- Definition
- Relation to other stochastic processes
- See also
- References and further reading
In probability and statistics a Markov renewal process is a random process that generalizes the notion of Markov jump processes. Other random processes like Markov chain, Poisson process, and renewal process can be derived as a special case of an MRP (Markov renewal process).
Definition
Consider a state space 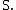 Consider a set of random variables
Consider a set of random variables  , where
, where  are the jump times and
are the jump times and  are the associated states in the Markov chain (see Figure). Let the inter-arrival time,
are the associated states in the Markov chain (see Figure). Let the inter-arrival time,  . Then the sequence
. Then the sequence  is called a Markov renewal process if
is called a Markov renewal process if
Relation to other stochastic processes
- If we define a new stochastic process
 for
for  , then the process
, then the process  is called a semi-Markov process. Note the main difference between an MRP and a semi-Markov process is that the former is defined as a two-tuple of states and times, whereas the latter is the actual random process that evolves over time and any realisation of the process has a defined state for any given time. The entire process is not Markovian, i.e., memoryless, as happens in a continuous time Markov chain/process (CTMC). Instead the process is Markovian only at the specified jump instants. This is the rationale behind the name, Semi-Markov.&91;1&93;&91;2&93;&91;3&93; (See also: hidden semi-Markov model.)
is called a semi-Markov process. Note the main difference between an MRP and a semi-Markov process is that the former is defined as a two-tuple of states and times, whereas the latter is the actual random process that evolves over time and any realisation of the process has a defined state for any given time. The entire process is not Markovian, i.e., memoryless, as happens in a continuous time Markov chain/process (CTMC). Instead the process is Markovian only at the specified jump instants. This is the rationale behind the name, Semi-Markov.&91;1&93;&91;2&93;&91;3&93; (See also: hidden semi-Markov model.) - A semi-Markov process (defined in the above bullet point) where all the holding times are exponentially distributed is called a CTMC. In other words, if the inter-arrival times are exponentially distributed and if the waiting time in a state and the next state reached are independent, we have a CTMC.

- The sequence
 in the MRP is a discrete-time Markov chain. In other words, if the time variables are ignored in the MRP equation, we end up with a DTMC.
in the MRP is a discrete-time Markov chain. In other words, if the time variables are ignored in the MRP equation, we end up with a DTMC.
- If the sequence of
 s are independent and identically distributed, and if their distribution does not depend on the state
s are independent and identically distributed, and if their distribution does not depend on the state  , then the process is a renewal process. So, if the states are ignored and we have a chain of iid times, then we have a renewal process.
, then the process is a renewal process. So, if the states are ignored and we have a chain of iid times, then we have a renewal process.
See also
- Markov process
- Renewal theory
- Variable-order Markov model
- Hidden semi-Markov model
References and further reading
1. ^{{cite book|last=Medhi|first=J.|title=Stochastic processes|year=1982|publisher=Wiley & Sons|location=New York|isbn=978-0-470-27000-4}}
2. ^{{cite book|last=Ross|first=Sheldon M.|title=Stochastic processes.|year=1999|publisher=Routledge.|location=New York [u.a.]|isbn=978-0-471-12062-9|edition=2nd}}
3. ^{{cite book|last=Barbu|first=Vlad Stefan|title=Semi-Markov chains and hidden semi-Markov models toward applications : their use in reliability and DNA analysis|year=2008|publisher=Springer|location=New York|isbn=978-0-387-73171-1|author2=Limnios, Nikolaos}}
2. ^{{cite book|last=Ross|first=Sheldon M.|title=Stochastic processes.|year=1999|publisher=Routledge.|location=New York [u.a.]|isbn=978-0-471-12062-9|edition=2nd}}
3. ^{{cite book|last=Barbu|first=Vlad Stefan|title=Semi-Markov chains and hidden semi-Markov models toward applications : their use in reliability and DNA analysis|year=2008|publisher=Springer|location=New York|isbn=978-0-387-73171-1|author2=Limnios, Nikolaos}}
1 : Markov processes
- Monetki
- Monetons
- Monetray policy
- Monette-Horwitz Trust
- Monette moore
- Monette Moore
- Monett Municipal Airport
- Monett Township, Barry County, Missouri
- Monetville Public School
- Monety
- Monety, Olecko County
- Monety, Pisz County
- Moneulia
- MonEUo
- Monewden
- Monex
- Monex Group
- Money (1993 film)
- Money 2 Blow
- Money and banking in britain from 1900-1910
- Money and happiness
- Money as Debt
- Money as debt
- Money As Debt
- Money (Australian TV program)
