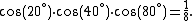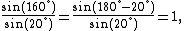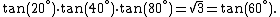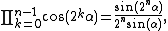- Proof
- References
- External links
It is a special case of the more general identity
with n = 3 and α = 20° and the fact that
since
The name is due to the physicist Richard Feynman, who used to refer to the identity under that name. Feynman picked that name because he learned it during his childhood from a boy with the name Morrie Jacobs and afterwards remembered it for all of his life.[1]
A similar identity for the sine function also holds:
Moreover, dividing the second identity by the first, the following identity is evident:
Proof
Recall the double angle formula for the sine function
Solve for 
It follows that:
Multiplying all of these expressions together yields:
The intermediate numerators and denominators cancel leaving only the first denominator, a power of 2 and the final numerator. Note that there are n terms in both sides of the expression. Thus,
which is equivalent to the generalization of Morrie's law.
References
External links
- {{MathWorld|title=Morrie's Law|urlname=MorriesLaw}}