- See also
| image = AngularFrequency.gif
| caption = Angular frequency ω (in radians per second), is larger than frequency ν (in cycles per second, also called Hz), by a factor of 2π, because 2π rad/s corresponds to 1 Hz.
| standard = SI derived unit
| quantity = rotational speed
| symbol = rad/s
| symbol2 = rad⋅s−1
}}
The radian per second (symbol: rad·s−1 or rad/s) is the SI unit of rotational speed (angular velocity), commonly denoted by the Greek letter ω (omega). The radian per second is also the unit of angular frequency.
The radian per second is defined as the change in the orientation of an object, in radians, every second.
| Angular frequency ω | (Ordinary) frequency 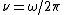 |
|---|---|
| 2π radians per second | exactly 1 hertz (Hz) |
| 1 radian per second | approximately 0.159155 Hz |
| 1 radian per second | approximately 57.29578 degrees per second |
| 1 radian per second | approximately 9.5493 revolutions per minute (rpm) |
| 0.1047 radians per second | approximately 1 rpm |
Since the radian is a dimensionless unit, the radian per second is dimensionally equivalent to the hertz—both are defined as s−1. This may lead to confusion between the quantities angular frequency ω and frequency ν.
A use of the unit radian per second is in calculation of the power transmitted by a shaft. In the International System of Units, widely used in physics and engineering, the power p is equal to the rotational speed ω (in radians per second) multiplied by the torque τ applied to the shaft, in newton-meters. Thus, {{nowrap|1=p = ω ⋅ τ}}, and the unit is the watt, with no numerical coefficient needed. In other systems, an additional factor may be necessary. For example, if one multiplies angular velocity in revolutions per minute (rpm) by the torque in pound-feet, then a factor is needed to convert the result in horsepower.
An angular frequency, {{nowrap|1=ω = 1 rad/s}}, corresponds to an ordinary frequency, {{nowrap|1=ν = 1/(2π) Hz ≈ 0.159 Hz}}, which corresponds to a frequency of rotation of {{nowrap|60/(2π) rpm ≈ 9.55 rpm}}.
See also
- Cycle per second
- Normalized frequency
- Order of magnitude (angular velocity)
- Moulton Courthouse Square Historic District
- Moultonianthus leembruggianus
- Moulton, John
- Moulton, John Fletcher
- Moulton Junction, Iowa
- Moulton-Levy
- Moulton, North Carolina
- Moulton School & Science College
- Moulton Seas End
- Moulton (surname)
- Moulton Township
- Moulton-Udell High School
- Moulton War Memorial
- Moultrie Athletics
- Moultrie/Brunswick Phillies
- Moultrie Colt .22s
- Moultrie Courthouse
- Moultrie Cubs
- Moultrie Cutoff
- Moultrie (disambiguation)
- Moultrie flag
- Moultrie Flag
- Moultrie, GA Micropolitan Statistical Area
- Moultrie, GA μSA
- Moultrie, Georgia micropolitan area