Dichomeris latipalpis
- Dichomeris latipennella
- Dichomeris lativalvata
- Dichomeris legnotoa
- Dichomeris leontovitchi
- Dichomeris leptosaris
- Dichomeris lespedezae
- Dichomeris leucocosma
- Dichomeris leuconotella
- Dichomeris leucostena
- Dichomeris leucothicta
- Dichomeris levigata
- Dichomeris levisella
- Dichomeris ligulacea
- Dichomeris ligyra
- Dichomeris limbipunctella
- Dichomeris limbipunctellus
- Dichomeris limitellus
- Dichomeris limosella
- Dichomeris limosellus
- Dichomeris linealis
- Dichomeris lissota
- Dichomeris litoxyla
- Dichomeris liui
- Dichomeris lividula