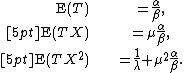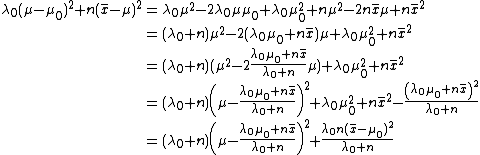- Definition
- Properties Probability density function Marginal distributions Exponential family Moments of the natural statistics Scaling
- Posterior distribution of the parameters Interpretation of parameters
- Generating normal-gamma random variates
- Related distributions
- Notes
- References
name =normal-gamma| type =density| pdf_image =| cdf_image =| parameters =location (real)
(real)
(real)
(real)| support =
| pdf =
| cdf =| mean =[1]
| median = | mode =
| variance =[1]
| skewness =| kurtosis =| entropy =| mgf =| char =|
}}
In probability theory and statistics, the normal-gamma distribution (or Gaussian-gamma distribution) is a bivariate four-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. It is the conjugate prior of a normal distribution with unknown mean and precision.[2]
Definition
For a pair of random variables, (X,T), suppose that the conditional distribution of X given T is given by
meaning that the conditional distribution is a normal distribution with mean  and precision
and precision 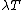 — equivalently, with variance
— equivalently, with variance 
Suppose also that the marginal distribution of T is given by
where this means that T has a gamma distribution. Here λ, α and β are parameters of the joint distribution.
Then (X,T) has a normal-gamma distribution, and this is denoted by
Properties
Probability density function
The joint probability density function of (X,T) is{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}
Marginal distributions
By construction, the marginal distribution over  is a gamma distribution, and the conditional distribution over
is a gamma distribution, and the conditional distribution over  given
given  is a Gaussian distribution. The marginal distribution over
is a Gaussian distribution. The marginal distribution over  is a three-parameter non-standardized Student's t-distribution with parameters
is a three-parameter non-standardized Student's t-distribution with parameters  .{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}
.{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}
Exponential family
The normal-gamma distribution is a four-parameter exponential family with natural parameters  and natural statistics
and natural statistics  .{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}
.{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}
Moments of the natural statistics
The following moments can be easily computed using the moment generating function of the sufficient statistic:{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}
where  is the digamma function,
is the digamma function,
Scaling
If  then for any b > 0, (bX,bT) is distributed as{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}
then for any b > 0, (bX,bT) is distributed as{{citation needed|date=April 2013}} 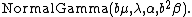 {{dubious|date=April 2013}}
{{dubious|date=April 2013}}
Posterior distribution of the parameters
Assume that x is distributed according to a normal distribution with unknown mean  and precision
and precision  .
.
and that the prior distribution on  and
and  ,
,  , has a normal-gamma distribution
, has a normal-gamma distribution
for which the density {{pi}} satisfies
Suppose
i.e. the components of  are conditionally independent given
are conditionally independent given  and the conditional distribution of each of them given
and the conditional distribution of each of them given  is normal with expected value
is normal with expected value  and variance
and variance  The posterior distribution of
The posterior distribution of  and
and  given this dataset
given this dataset  can be analytically determined by Bayes' theorem.[3] Explicitly,
can be analytically determined by Bayes' theorem.[3] Explicitly,
where  is the likelihood of the data given the parameters.
is the likelihood of the data given the parameters.
Since the data are i.i.d, the likelihood of the entire dataset is equal to the product of the likelihoods of the individual data samples:
This expression can be simplified as follows:
where  , the mean of the data samples, and
, the mean of the data samples, and 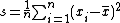 , the sample variance.
, the sample variance.
The posterior distribution of the parameters is proportional to the prior times the likelihood.
The final exponential term is simplified by completing the square.
On inserting this back into the expression above,
This final expression is in exactly the same form as a Normal-Gamma distribution, i.e.,
Interpretation of parameters
The interpretation of parameters in terms of pseudo-observations is as follows:
- The new mean takes a weighted average of the old pseudo-mean and the observed mean, weighted by the number of associated (pseudo-)observations.
- The precision was estimated from
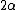 pseudo-observations (i.e. possibly a different number of pseudo-observations, to allow the variance of the mean and precision to be controlled separately) with sample mean
pseudo-observations (i.e. possibly a different number of pseudo-observations, to allow the variance of the mean and precision to be controlled separately) with sample mean  and sample variance
and sample variance  (i.e. with sum of squared deviations
(i.e. with sum of squared deviations  ).
). - The posterior updates the number of pseudo-observations (
 ) simply by adding up the corresponding number of new observations (
) simply by adding up the corresponding number of new observations ( ).
). - The new sum of squared deviations is computed by adding the previous respective sums of squared deviations. However, a third "interaction term" is needed because the two sets of squared deviations were computed with respect to different means, and hence the sum of the two underestimates the actual total squared deviation.
As a consequence, if one has a prior mean of  from
from 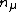 samples and a prior precision of
samples and a prior precision of  from
from  samples, the prior distribution over
samples, the prior distribution over  and
and  is
is
and after observing  samples with mean
samples with mean  and variance
and variance  , the posterior probability is
, the posterior probability is
Note that in some programming languages, such as Matlab, the gamma distribution is implemented with the inverse definition of 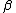 , so the fourth argument of the Normal-Gamma distribution is
, so the fourth argument of the Normal-Gamma distribution is  .
.
Generating normal-gamma random variates
Generation of random variates is straightforward:
- Sample
 from a gamma distribution with parameters
from a gamma distribution with parameters  and
and 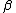
- Sample
 from a normal distribution with mean
from a normal distribution with mean  and variance
and variance 
Related distributions
- The normal-inverse-gamma distribution is essentially the same distribution parameterized by variance rather than precision
- The normal-exponential-gamma distribution
Notes
2. ^Bernardo & Smith (1993, pages 136, 268, 434)
3. ^{{cite web |url=http://www.trinity.edu/cbrown/bayesweb/ |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2014-08-05 |deadurl=no |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140807091855/http://www.trinity.edu/cbrown/bayesweb/ |archivedate=2014-08-07 |df= }}
References
- Bernardo, J.M.; Smith, A.F.M. (1993) Bayesian Theory, Wiley. {{ISBN|0-471-49464-X}}
- Dearden et al. "Bayesian Q-learning", Proceedings of the Fifteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-98), July 26–30, 1998, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fighting The World
- Fighting the world
- Fighting top
- Fighting Téméraire
- Fighting varietal
- Fighting varietals
- Fighting vehicle
- Fighting videogame
- Fighting Wire Frame
- Fighting Wireframes
- Fighting with Kit Carson
- Fighting with kit carson
- Fighting With Wire
- Fighting with Wire
- Fightingwithwire
- Fighting with wire
- Fighting word
- Fighting Words
- Fighting world of japan pro wrestling
- Fighting Yank
- Fight in the Skies
- Fight In The Skies
- Fight in the skies
- Fightin' Whites
- Fight Like a Brave