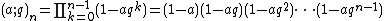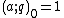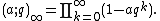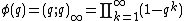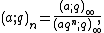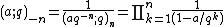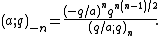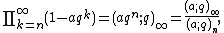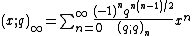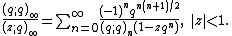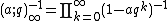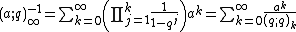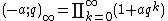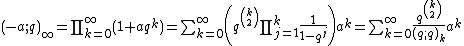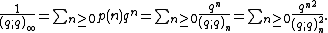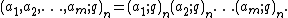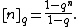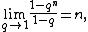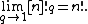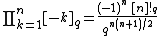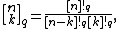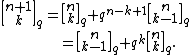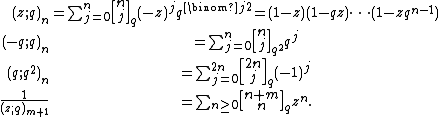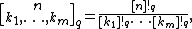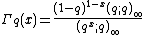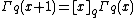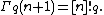- Identities
- Combinatorial interpretation
- Multiple arguments convention
- q-series
- Relationship to other q-functions
- See also
- References
- External links
In mathematics, in the area of combinatorics, a q-Pochhammer symbol, also called a q-shifted factorial, is a q-analog of the Pochhammer symbol. It is defined as
with
by definition. The q-Pochhammer symbol is a major building block in the construction of q-analogs; for instance, in the theory of basic hypergeometric series, it plays the role that the ordinary Pochhammer symbol plays in the theory of generalized hypergeometric series.
Unlike the ordinary Pochhammer symbol, the q-Pochhammer symbol can be extended to an infinite product:
This is an analytic function of q in the interior of the unit disk, and can also be considered as a formal power series in q. The special case
is known as Euler's function, and is important in combinatorics, number theory, and the theory of modular forms.
Identities
The finite product can be expressed in terms of the infinite product:
which extends the definition to negative integers n. Thus, for nonnegative n, one has
and
Alternatively,
which is useful for some of the generating functions of partition functions.
The q-Pochhammer symbol is the subject of a number of q-series identities, particularly the infinite series expansions
and
,
which are both special cases of the q-binomial theorem:
Fridrikh Karpelevich found the following identity (see {{harvs|txt|last1=Olshanetsky|last2=Rogov|year=1995}} for the proof):
Combinatorial interpretation
The q-Pochhammer symbol is closely related to the enumerative combinatorics of partitions. The coefficient of 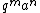 in
in
is the number of partitions of m into at most n parts.
Since, by conjugation of partitions, this is the same as the number of partitions of m into parts of size at most n, by identification of generating series we obtain the identity:
as in the above section.
We also have that the coefficient of 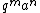 in
in
is the number of partitions of m into n or n-1 distinct parts.
By removing a triangular partition with n − 1 parts from such a partition, we are left with an arbitrary partition with at most n parts. This gives a weight-preserving bijection between the set of partitions into n or n − 1 distinct parts and the set of pairs consisting of a triangular partition having n − 1 parts and a partition with at most n parts. By identifying generating series, this leads to the identity:
also described in the above section.
The reciprocal of the function 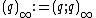 similarly arises as the generating function for the partition function,
similarly arises as the generating function for the partition function,  , which is also expanded by the second two q-series expansions given below:[1]
, which is also expanded by the second two q-series expansions given below:[1]
The q-binomial theorem itself can also be handled by a slightly more involved combinatorial argument of a similar flavor (see also the expansions given in the next subsection) .
Multiple arguments convention
Since identities involving q-Pochhammer symbols so frequently involve products of many symbols, the standard convention is to write a product as a single symbol of multiple arguments:
q-series
A q-series is a series in which the coefficients are functions of q, typically expressions of 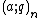 .[2] Early results are due to Euler, Gauss, and Cauchy. The systematic study begins with Eduard Heine (1843).[3]
.[2] Early results are due to Euler, Gauss, and Cauchy. The systematic study begins with Eduard Heine (1843).[3]
Relationship to other q-functions
The q-analog of n, also known as the q-bracket or q-number of n, is defined to be
From this one can define the q-analog of the factorial, the q-factorial, as
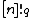 | 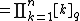 |
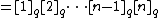 | |
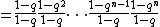 | |
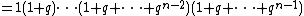 | |
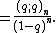 |
These numbers are analogues in the sense that
and so also
The limit value n! counts permutations of an n-element set S. Equivalently, it counts the number of sequences of nested sets 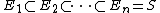 such that
such that  contains exactly i elements.[4] By comparison, when q is a prime power and V is an n-dimensional vector space over the field with q elements, the q-analogue
contains exactly i elements.[4] By comparison, when q is a prime power and V is an n-dimensional vector space over the field with q elements, the q-analogue 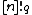 is the number of complete flags in V, that is, it is the number of sequences
is the number of complete flags in V, that is, it is the number of sequences  of subspaces such that
of subspaces such that  has dimension i.[4] The preceding considerations suggest that one can regard a sequence of nested sets as a flag over a conjectural field with one element.
has dimension i.[4] The preceding considerations suggest that one can regard a sequence of nested sets as a flag over a conjectural field with one element.
