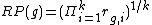- Calculation of the rank product
- Determination of significance levels
- Exact probability distribution and accurate approximation
- See also
- References
The rank product is a biologically motivated test for the detection of differentially expressed genes in replicated microarray experiments.
It is a simple non-parametric statistical method based on ranks of fold changes. In addition to its use in expression profiling, it can be used to combine ranked lists in various application domains, including proteomics, metabolomics, statistical meta-analysis, and general feature selection.
Calculation of the rank product
Given n genes and k replicates, let 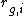 the rank of gene g in the i-th replicate.
the rank of gene g in the i-th replicate.
Compute the rank product via the geometric mean:
Determination of significance levels
Simple permutation-based estimation is used to determine how likely a given RP value or better is observed in a random experiment.
- generate p permutations of k rank lists of length n.
- calculate the rank products of the n genes in the p permutations.
- count how many times the rank products of the genes in the permutations are smaller or equal to the observed rank product. Set c to this value.
- calculate the average expected value for the rank product by:
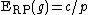 .
. - calculate the percentage of false positives as :
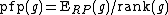 where
where 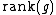 is the rank of gene g in a list of all n genes sorted by increasing
is the rank of gene g in a list of all n genes sorted by increasing 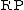 .
.
Exact probability distribution and accurate approximation
Permutation re-sampling requires a computationally demanding number of permutations to get reliable estimates of the p-values for the most differentially expressed genes, if n is large. Eisinga, Breitling and Heskes (2013) provide the exact probability mass distribution of the rank product statistic. Calculation of the exact p-values offers a substantial improvement over permutation approximation, most significantly for that part of the distribution rank product analysis is most interested in, i.e., the thin right tail. However, exact statistical significance of large rank products may take unacceptable long amounts of time to compute. Heskes, Eisinga and Breitling (2014) provide a method to determine accurate approximate p-values of the rank product statistic in a computationally fast manner.
See also
- Ranking
- Schulze method
- Comparison of electoral systems–––—§§·
- Arrow's impossibility theorem
References
- Breitling, R., Armengaud, P., Amtmann, A., and Herzyk, P. (2004) Rank Products: A simple, yet powerful, new method to detect differentially regulated genes in replicated microarray experiments, FEBS Letters, 573:83–-92
- {{cite journal | last1 = Eisinga | first1 = R. | last2 = Breitling | first2 = R. | last3 = Heskes | first3 = T. | year = 2013 | title = The exact probability distribution of the rank product statistics for replicated experiments | doi = 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.037 | journal = FEBS Letters | volume = 587 | issue = | pages = 677–682 | pmid=23395607}}
- {{cite journal | last1 = Heskes | first1 = T. | last2 = Eisinga | first2 = R. | last3 = Breitling | first3 = R. | year = 2014 | title = A fast algorithm for determining bounds and accurate approximate p-values of the rank product statistic for replicate experiments | url = http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/15/367 | journal = BMC Bioinformatics | volume = 15 | issue = | page = 367 | doi=10.1186/preaccept-1857144210135244}}
- 474th Fighter Bomber Group
- 474th Fighter-Bomber Group
- 474th Fighter Bomber Wing
- 474th Fighter-Day Squadron
- 474th Infantry Regiment (United States)
- 474th Regiment (separate)
- 474th Tactical Fighter Squadron
- 474 U.S. 121
- 474 U.S. 254
- 474 U.S. 284
- 474 U.S. 82
- 4750 BC
- 4750th Air Defense Group
- 4751st Air Defense Missile Squadron
- 4751st Air Defense Missile Wing
- 4751st Air Defense Squadron
- 4754th Radar Evaluation Electronics Counter-Countermeasure Flight
- (4759) 1978 VG10
- 4759 Aretta
- 475 area code
- 475 in poetry
- 475th
- 475th Fighter-Interceptor Group
- 475th Weapons Evaluation Group
- 475 U.S. 1