- Examples and properties
- Footnotes
- References
- External links
In mathematics, specifically commutative algebra, a proper ideal Q of a commutative ring A is said to be primary if whenever xy is an element of Q then x or yn is also an element of Q, for some n>0. For example, in the ring of integers Z, (pn) is a primary ideal if p is a prime number.
The notion of primary ideals is important in commutative ring theory because every ideal of a Noetherian ring has a primary decomposition, that is, can be written as an intersection of finitely many primary ideals. This result is known as the Lasker–Noether theorem. Consequently,[1] an irreducible ideal of a Noetherian ring is primary.
Various methods of generalizing primary ideals to noncommutative rings exist[2] but the topic is most often studied for commutative rings. Therefore, the rings in this article are assumed to be commutative rings with identity.
Examples and properties
- The definition can be rephrased in a more symmetric manner: an ideal
 is primary if, whenever
is primary if, whenever  , we have either
, we have either 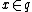 or
or  or
or  . (Here
. (Here  denotes the radical of
denotes the radical of  .)
.) - An ideal Q of R is primary if and only if every zerodivisor in R/Q is nilpotent. (Compare this to the case of prime ideals, where P is prime if every zerodivisor in R/P is actually zero.)
- Any prime ideal is primary, and moreover an ideal is prime if and only if it is primary and semiprime.
- Every primary ideal is primal.[3]
- If Q is a primary ideal, then the radical of Q is necessarily a prime ideal P, and this ideal is called the associated prime ideal of Q. In this situation, Q is said to be P-primary.
- On the other hand, an ideal whose radical is prime is not necessarily primary: for example, if
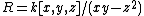 ,
, 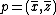 , and
, and  , then
, then  is prime and
is prime and  , but we have
, but we have 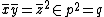 ,
,  , and
, and 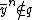 for all n > 0, so
for all n > 0, so  is not primary. The primary decomposition of
is not primary. The primary decomposition of  is
is  ; here
; here  is
is  -primary and
-primary and  is
is  -primary.
-primary. - An ideal whose radical is maximal, however, is primary.
- On the other hand, an ideal whose radical is prime is not necessarily primary: for example, if
- If P is a maximal prime ideal, then any ideal containing a power of P is P-primary. Not all P-primary ideals need be powers of P; for example the ideal (x, y2) is P-primary for the ideal P = (x, y) in the ring k[x, y], but is not a power of P.
- In general powers of a prime ideal P need not be P-primary. (An example is given by taking R to be the ring k[x, y, z]/(xy − z2), with P the prime ideal (x, z). If Q = P2, then xy ∈ Q, but x is not in Q and y is not in the radical P of Q, so Q is not P-primary.) However every ideal Q with radical P is contained in a smallest P-primary ideal, consisting of all elements a such that ax is in Q for some x not in P. In particular there is a smallest P-primary ideal containing Pn, called the nth symbolic power of P.
- If A is a Noetherian ring and P a prime ideal, then the kernel of
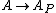 , the map from A to the localization of A at P, is the intersection of all P-primary ideals.[4]
, the map from A to the localization of A at P, is the intersection of all P-primary ideals.[4]
Footnotes
2. ^See the references to Chatters-Hajarnavis, Goldman, Gorton-Heatherly, and Lesieur-Croisot.
3. ^For the proof of the second part see the article of Fuchs
4. ^Atiyah-Macdonald, Corollary 10.21
References
- {{Citation | last1=Atiyah | first1=Michael Francis | author1-link=Michael Atiyah | last2=Macdonald | first2=I.G. | author2-link=Ian G. Macdonald | title=Introduction to Commutative Algebra | publisher=Westview Press | isbn=978-0-201-40751-8 | year=1969 |page=50}}
- {{citation |author1=Chatters, A. W. |author2=Hajarnavis, C. R. |title=Non-commutative rings with primary decomposition
|journal=Quart. J. Math. Oxford Ser. (2) |volume=22 |year=1971 |pages=73–83 |issn=0033-5606 |mr=0286822 |doi=10.1093/qmath/22.1.73}}
- {{citation |author=Goldman, Oscar |title=Rings and modules of quotients |journal=J. Algebra |volume=13 |year=1969 |pages=10–47 |issn=0021-8693 |mr=0245608 |doi=10.1016/0021-8693(69)90004-0}}
- {{citation |author1=Gorton, Christine |author2=Heatherly, Henry |title=Generalized primary rings and ideals |journal=Math. Pannon. |volume=17 |year=2006 |issue=1 |pages=17–28 |issn=0865-2090 |mr=2215638}}
- On primal ideals, Ladislas Fuchs
- {{citation |author1=Lesieur, L. |author2=Croisot, R. |title=Algèbre noethérienne non commutative |language=French |publisher=Mémor. Sci. Math., Fasc. CLIV. Gauthier-Villars & Cie, Editeur -Imprimeur-Libraire, Paris |year=1963 |pages=119 |mr=0155861 }}
External links
- [https://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php/Primary_ideal Primary ideal at Encyclopaedia of Mathematics]
- Howard Hawks baseball
- Howard H. Baker, Jr. Center for Public Policy
- Howard H. Baker Sr.
- Howard H. Callaway Sr.
- Howard H Cherry Scout Reservation
- Howard H. Cooksey
- Howard Henry Baker Sr.
- Howard Henry Lederer
- Howard Henry Peckham
- Howard Hewett discography
- Howard Hewlett Clark
- Howard Hibbard
- Howard High School (Georgetown, South Carolina)
- Howard High School, Mazowe
- Howard Hinton (art patron)
- Howard Hinton (disambiguation)
- Howard H. Kendler
- Howard Hollis "Bo" Callaway Sr.
- Howard Hollis Callaway Sr.
- Howard Home for Aged Men
- Howard Hopson
- Howard Horne
- Howard Hotel
- Howard House (hotel)
- Howard H. Shore