A product of negative integer q-brackets can be expressed in terms of the q-factorial as
From the q-factorials, one can move on to define the q-binomial coefficients, also known as the Gaussian binomial coefficients, as
where it is easy to see that the triangle of these coefficients is symmetric in the sense that 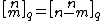 for all
for all 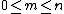 .
.
One can check that
One can also see from the previous recurrence relations that the next variants of the  -binomial theorem are expanded in terms of these coefficients as follows:[5]
-binomial theorem are expanded in terms of these coefficients as follows:[5]
One may further define the q-multinomial coefficients
where the arguments 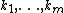 are nonnegative integers that satisfy
are nonnegative integers that satisfy 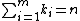 . The coefficient above counts the number of flags
. The coefficient above counts the number of flags
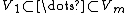
of subspaces in an n-dimensional vector space over the field with q elements such that 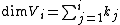 .
.
The limit 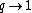 gives the usual multinomial coefficient
gives the usual multinomial coefficient 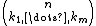 , which counts words in n different symbols
, which counts words in n different symbols 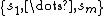 such that each
such that each  appears
appears  times.
times.
One also obtains a q-analog of the Gamma function, called the q-gamma function, and defined as
This converges to the usual Gamma function as q approaches 1 from inside the unit disc. Note that
for any x and
for non-negative integer values of n. Alternatively, this may be taken as an extension of the q-factorial function to the real number system.
See also
- Basic hypergeometric series
- Elliptic gamma function
- Jacobi theta function
- Lambert series
- Pentagonal number theorem
- q-derivative
- q-theta function
- q-Vandermonde identity
- Rogers-Ramanujan identities
- Rogers-Ramanujan continued fraction
References
2. ^Bruce C. Berndt, What is a q-series?, in Ramanujan Rediscovered: Proceedings of a Conference on Elliptic Functions, Partitions, and q-Series in memory of K. Venkatachaliengar: Bangalore, 1–5 June 2009, N. D. Baruah, B. C. Berndt, S. Cooper, T. Huber, and M. J. Schlosser, eds., Ramanujan Mathematical Society, Mysore, 2010, pp. 31-51
3. ^E. Heine, [https://archive.org/details/abw7150.0001.001.umich.edu Untersuchungen über die Reihe], J. Reine Angew. Math. 34 (1847), 285-328
4. ^1 {{citation | last = Stanley | first = Richard P. | authorlink = Richard P. Stanley | title = Enumerative Combinatorics | volume = 1 | edition = 2 | publisher = Cambridge University Press | year = 2011}}, Section 1.10.2.
5. ^{{cite book|last1=Olver et. al.|title=NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions|date=2010|location=Section 17.2|page=421|url=http://dlmf.nist.gov/}}
- George Gasper and Mizan Rahman, Basic Hypergeometric Series, 2nd Edition, (2004), Encyclopedia of Mathematics and Its Applications, 96, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. {{ISBN|0-521-83357-4}}.
- Roelof Koekoek and Rene F. Swarttouw, The Askey scheme of orthogonal polynomials and its q-analogues, section 0.2.
- Exton, H. (1983), q-Hypergeometric Functions and Applications, New York: Halstead Press, Chichester: Ellis Horwood, 1983, {{ISBN|0853124914}}, {{ISBN|0470274530}}, {{ISBN|978-0470274538}}
- M.A. Olshanetsky and V.B.K. Rogov (1995), The Modified q-Bessel Functions and the q-Bessel-Macdonald Functions, arXiv:q-alg/9509013.
External links
- {{MathWorld|urlname=q-Analog|title=q-Analog}}
- {{MathWorld|urlname=q-Bracket|title=q-Bracket}}
- {{MathWorld|urlname=q-Factorial|title=q-Factorial}}
- {{MathWorld|urlname=q-Factorial|title=q-Series}}
- {{MathWorld|urlname=q-BinomialCoefficient|title=q-Binomial Coefficient}}
- Julian Grobelny
- Julian Grundt
- Julian Gërxho
- Julian Gómez
- Julian Hails
- Julian Hammond
- Julian Harcourt Ferguson
- Julian Harper
- Julian Hatton
- Julian Hee
- Julian Heller
- Julian Henry Charles Fane
- Julian Hernández (disambiguation)
- Julian hibberd
- Julian Hibberd
- Julian High School
- Julian High School (Chicago)
- Julian Himely Bigelow
- Julian Hirsch
- Julian Hochfeld
- Julian Holland
- Julianhong
- Julian Hope
- Julian House (musician)
- Julian Howard Beale