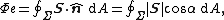- Mathematical definitions Radiant flux Spectral flux
- Relationship with the Poynting vector
- {{anchor|units}}SI radiometry units
- See also
- References
- Further reading
In radiometry, radiant flux or radiant power is the radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit time, and spectral flux or spectral power is the radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The SI unit of radiant flux is the watt (W), that is the joule per second ({{nobreak|J/s}}) in SI base units, while that of spectral flux in frequency is the watt per hertz ({{nobreak|W/Hz}}) and that of spectral flux in wavelength is the watt per metre ({{nobreak|W/m}})—commonly the watt per nanometre ({{nobreak|W/nm}}).
Mathematical definitions
Radiant flux
Radiant flux, denoted Φe ("e" for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities), is defined aswhere
- ∂ is the partial derivative symbol;
- Qe is the radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received;
- t is the time.
Spectral flux
Spectral flux in frequency, denoted Φe,ν, is defined aswhere ν is the frequency.
Spectral flux in wavelength, denoted Φe,λ, is defined aswhere λ is the wavelength.
Relationship with the Poynting vector
One can show that the radiant flux of a surface is the flux of the Poynting vector through this surface, hence the name "radiant flux":
where
- Σ is the surface;
- S is the Poynting vector;
- n is a unit normal vector to that surface;
- A is the area of that surface;
- α is the angle between n and S.
But the time-average of the norm of the Poynting vector is used instead, because in radiometry it is the only quantity that radiation detectors are able to measure:
where < • > is the time-average.
{{anchor|units}}SI radiometry units
{{SI radiometry units}}See also
- Luminous flux
- Heat flux
- Power (physics)
- Radiosity (heat transfer)
References
}}
Further reading
- {{cite book
|title= Radiometry and the Detection of Optical Radiation (Pure & Applied Optics Series)
|last = Boyd
|first = Robert
|authorlink = Robert W. Boyd (physicist)
|year = 1983
|publisher = Wiley-Interscience
|isbn = 978-0-471-86188-1
|url = https://www.amazon.com/Radiometry-Detection-Optical-Radiation-Applied/dp/047186188X/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1313084491&sr=1-1}}
- Di An(writer)
- Dian yang Tak Kunjung Padam
- Dianzhongia
- Dianzi, Guan County
- Dianzi Keji Daxue
- Diao
- Diaobingshan, Liaoning
- Diaofang
- Diaofang Town, Meizhou
- Diaosi
- Diao (surname)
- Diao Xiaojuan
- Diaoyucheng (opera)
- Diao Yu Dao
- Diaoyudao
- Diaoyu (disambiguation)
- Diaoyu Islands dispute
- Diaoyu Islands: The Truth
- Diaoyu Islands - The Truth
- Diaoyu Islands - The Truth (2014 Film)
- Diaoyu/Senkaku Islands
- Diaoyu/Senkaku Islands dispute
- Diao yu tai
- Diao Yu Tai
- Diaoyutai Mole